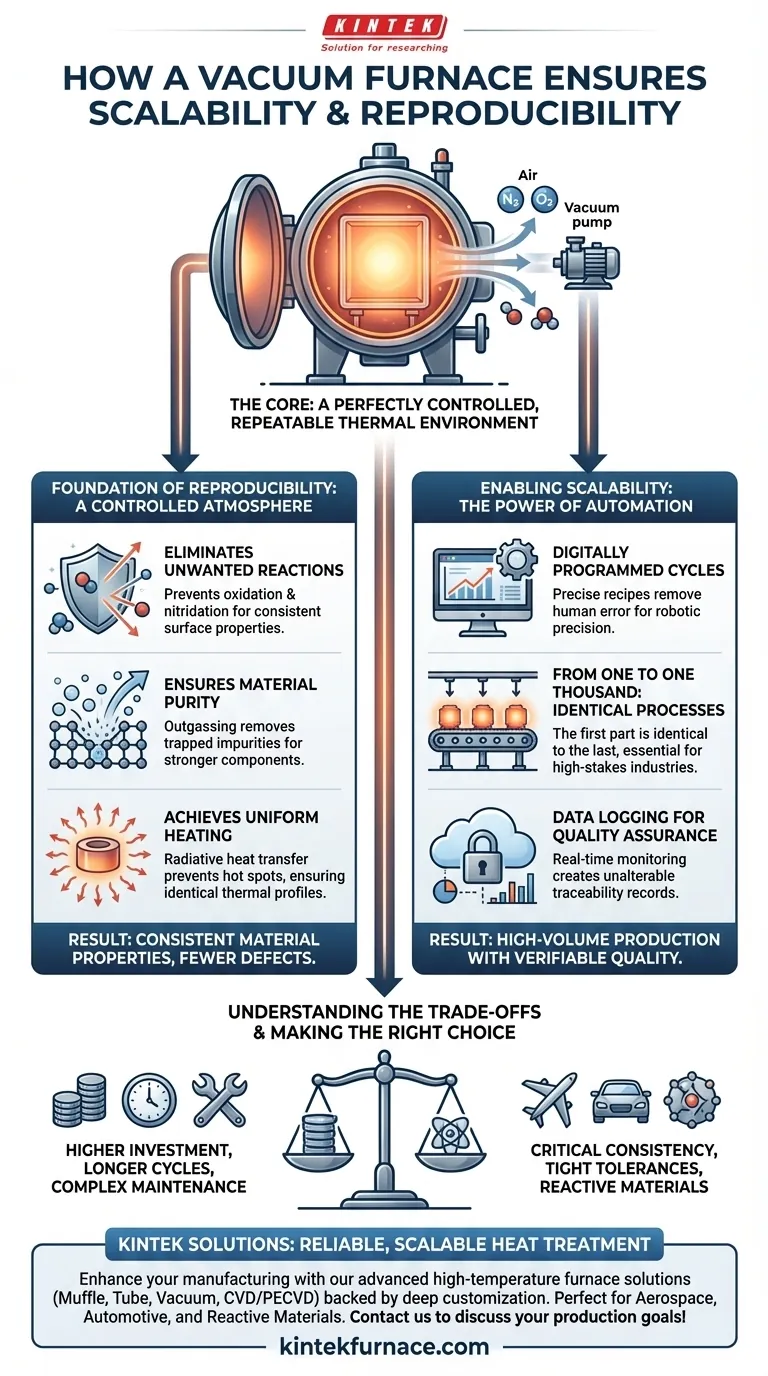
At its core, a vacuum furnace achieves exceptional scalability and reproducibility by creating a perfectly controlled and repeatable thermal environment. By removing atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, the furnace eliminates the primary source of process variability and material contamination, ensuring that every component undergoes the exact same treatment cycle, every time.
The fundamental advantage of a vacuum furnace is its ability to create a chemically inert and thermally stable environment. This level of control is what makes it possible to produce identical parts in large quantities, a requirement for any high-stakes manufacturing process.

The Foundation of Reproducibility: A Controlled Atmosphere
Reproducibility isn't an accident; it's the result of eliminating variables. A vacuum furnace is designed specifically to control the most critical variable in heat treatment: the atmosphere surrounding the part.
Eliminating Unwanted Reactions
The air we breathe is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. At the high temperatures used in heat treating, these gases become highly reactive.
Removing them from the furnace chamber prevents undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation and nitridation, which can alter a material's surface, compromise its structural integrity, and lead to inconsistent results.
Ensuring Material Purity
The vacuum does more than just remove the atmosphere in the chamber. It also actively pulls trapped gases and volatile impurities out of the material being processed, a phenomenon known as outgassing.
This purification process results in a cleaner, stronger, and more metallurgically sound component, free from the internal defects that can cause failures.
Achieving Uniform Heating
In a high-vacuum environment, heat is transferred primarily through radiation, not convection (air currents). This allows for extremely uniform and predictable heating across the entire surface of a part, even for complex geometries.
This uniformity prevents hot spots and ensures that the entire component experiences the exact same thermal profile, which is critical for achieving consistent material properties like hardness and grain structure.
Enabling Scalability: The Power of Automation
Once you have a reproducible process for one part, scaling it to thousands becomes a matter of automation and precision control.
Digitally Programmed Cycles
Modern vacuum furnaces are not manual tools; they are sophisticated, computer-controlled systems. Key process parameters—including temperature ramp rates, hold times, pressure levels, and cooling rates—are programmed into a precise recipe.
This digital control removes the element of human error and ensures the thermal cycle is executed with robotic precision.
From One to One Thousand: Identical Processes
Because the process is defined by a digital recipe in a perfectly controlled environment, the furnace can execute the exact same cycle indefinitely.
This ensures that the first part produced in a run is identical to the last, a core requirement for industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing where consistency is directly tied to safety and performance.
Data Logging for Quality Assurance
Every parameter of the heat treatment cycle is monitored and logged in real-time. This creates an unalterable data record for each batch of parts.
This traceability is essential for quality control and certification, providing verifiable proof that every component was processed according to strict specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces and their supporting systems (pumps, controls, cooling) represent a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping the chamber down to the required vacuum level and then, in some cases, backfilling with an inert gas adds time to the overall process cycle.
Increased Maintenance Complexity
The high-performance vacuum pumps, seals, and sophisticated control systems require specialized and diligent maintenance to ensure they operate correctly and prevent leaks, which could compromise the entire process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is absolute part consistency for critical applications: The controlled, inert environment of a vacuum furnace is the only way to guarantee the elimination of atmospheric contamination and achieve repeatable material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with tight metallurgical tolerances: The automated, programmable nature of a vacuum furnace ensures that every part in a large run meets the exact same specification.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or exotic materials like titanium or superalloys: A vacuum environment is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic contamination and achieve the desired performance characteristics.
Ultimately, investing in a vacuum furnace is an investment in process control, and that control is what delivers unwavering confidence in the quality of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Reproducibility | Controlled inert atmosphere, elimination of oxidation/nitridation, uniform radiative heating | Consistent material properties, reduced variability, fewer defects |
| Scalability | Digital programming, automated cycles, real-time data logging | High-volume production, identical parts, traceability for quality assurance |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, reactive materials processing | Guaranteed part consistency, safety, performance in critical uses |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing with reliable, scalable heat treatment? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, or handling reactive materials, our vacuum furnaces deliver the control and consistency you demand. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance



















