In a rotary kiln, heat transfer occurs through a complex combination of radiation, convection, and conduction. Heat is generated either by a direct internal flame or by external heaters and is transferred to the processing material from the hot gases and the kiln's heated refractory brick lining as the material tumbles and moves down the inclined cylinder.
The goal is not just to generate heat, but to efficiently transfer it to achieve a specific temperature profile along the kiln's length. Effective control relies on managing the dynamic interplay between the hot gas, the radiating brick walls, and direct contact with the tumbling material bed.
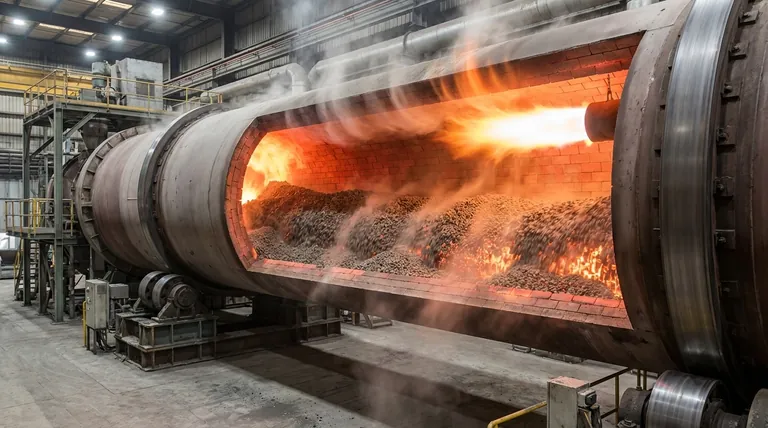

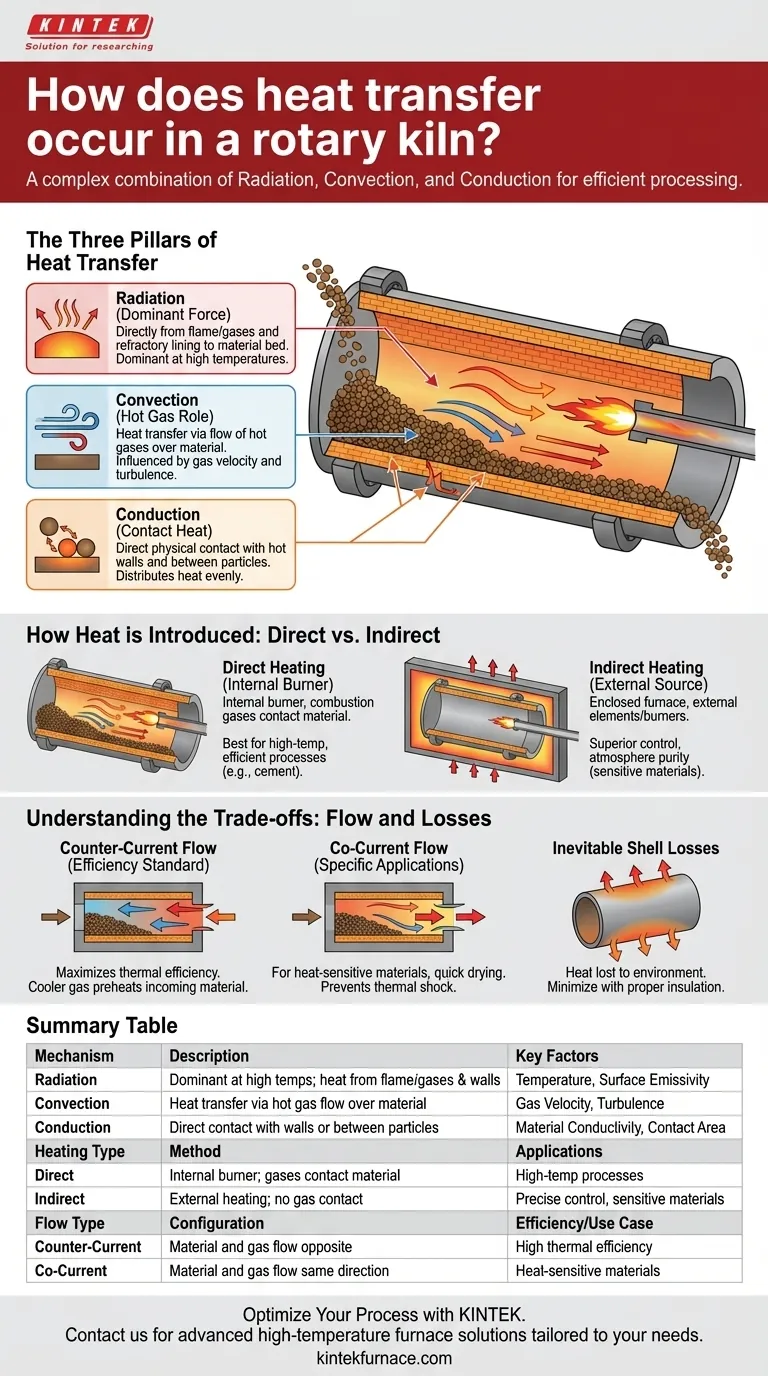
The Three Pillars of Heat Transfer
Heat transfer within the kiln is not a single event but a continuous process involving three distinct mechanisms that often work in parallel.
Radiation: The Dominant Force
At the high operating temperatures typical of most kilns, radiation is the most significant mode of heat transfer.
Heat radiates directly from the flame and hot combustion gases to the surface of the material bed. Simultaneously, the refractory brick lining absorbs immense heat and radiates it back down onto the material.
Convection: The Role of Hot Gas
Convection involves the transfer of heat through the flow of hot gases over the material.
As gas generated by a burner moves through the kiln, it transfers thermal energy to the solid particles it passes over. The efficiency of this process is heavily influenced by gas velocity and the degree of turbulence inside the kiln.
Conduction: Heat Through Contact
Conduction is heat transfer through direct physical contact. This happens in two primary ways.
First, as the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and makes direct contact with the hot refractory walls, conducting heat into the bed. Second, heat conducts between particles within the material bed itself, helping to distribute temperature more evenly.
How Heat is Introduced: Direct vs. Indirect
The method used to generate heat fundamentally defines the kiln's operating characteristics and applications.
Direct Heating: The Internal Burner
In a direct-fired kiln, a burner firing fuel like gas or oil is located inside the kiln shell, and the combustion gases are in direct contact with the material.
This is the most common method for high-temperature processes like cement production, as it allows for very efficient and rapid heat generation.
Indirect Heating: The External Source
In an indirect kiln, the rotating cylinder (retort) is enclosed within a furnace, and heat is supplied externally by electric elements or gas burners. The material never touches the combustion gases.
This approach offers superior temperature control and is essential when the processing atmosphere must be precisely controlled or kept free of contamination from combustion byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Flow and Losses
The direction of gas flow relative to the material has a profound impact on thermal efficiency and suitability for a given process.
Counter-Current Flow: The Standard for Efficiency
In a counter-current configuration, the material moves from the feed end to the discharge end, while the hot gas flows in the opposite direction.
This is the preferred arrangement for most applications because it maximizes thermal efficiency. Cold incoming material is preheated by the cooler outgoing gases, while the hottest gases treat the nearly finished product, maximizing the temperature difference along the entire length of the kiln.
Co-Current Flow: For Specific Applications
In a co-current setup, both the material and the hot gas flow in the same direction. The coldest material is met by the hottest gas.
This design is less common but is valuable for processing heat-sensitive materials that could be damaged by rapid temperature changes, or for applications where quick drying or ignition is desired at the entry point.
Inevitable Shell Losses
No kiln is perfectly efficient. A portion of the heat conducted to the refractory walls will continue through the kiln's steel shell and be lost to the surrounding environment.
Minimizing these shell losses through proper insulation is a critical aspect of efficient kiln design and operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of kiln configuration depends directly on your process requirements for temperature precision, efficiency, and material properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency and high temperatures: A direct-fired, counter-current system is the most effective and common choice.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control and atmosphere purity: An indirectly heated system offers unmatched control, protecting sensitive materials from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is processing volatile or heat-sensitive materials: A co-current flow configuration may be necessary to prevent thermal shock at the inlet.
Understanding these fundamental heat transfer dynamics is the key to mastering your kiln's performance and achieving consistent product quality.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Description | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation | Dominant at high temps; heat from flame/gases and refractory walls to material | Temperature, surface emissivity |
| Convection | Heat transfer via hot gas flow over material | Gas velocity, turbulence |
| Conduction | Heat through direct contact with walls or between particles | Material conductivity, contact area |
| Heating Type | Method | Applications |
| Direct | Internal burner; gases contact material | High-temp processes like cement |
| Indirect | External heating; no gas contact | Precise control, sensitive materials |
| Flow Type | Configuration | Efficiency/Use Case |
| Counter-Current | Material and gas flow opposite | High thermal efficiency |
| Co-Current | Material and gas flow same direction | Heat-sensitive materials |
Ready to optimize your rotary kiln's heat transfer for superior efficiency and control? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process with reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















