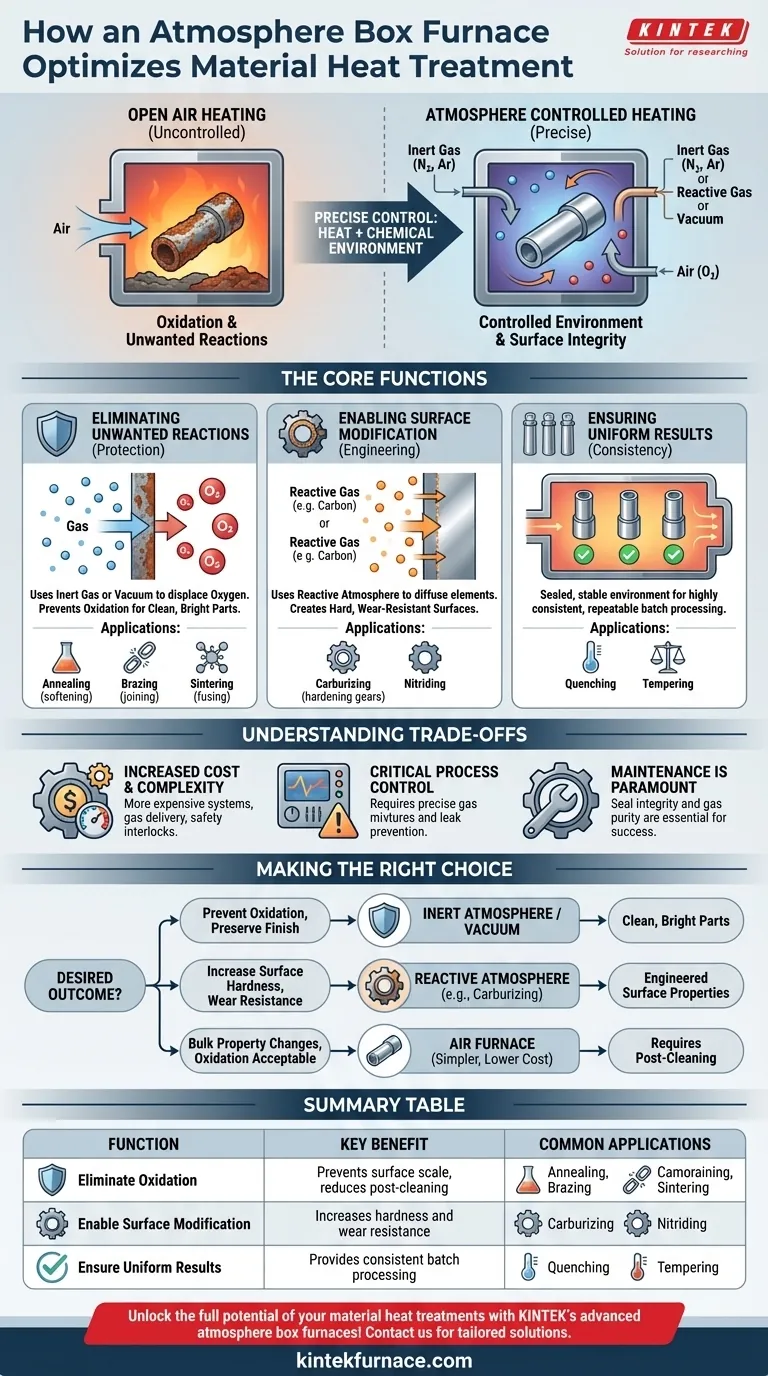
At its core, an atmosphere box furnace contributes to material heat treatment by giving you precise control over the chemical environment surrounding a part, in addition to controlling temperature. This control prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation and enables specific surface modifications, allowing you to achieve material properties that are impossible to create when heating in open air.
The crucial advantage of an atmosphere furnace is its ability to transform the furnace environment from a potential contaminant (air) into an active, beneficial tool. It's not just about applying heat; it's about controlling the chemical interactions at the material's surface to protect it or intentionally change it.

The Core Function: Moving Beyond Just Heat
Heating a material in open air invites chemical reactions, primarily oxidation (rust or scale). An atmosphere furnace manages the environment to either prevent these reactions or introduce new, desirable ones.
Eliminating Unwanted Reactions
An atmosphere furnace can be filled with a non-reactive (inert) gas like nitrogen or argon, or be put under a vacuum.
This controlled environment physically displaces the oxygen, preventing it from reacting with the hot metal surface. The result is a clean, bright part that retains its original surface composition and finish, eliminating the need for costly and damaging post-process cleaning.
Enabling Chemical Surface Modification
Alternatively, the furnace can be filled with a chemically reactive atmosphere. The gases become an active ingredient in the heat treatment process.
For example, in carburizing, a carbon-rich atmosphere is used to diffuse carbon atoms into the surface of steel. This creates a part with a very hard, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a softer, tougher core.
Ensuring Uniform and Consistent Results
By sealing the chamber, an atmosphere furnace provides a completely stable and predictable environment.
This combination of precise temperature management and a regulated atmosphere ensures that every part in a batch, and every batch over time, receives the exact same treatment, leading to highly consistent and reliable material properties.
Key Processes Enabled by Atmosphere Control
The ability to manipulate the furnace atmosphere makes it a versatile tool for a wide range of treatments that demand high levels of precision and surface integrity.
Protective Processes (Annealing, Quenching, Tempering)
For standard processes like annealing (softening) or quenching (hardening), a protective atmosphere is vital. It ensures the material's bulk properties are changed without forming surface scale, which can compromise part dimensions and require secondary removal operations.
Surface Hardening Processes (Carburizing)
As mentioned, carburizing is a prime example where the atmosphere is the key agent of change. This process is fundamental in manufacturing gears, bearings, and other components that require exceptional surface durability.
Advanced Joining and Consolidation (Brazing & Sintering)
In brazing, an oxygen-free environment prevents oxides from forming on the joint surfaces, allowing the brazing filler metal to flow cleanly and create a strong bond.
In sintering, a controlled atmosphere is used to fuse powdered metal particles together below their melting point. Preventing oxidation is critical for achieving a strong, dense final part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace introduces complexities not present in a simple air furnace.
Increased Cost and Complexity
Atmosphere furnaces require gas delivery systems, robust seals, and often complex safety interlocks. This makes them more expensive to acquire, operate, and maintain compared to standard air furnaces.
Critical Need for Process Control
The choice of atmosphere is critical and process-dependent. Using the wrong gas mixture or allowing leaks to contaminate the chamber can completely ruin a workload. This demands a higher level of operator knowledge and process development.
Maintenance is Paramount
The effectiveness of the furnace relies entirely on the integrity of its seals and the purity of its atmosphere. Any leaks that allow air to enter defeat the purpose of the system, making diligent maintenance essential for consistent results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an atmosphere furnace depends entirely on the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and preserving surface finish: An inert atmosphere (nitrogen, argon) or a vacuum is the correct choice for producing clean, bright parts.
- If your primary focus is increasing surface hardness and wear resistance: A reactive atmosphere, such as one for carburizing or nitriding, is necessary to chemically engineer the part's surface.
- If your primary focus is achieving bulk property changes where surface oxidation is acceptable: A simpler, less expensive air furnace may be sufficient, assuming post-process cleaning is factored into the workflow.
Ultimately, mastering atmosphere control transforms heat treatment from a simple heating process into a precise material engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminate Oxidation | Prevents surface scale, reduces post-cleaning | Annealing, brazing, sintering |
| Enable Surface Modification | Increases hardness and wear resistance | Carburizing, nitriding |
| Ensure Uniform Results | Provides consistent batch processing | Quenching, tempering |
Unlock the full potential of your material heat treatments with KINTEK's advanced atmosphere box furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse range of high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or composites. Don't let oxidation or inconsistent results hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and deliver superior outcomes for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity



















