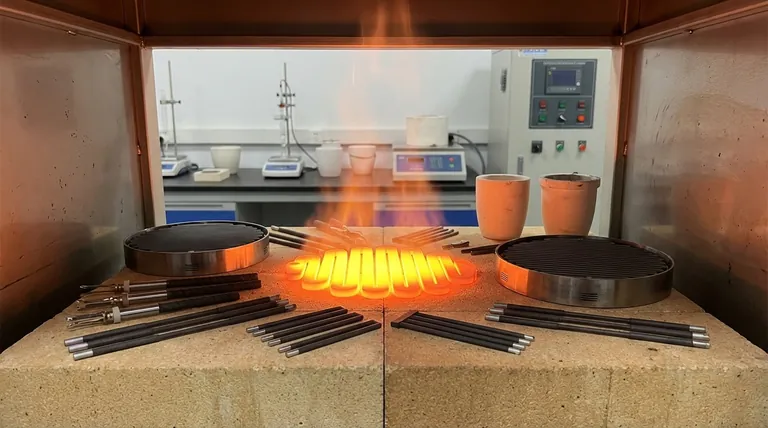
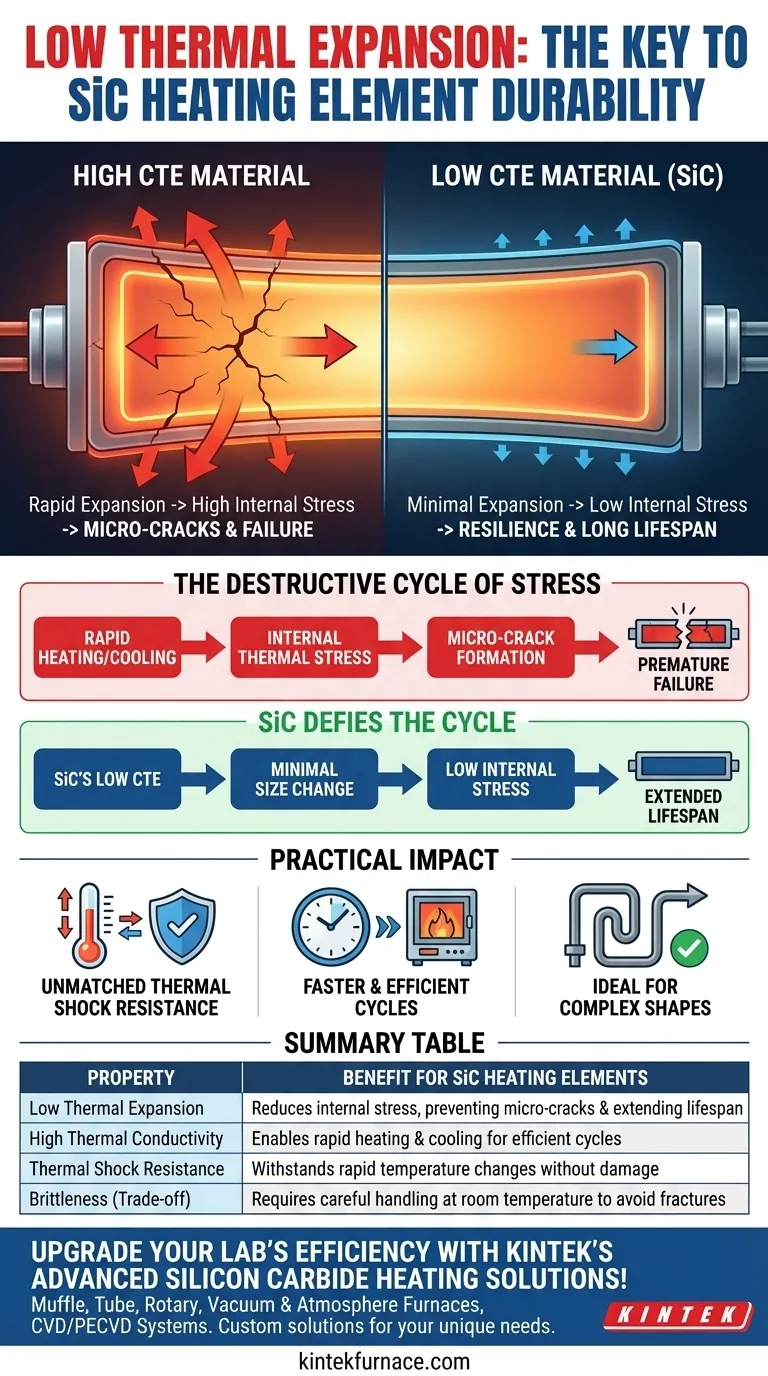
At its core, low thermal expansion is the key to silicon carbide's exceptional resilience. This property means the heating element physically expands and contracts very little, even when its temperature changes drastically. This stability minimizes the internal mechanical stress that builds up during heating and cooling cycles, preventing the formation of micro-cracks and fractures that would otherwise lead to premature failure and a shortened lifespan.
The primary reason silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are so durable is their fundamental resistance to thermal shock. Because they do not change size significantly when heated or cooled, they avoid the self-destructive internal stresses that cause other materials to degrade and fail over time.

The Physics of Thermal Stress: Why Expansion Matters
To understand durability, we must first understand the primary force that destroys heating elements: internal stress caused by temperature change.
What is Thermal Expansion?
Nearly all materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. This change in size is quantified by the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE).
A material with a high CTE, like aluminum, will experience a significant size change for a given temperature increase. A material with a low CTE, like silicon carbide, will experience a much smaller change.
The Destructive Cycle of Stress
When a heating element is powered on, it heats up rapidly. As it heats, it tries to expand. If different parts of the element heat at different rates, or if the element is constrained by its mounting, this expansion creates immense internal tension and compression.
This process, known as thermal stress, is repeated every time the element heats up and cools down. Each cycle acts like bending a paperclip back and forth, gradually weakening the material's structure until it eventually breaks.
How SiC Defies This Cycle
Silicon carbide's extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion is its defining advantage. It simply does not want to change size very much, regardless of the temperature swing.
Because it expands and contracts so little, the level of internal stress generated during a heat-up or cool-down cycle is dramatically reduced. This inherent stability is what prevents the cyclical damage that destroys elements made from other materials.
Practical Impact in High-Temperature Furnaces
This fundamental principle has direct, practical consequences for furnace operation and efficiency.
Unmatched Resistance to Thermal Shock
Thermal shock occurs when an object undergoes a rapid change in temperature. For a heating element, this happens during every startup, shutdown, or even when a cool furnace door is opened.
SiC's low thermal expansion makes it exceptionally resistant to thermal shock. It can endure these rapid temperature fluctuations without sustaining the structural damage that would crack or shatter a more sensitive material.
Enabling Faster and More Efficient Cycles
Silicon carbide also possesses excellent thermal conductivity, meaning it transfers heat very quickly. This allows for rapid heating and cooling of the furnace chamber.
The combination of high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion is critical. SiC can be heated and cooled quickly (a benefit of high conductivity) without destroying itself (a benefit of low expansion). This allows for shorter process cycle times, improving throughput and operational efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal properties are exceptional, no material is without its considerations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to proper application.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like most ceramics, silicon carbide is very hard but can be brittle before it reaches operating temperature. It must be handled with care during shipping and installation to prevent mechanical shock from causing fractures.
Atmospheric Sensitivity and Aging
Over hundreds or thousands of hours of operation, SiC elements can be affected by the furnace atmosphere. Processes like oxidation can slowly change the element's electrical resistance, which is a normal part of the aging process that must be accounted for in the system design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the low thermal expansion of SiC is not just a technical specification; it is the reason for its superior performance in demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is maximum lifespan and reliability: SiC's low thermal expansion directly translates to fewer failures from thermal shock, making it the most durable choice for cyclical operations.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: SiC's ability to withstand the rapid heating enabled by its high conductivity allows for shorter cycle times and higher throughput.
- If you are designing a furnace with complex element shapes: The minimal size change of SiC reduces the risk of stress concentration and mechanical failure at bends or connection points.
Understanding this fundamental property empowers you to select a material that doesn't just work, but endures.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for SiC Heating Elements |
|---|---|
| Low Thermal Expansion | Reduces internal stress, preventing micro-cracks and extending lifespan |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Enables rapid heating and cooling for efficient cycles |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temperature changes without damage |
| Brittleness (Trade-off) | Requires careful handling at room temperature to avoid fractures |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced silicon carbide heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, delivering durability and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















