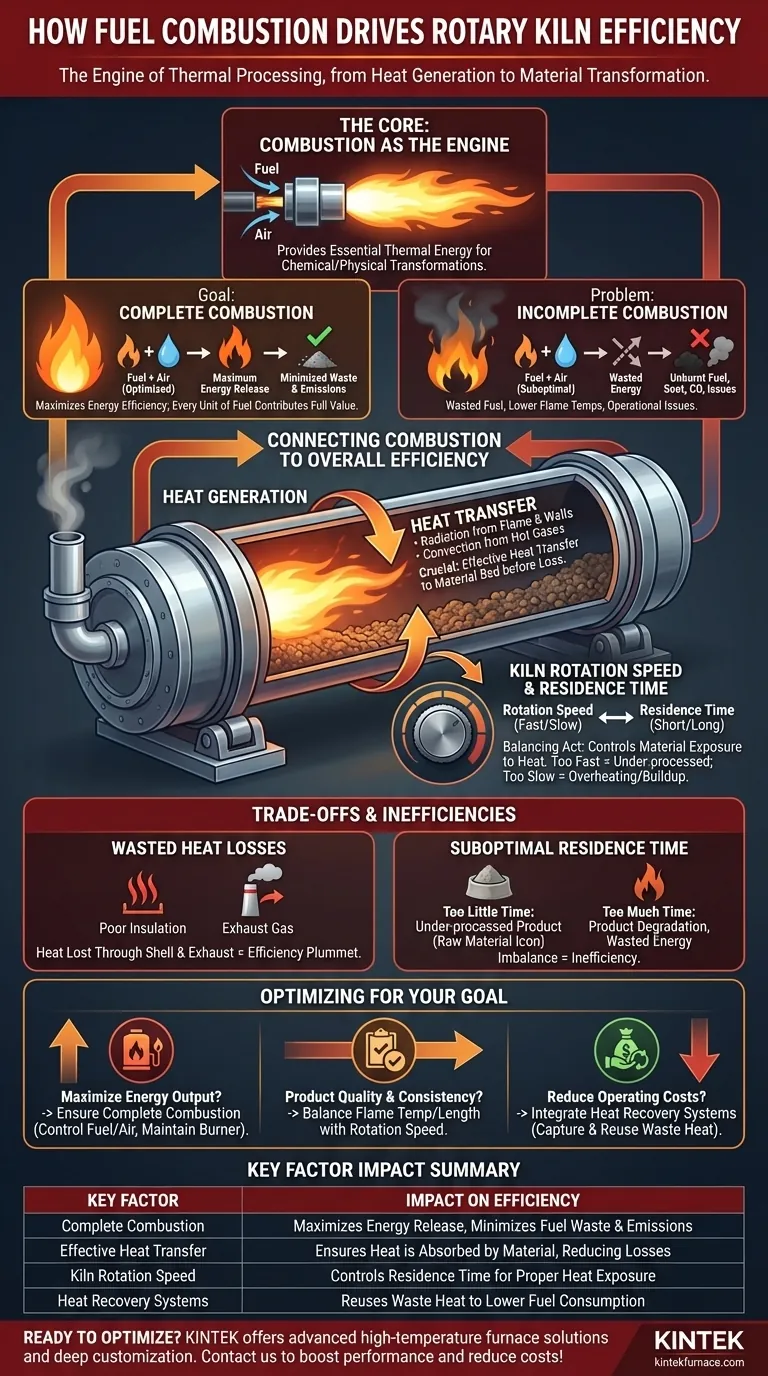
At its core, fuel combustion is the engine that drives a rotary kiln. It provides the essential thermal energy required for the chemical and physical transformations of the material being processed. The efficiency of the entire operation hinges directly on how completely and effectively this fuel is burned to generate and transfer heat.
True kiln efficiency is not just about generating heat, but about achieving complete combustion to maximize energy release from the fuel and then ensuring that heat is optimally transferred to the material before it can be lost.
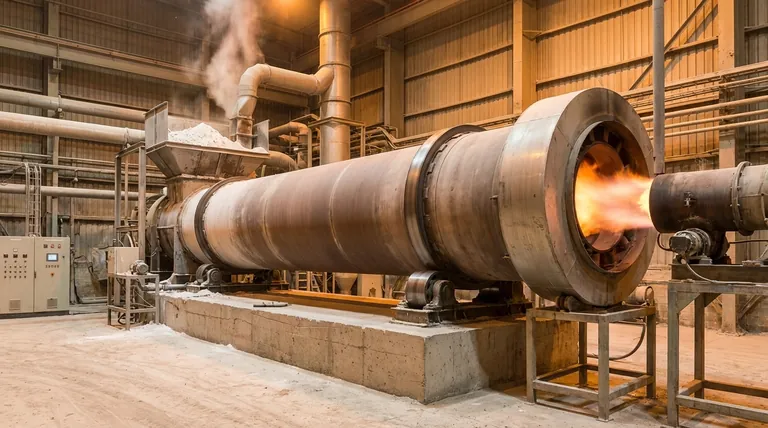

The Primary Role of Combustion: Heat Generation
Fuel combustion is the foundational process in any rotary kiln. Its quality dictates the thermal potential of the entire system.
Providing Essential Thermal Energy
The fundamental purpose of combustion is to release the chemical energy stored in fuel as heat. This heat raises the temperature inside the kiln to the specific levels required for processes like calcination, sintering, or drying.
The Critical Goal of Complete Combustion
Complete combustion is the ideal state where fuel reacts with a sufficient amount of oxygen to release its maximum possible energy. This ensures that every unit of fuel contributes its full heating value to the process, directly maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing the amount of fuel consumed.
Minimizing Waste and Byproducts
When combustion is incomplete, unburnt fuel particles (like soot) and carbon monoxide are created. This represents wasted energy and can lead to operational issues and increased emissions, making the process both inefficient and less environmentally sound.
How Combustion Connects to Overall Efficiency
Generating heat is only the first step. True efficiency is determined by how that heat is used within the dynamic environment of the kiln.
Effective Heat Transfer to the Material
The heat generated by the flame must be effectively transferred to the material bed. This occurs through a combination of radiation from the flame and hot refractory walls, and convection from the hot gases flowing through the kiln. Poor heat transfer means heat is simply lost out the exhaust stack.
The Balancing Act with Kiln Rotation
The rotation speed of the kiln drum is a critical variable that works in tandem with combustion. It dictates the residence time—how long the material is exposed to the heat.
If the rotation is too fast, the material passes through the kiln before it can absorb enough heat, regardless of how hot the flame is. If it's too slow, it can lead to overheating, material buildup, and inefficient tumbling, creating cold spots and an inconsistent product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inefficiencies
Optimizing a rotary kiln involves balancing competing factors. Mismanagement of combustion or its related parameters leads to significant efficiency losses.
The Cost of Incomplete Combustion
This is the most direct form of inefficiency. Every particle of unburnt fuel is wasted money. It also results in lower flame temperatures, forcing the system to consume even more fuel to reach the target processing temperature.
The Problem of Wasted Heat
Even with perfect combustion, efficiency plummets if the heat isn't used. Heat can be lost through the kiln shell (poor insulation) or carried away by exhaust gases. This is why many efficient designs incorporate heat recovery systems to preheat raw materials or combustion air using waste heat.
The Risk of Suboptimal Residence Time
An imbalance between the combustion rate and rotation speed is a primary source of inefficiency. Too much heat and too little time leads to an under-processed product. Too much time can degrade or damage the product, wasting both energy and raw material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your kiln's performance, you must align your combustion strategy with your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy output from fuel: Ensure complete combustion by meticulously controlling the fuel-to-air ratio and maintaining your burner system.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: Balance the flame temperature and length with the kiln's rotation speed to achieve the ideal residence time and heat exposure for your material.
- If your primary focus is reducing overall operating costs: Integrate heat recovery systems to capture and reuse waste heat from the exhaust gases, significantly lowering your net fuel consumption.
Mastering the dynamic interplay between combustion, heat transfer, and material mechanics is the key to unlocking peak rotary kiln efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Complete Combustion | Maximizes energy release, minimizes fuel waste and emissions |
| Effective Heat Transfer | Ensures heat is absorbed by material, reducing losses |
| Kiln Rotation Speed | Controls residence time for proper heat exposure |
| Heat Recovery Systems | Reuses waste heat to lower fuel consumption |
Ready to optimize your rotary kiln efficiency? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can boost your performance and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials



















