In the high-stakes environment of a vacuum furnace, graphite's chemical resistance is a cornerstone of process integrity and product quality. This property ensures that the furnace components themselves do not react with the workpiece, trace atmospheric gases, or other materials present at extreme temperatures. The primary benefit is the prevention of chemical contamination, which is critical for producing high-purity, defect-free materials.
The true value of graphite's chemical resistance isn't just that it survives the process, but that it remains a neutral, non-participating bystander. This chemical stability under vacuum is the foundation for achieving predictable, high-purity results in applications from metallurgy to electronics manufacturing.
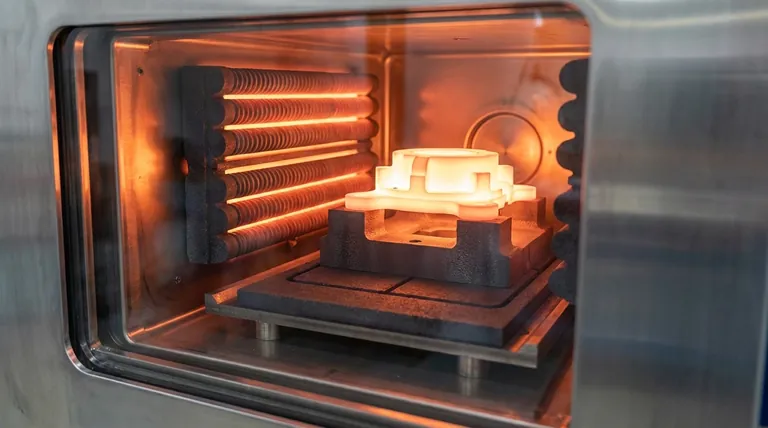

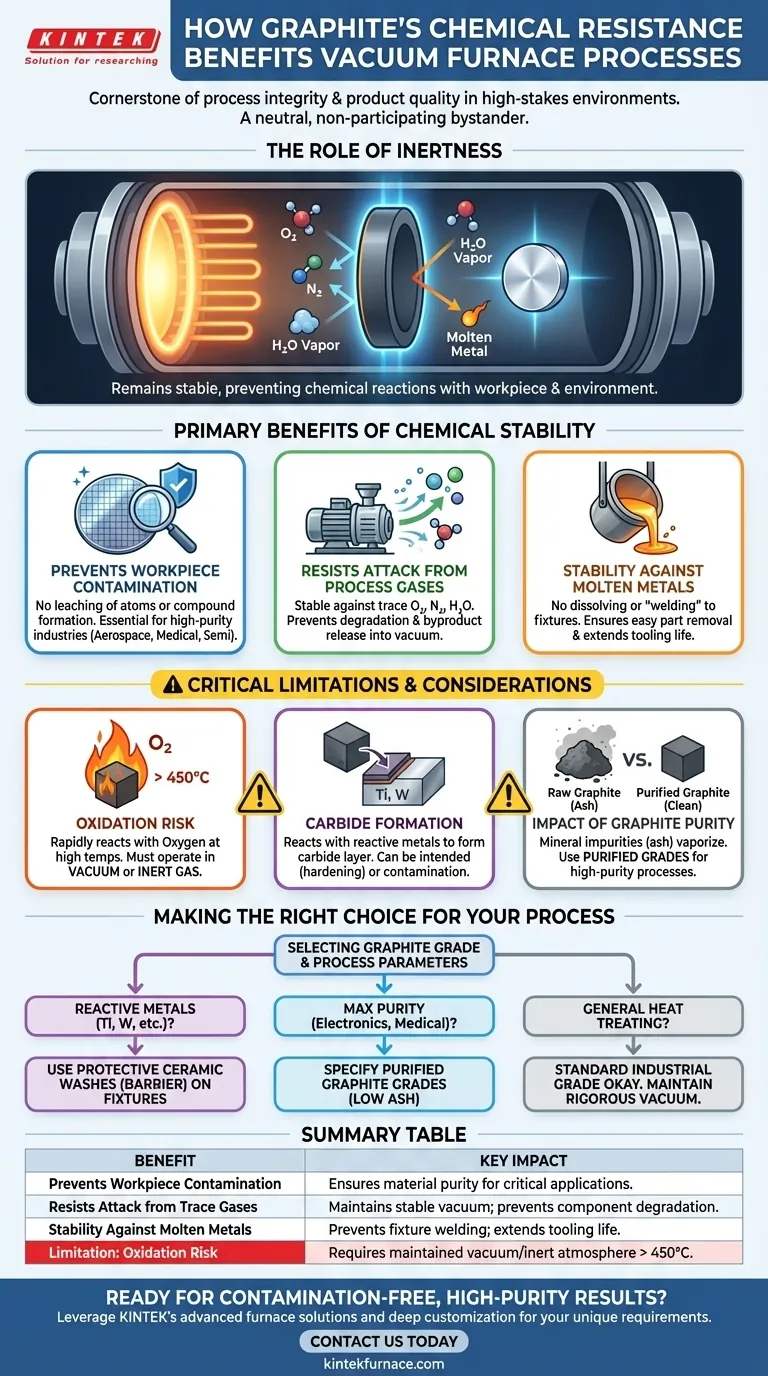
The Role of Inertness in a High-Purity Environment
A vacuum furnace is designed to create a controlled, clean environment. The chemical stability of the internal components, like heating elements and fixtures, is just as important as the vacuum itself.
Preventing Workpiece Contamination
The most direct benefit is the protection of the material being heat-treated. Graphite's inertness means it will not leach atoms or form unwanted compounds on the surface of the workpiece.
This is non-negotiable in industries like aerospace, medical implants, and semiconductors, where even parts-per-million levels of contamination can lead to component failure.
Resisting Attack from Process Gases
No vacuum is perfect. Trace amounts of oxygen, nitrogen, or water vapor are always present. Unlike many metals that would oxidize or form nitrides, graphite remains stable and unreactive with these residual gases at typical process temperatures.
This prevents the furnace components from degrading and, more importantly, from releasing reaction byproducts that could contaminate the vacuum environment and the workpiece.
Stability Against Molten Metals
Graphite maintains its structural integrity when in contact with most molten metals. It does not readily dissolve or form low-melting-point alloys (eutectics).
This prevents expensive fixtures from "welding" to the parts they are holding, ensuring easy removal of the finished product and maximizing the life of the furnace tooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While chemically resistant, graphite is not universally inert. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful furnace operation and process design.
The Critical Exception: Oxidation
Graphite's primary chemical vulnerability is its reaction with oxygen at elevated temperatures (typically above 450°C / 842°F). It will rapidly oxidize, forming CO and CO2 gas.
This is precisely why graphite is used in vacuum or inert gas furnaces. A significant air leak during a high-temperature cycle can lead to the catastrophic failure of all internal graphite components, including heating elements and insulation.
The Potential for Carbide Formation
Graphite is carbon. Certain reactive and refractory metals (such as titanium, tungsten, tantalum, and zirconium) can react with it at high temperatures to form a hard, stable carbide layer on their surface.
While sometimes this is an intended outcome (as in case hardening), it can be an undesirable form of contamination if you need to maintain the base metal's purity. This interaction must be accounted for in process design.
The Impact of Graphite Purity
Not all graphite is created equal. Raw graphite contains ash (mineral impurities) that can vaporize at high temperatures and become a source of contamination.
For high-purity processes, it is essential to use purified graphite, where the ash content has been reduced to extremely low levels through specialized high-temperature gas treatments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Leveraging graphite's chemical properties requires matching the material grade and process parameters to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium: Be aware of the potential for carbide formation and consider using protective ceramic washes (like yttria or zirconia) on fixtures to create a barrier.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity for electronics or medical devices: You must specify and invest in high-purity or purified graphite grades to eliminate the risk of ash-related contamination.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating or brazing: A standard industrial-grade graphite is often sufficient and cost-effective, but rigorous vacuum integrity must be maintained to prevent oxidation.
By understanding these chemical principles, you can transform your vacuum furnace from a simple oven into a precision manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Prevents Workpiece Contamination | Ensures material purity for critical applications like aerospace and semiconductors. |
| Resists Attack from Trace Gases | Maintains a stable vacuum environment, preventing component degradation. |
| Stability Against Molten Metals | Prevents fixture welding, extends tooling life, and ensures easy part removal. |
| Limitation: Oxidation Risk | Requires a maintained vacuum or inert atmosphere above 450°C to prevent failure. |
Ready to achieve contamination-free, high-purity results in your lab?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements, especially those demanding the chemical stability of high-purity graphite components.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnace solutions can enhance your process integrity and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency



















