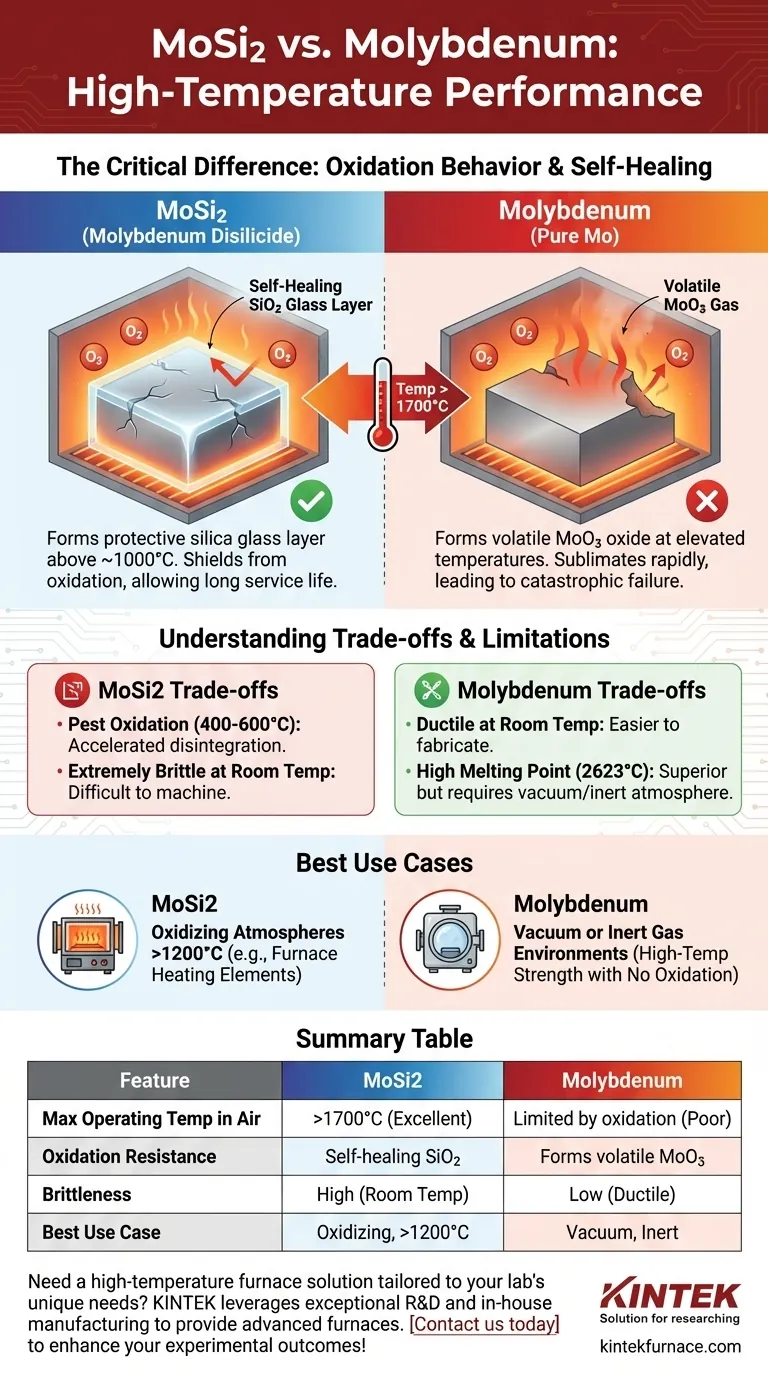
In high-temperature environments, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) significantly outperforms pure molybdenum, especially at temperatures exceeding 1700°C. While molybdenum rapidly oxidizes, becomes brittle, and fails, MoSi2 maintains its structural integrity. This is due to a unique self-healing protective layer that forms on its surface when heated in the presence of oxygen.
The critical difference is not just melting point, but how each material reacts to oxygen at high temperatures. Molybdenum rapidly oxidizes and fails, while MoSi2 forms a protective silica glass layer, effectively shielding itself from further degradation.

The Fundamental Difference: Oxidation Behavior
To select the right material, you must understand the chemical reaction that occurs on the surface of each metal at high temperatures. This behavior, not simply the melting point, dictates its useful service life.
MoSi2’s Self-Healing Mechanism
Molybdenum disilicide is prized for its outstanding oxidation resistance. Above approximately 1000°C, the silicon within the material reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
This reaction forms a thin, dense, and continuous layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2), which is essentially a form of quartz glass.
This glassy layer is self-healing and acts as a barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching and degrading the underlying MoSi2. This allows it to function reliably for long periods in extreme heat, granting it high thermal shock resistance and a long service life.
Molybdenum's High-Temperature Weakness
Pure molybdenum has a very high melting point (2623°C), which is technically higher than that of MoSi2 (2030°C). However, its performance in air is limited by oxidation.
At elevated temperatures, molybdenum reacts with oxygen to form molybdenum trioxide (MoO3). This oxide is volatile, meaning it turns directly into a gas and evaporates from the surface well below the metal's melting point.
This process, known as sublimation, leads to rapid material loss, component thinning, and ultimately, catastrophic failure. This is why pure molybdenum is unsuitable for high-temperature use in oxidizing atmospheres.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. The superiority of MoSi2 at extreme temperatures comes with critical trade-offs that are important for engineering design.
The 'Pest' Oxidation of MoSi2
While exceptional at very high temperatures, MoSi2 suffers from a phenomenon known as "pest oxidation" at intermediate temperatures (typically 400°C to 600°C).
In this range, it undergoes accelerated, non-protective oxidation that can cause the material to disintegrate into a powder. This makes it unsuitable for applications that dwell for long periods in this intermediate temperature range.
Brittleness and Fabrication
MoSi2 is a cermet (ceramic-metal composite), making it very hard and extremely brittle at room temperature. This makes it difficult and expensive to machine or form into complex shapes.
In contrast, pure molybdenum is a refractory metal with much higher ductility at room temperature, making it significantly easier and more cost-effective to fabricate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice between molybdenum and MoSi2 depends entirely on the specific operating temperature range, atmosphere, and mechanical requirements of your design.
- If your primary focus is sustained operation above 1200°C in an oxidizing atmosphere: MoSi2 is the definitive choice due to its self-forming protective silica layer, making it ideal for furnace heating elements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength in a vacuum or inert gas: Pure molybdenum is often a more cost-effective and fabricable solution, as its primary weakness (oxidation) is not a factor.
- If your primary focus is mechanical toughness and ease of fabrication: Molybdenum's superior ductility at room temperature makes it a more practical choice for components that do not face extreme, prolonged oxidation.
Understanding the underlying chemistry of material failure is the key to selecting a component that will not just survive, but thrive in its intended environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | MoSi2 | Molybdenum |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp in Air | >1700°C | Limited by oxidation |
| Oxidation Resistance | Excellent (self-healing SiO2 layer) | Poor (forms volatile MoO3) |
| Brittleness | High at room temperature | Low (more ductile) |
| Best Use Case | Oxidizing atmospheres above 1200°C | Vacuum or inert atmospheres |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise performance for your high-temperature applications—whether you're working with MoSi2, molybdenum, or other materials. Contact us today to enhance your experimental outcomes with reliable, efficient equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments



















