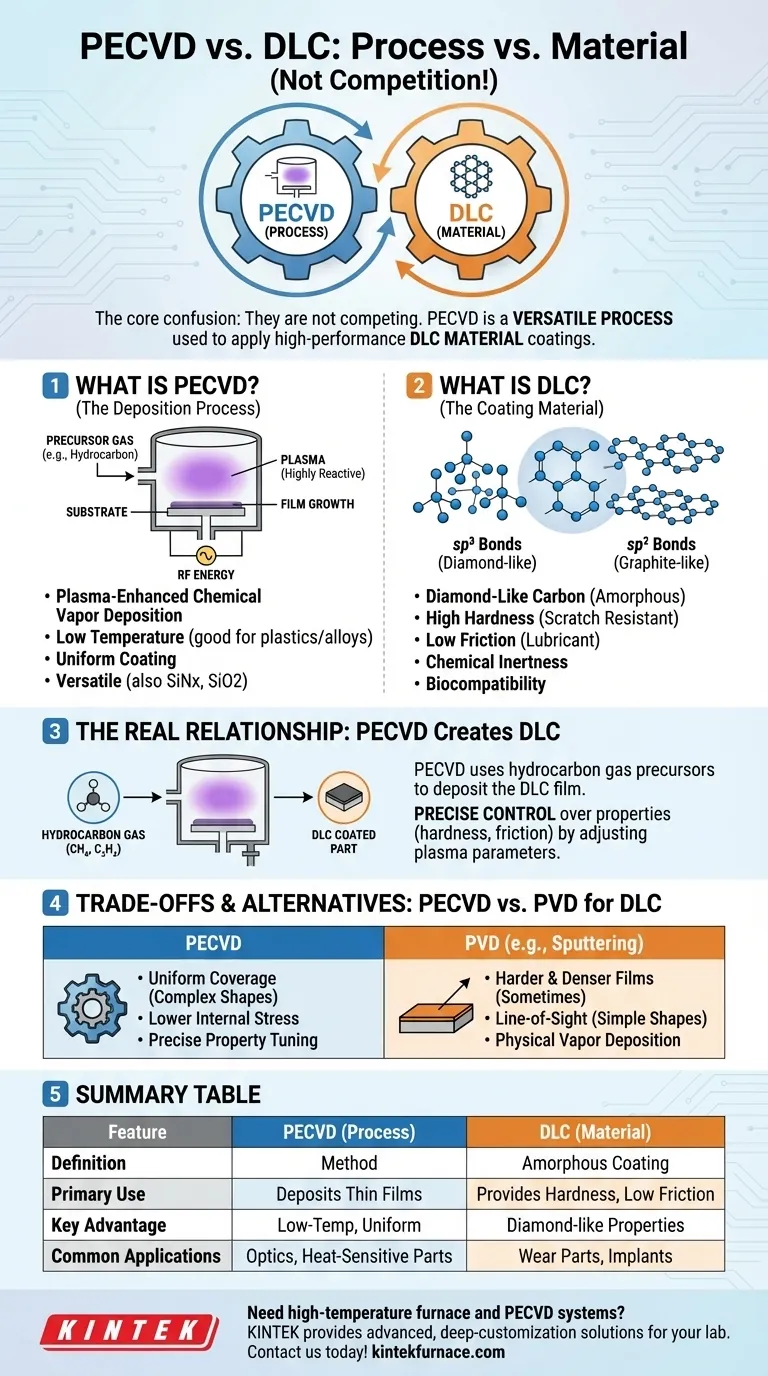
The fundamental point of confusion is that Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) and Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) are not competing technologies. PECVD is a process used to apply a thin film coating, while DLC is a specific material or type of coating. In fact, PECVD is one of the primary industrial processes used to deposit DLC coatings onto a surface.
The core misunderstanding is framing this as "PECVD vs. DLC." The correct relationship is that PECVD is a versatile process that can be used to create high-performance DLC material coatings, among many others.
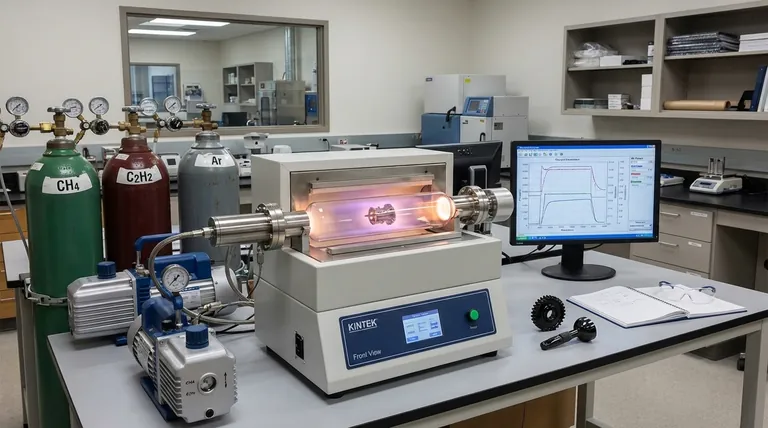

What is PECVD? The Deposition Process
PECVD stands for Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is a method for applying extremely thin films of material onto a substrate.
How It Works
The process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. A precursor gas (or a mix of gases) containing the elements for the desired film is introduced.
Energy, typically radio-frequency (RF), is applied to the chamber, which ignites the gas into a plasma—a highly reactive, ionized state of matter.
This reactive plasma breaks the precursor gases down, and the resulting atoms or molecular fragments then condense and recombine on the substrate's surface, building the film layer by layer.
The Key Advantage: Low Temperature
The "plasma-enhanced" aspect allows this entire process to occur at much lower temperatures than traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
This is critical for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics, polymers, or certain metal alloys that would be damaged or warped by high-temperature processes.
A Versatile Tool
PECVD is not limited to one type of coating. By changing the precursor gases, it can be used to deposit a wide array of materials, including silicon nitride (SiNx), silicon dioxide (SiO2) for optical applications, and various carbon-based films.
What is DLC? The Coating Material
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a class of amorphous carbon material. It is not pure diamond, but it exhibits many of the desirable properties of diamond.
A Unique Atomic Structure
DLC films contain a mixture of two types of carbon bonds: sp³ bonds (the type found in diamond) and sp² bonds (the type found in graphite).
The ratio of these bonds determines the material's properties. A higher percentage of sp³ bonds generally results in a harder, more "diamond-like" coating.
Core Properties and Benefits
Engineers choose DLC for its exceptional combination of properties:
- High Hardness: Provides excellent scratch and wear resistance.
- Low Friction: Acts as a solid lubricant, reducing energy loss and component wear.
- Chemical Inertness: Protects the underlying part from corrosion and chemical attack.
- Biocompatibility: Makes it suitable for medical implants and devices.
The Real Relationship: Using PECVD to Create DLC
PECVD is the engine that drives the creation of many DLC coatings. The process and material work together.
How PECVD Deposits a DLC Film
To create a DLC coating, a hydrocarbon gas like methane (CH₄) or acetylene (C₂H₂) is used as the precursor in the PECVD chamber.
The plasma breaks down these hydrocarbon molecules. The carbon and hydrogen atoms then recombine on the component's surface, forming the hard, amorphous DLC film (often designated a-C:H).
Precise Control Over Properties
This is where the power of PECVD becomes clear. By carefully managing the plasma parameters—gas flow rates, pressure, and power—an engineer can precisely control the final properties of the DLC film.
Adjusting these parameters directly influences the sp³/sp² bond ratio and the amount of hydrogen incorporated into the film. This allows the coating's hardness, friction coefficient, internal stress, and even optical properties to be tuned for a specific application.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While PECVD is a powerful method for depositing DLC, it is not the only one. Understanding the alternatives clarifies its specific advantages.
PVD: The Other Major Process
The other primary method for depositing DLC is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). PVD processes, like sputtering or cathodic arc evaporation, work by physically knocking atoms off a solid graphite target and depositing them onto the substrate.
PVD vs. PECVD for DLC
The choice between these methods involves engineering trade-offs.
PECVD is often favored for its ability to uniformly coat complex, 3D shapes because the precursor gas can reach all surfaces. It also generally produces films with lower internal stress.
PVD methods, particularly cathodic arc, can sometimes produce harder and denser DLC films. However, PVD is a line-of-sight process, which can make it challenging to coat intricate geometries uniformly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice is not between PECVD and DLC. It is about selecting the right deposition process to achieve the specific DLC properties your application demands.
- If your primary focus is coating complex or heat-sensitive parts: PECVD is an excellent choice due to its low-temperature operation and superior conformal coverage.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and density on a simpler geometry: A PVD process like cathodic arc evaporation may be a better fit for your requirements.
- If your primary focus is tuning optical properties or ensuring low internal stress: The precise chemical control offered by PECVD makes it the superior technology.
Ultimately, selecting the correct manufacturing process is how you engineer the ideal material properties for your component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PECVD (Process) | DLC (Material) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition method | Diamond-Like Carbon amorphous coating material |
| Primary Use | Deposits thin films like DLC, SiNx, SiO2 | Provides hardness, low friction, chemical inertness |
| Key Advantage | Low-temperature, uniform coating of complex shapes | Combines diamond-like properties with versatility |
| Common Applications | Optics, electronics, medical devices on heat-sensitive materials | Wear-resistant parts, medical implants, corrosion protection |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications



















