In short, a vacuum environment purifies molten metal in two fundamental ways: it forces certain impurities to boil out of the liquid, and it prevents the air itself from creating new impurities. This dual-action process creates a level of purity that is often impossible to achieve in a standard atmospheric environment.
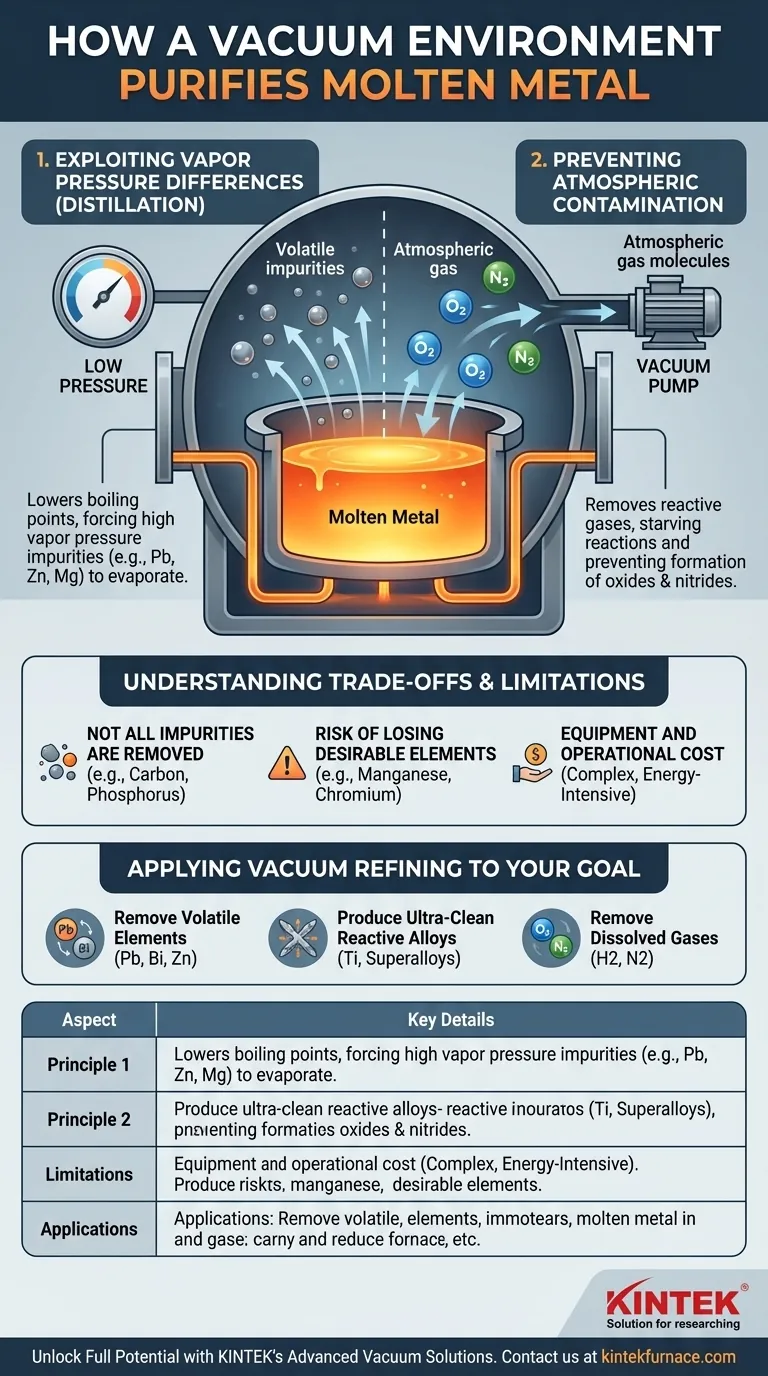
A vacuum purifies molten metal by fundamentally altering the physical and chemical environment. It lowers the boiling point of volatile impurities, causing them to evaporate, and simultaneously removes atmospheric gases like oxygen, preventing the formation of new impurities like oxides.

The Two Core Principles of Vacuum Purification
To truly understand the power of vacuum metallurgy, you must grasp the two distinct physical and chemical principles at work. It's not just about sucking air out; it's about controlling the state of matter and preventing unwanted reactions.
Principle 1: Exploiting Vapor Pressure Differences
At the high temperatures of molten metal, every element in the melt has a tendency to turn into a gas, a property known as vapor pressure. Some elements, like lead, zinc, and magnesium, have a very high vapor pressure, meaning they want to "escape" the liquid.
By creating a vacuum, you dramatically lower the pressure pushing down on the surface of the molten metal. This makes it significantly easier for elements with high vapor pressure to boil away and be drawn out by the vacuum system.
This process is essentially a form of distillation. It selectively targets and removes specific volatile impurities, leaving the base metal behind in a purer state.
Principle 2: Preventing Atmospheric Contamination
The air around us is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. At the extreme temperatures required to melt metals, these gases become highly reactive.
When molten metal is exposed to air, the oxygen rapidly forms oxides, and nitrogen can form nitrides. These compounds are impurities that can degrade the mechanical properties of the final product, causing brittleness or weakness.
A vacuum chamber physically removes the vast majority of these reactive gas molecules. This starves the chemical reaction, effectively preventing the formation of these oxide and nitride impurities from the start. This is especially critical for highly reactive metals like titanium, aluminum, and various superalloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum refining is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Not All Impurities Are Removed
This method is only effective for impurities that have a higher vapor pressure than the base metal you are trying to purify.
Elements with very low vapor pressure (like carbon or phosphorus in steel) will not evaporate under vacuum. They remain in the melt and must be removed using other metallurgical processes, such as chemical fluxing or gas injection.
Risk of Losing Desirable Elements
The process is non-selective; it removes any element with a high vapor pressure. This can include desirable alloying elements.
For example, manganese and chromium, which are critical components in many steel alloys, also have relatively high vapor pressures. A vacuum process must be carefully controlled—managing temperature and pressure levels precisely—to remove unwanted impurities without stripping away essential alloy components.
Equipment and Operational Cost
Vacuum furnaces and their associated pumping systems are complex, expensive to procure, and require significant energy and maintenance to operate. This cost must be justified by the need for superior material purity and performance.
Applying Vacuum Refining to Your Goal
Your choice to use a vacuum process depends entirely on the specific impurities you need to remove and the quality requirements for your final material.
- If your primary focus is removing volatile elements like lead, bismuth, or zinc: Vacuum treatment is a highly effective and direct method for this specific type of purification.
- If your primary focus is producing ultra-clean, reactive alloys (e.g., titanium or superalloys): A vacuum is non-negotiable to prevent the formation of performance-degrading oxides and nitrides.
- If your primary focus is removing dissolved gases like hydrogen or nitrogen: Vacuum degassing is the industry standard for reducing gas porosity and preventing issues like hydrogen embrittlement.
Ultimately, understanding these principles allows you to wield vacuum metallurgy not as a blunt instrument, but as a precise tool for achieving specific material properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Principle 1: Vapor Pressure Exploitation | Lowers boiling points of volatile impurities (e.g., lead, zinc) for evaporation and removal via distillation. |
| Principle 2: Atmospheric Contamination Prevention | Removes oxygen and nitrogen to avoid oxide and nitride formation, crucial for reactive metals like titanium. |
| Limitations | Ineffective for low vapor pressure impurities (e.g., carbon); risk of losing desirable alloying elements; high equipment costs. |
| Applications | Ideal for removing volatile elements, producing ultra-clean reactive alloys, and degassing to reduce porosity. |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Materials with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're refining reactive alloys or removing volatile impurities, our expertise ensures superior purity and performance for your specific goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored vacuum furnace systems can enhance your metal purification processes and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















