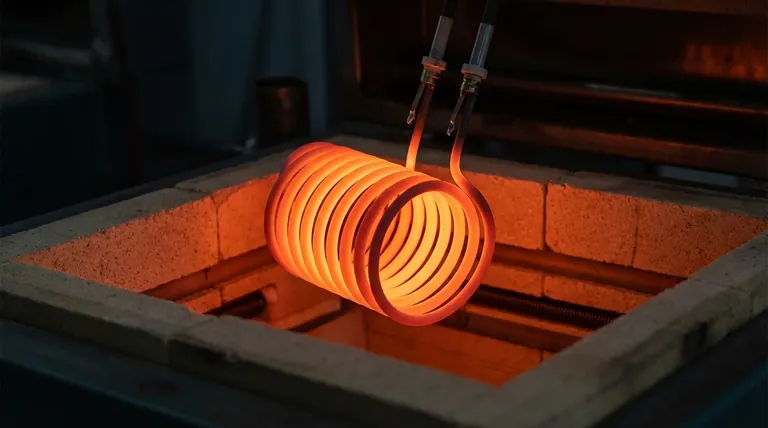
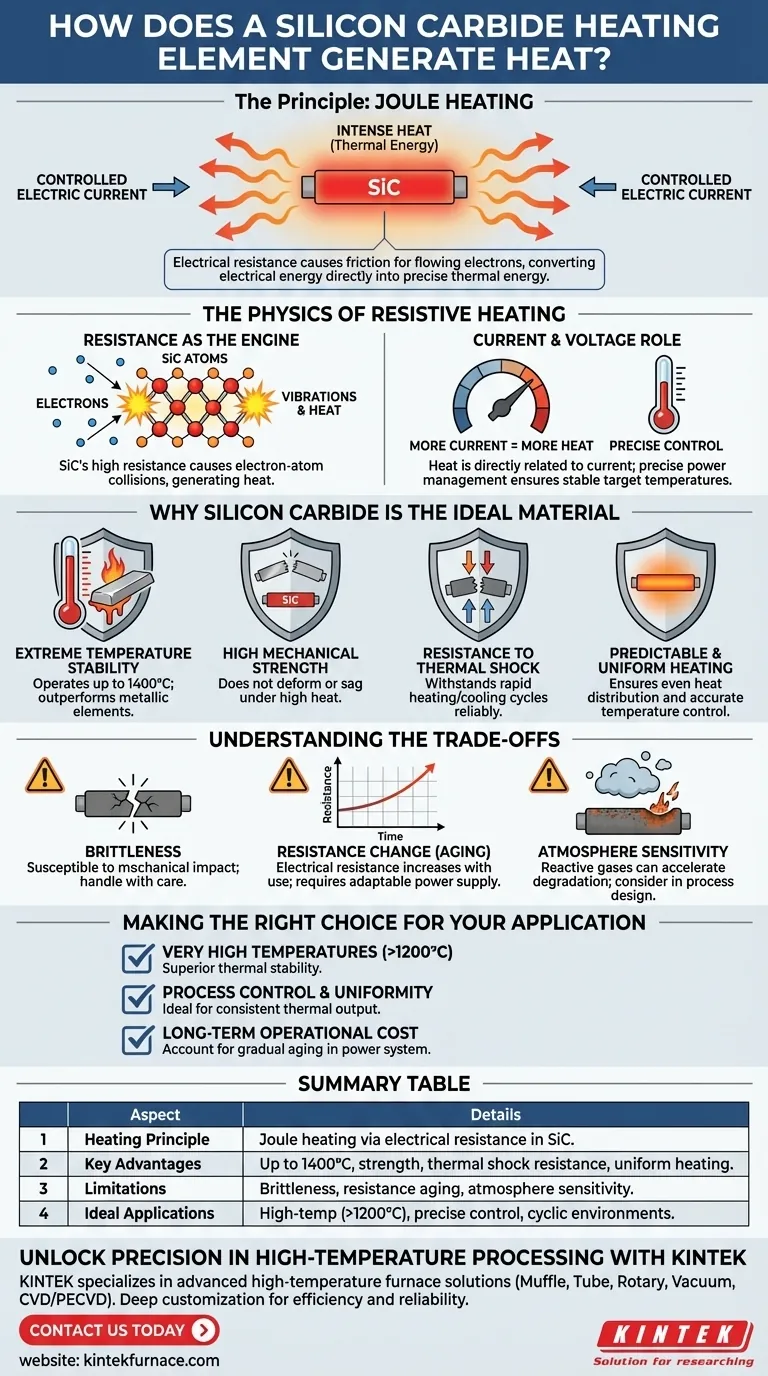
At its core, a silicon carbide heating element operates on a fundamental principle of physics known as Joule heating. When a controlled electric current is forced through the silicon carbide (SiC) material, its inherent electrical resistance causes friction for the flowing electrons. This friction generates intense heat, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy that can be precisely controlled for demanding industrial applications.
The mechanism is simple resistive heating, but the true value of a silicon carbide element lies in the material's unique ability to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock without deforming or degrading, making it an indispensable tool for high-temperature processes.

The Physics of Resistive Heating
To understand why SiC elements are so effective, we must first grasp the underlying principle of how they convert electricity into heat. The process is elegant in its simplicity.
Resistance as the Engine of Heat
Every material has some level of resistance to the flow of electricity. Silicon carbide is specifically engineered to have a relatively high electrical resistance.
When current flows, electrons collide with the atoms of the SiC material. These collisions generate vibrations in the atomic lattice, which we perceive and measure as heat.
The Role of Current and Voltage
The amount of heat produced is directly related to the amount of current passing through the element and its resistance. More current leads to more collisions and, therefore, more heat.
This relationship allows for very precise temperature control. By accurately managing the power supplied to the element, you can achieve and maintain a stable target temperature within the furnace or kiln.
Why Silicon Carbide Is the Ideal Material
The principle of resistive heating can be applied to many materials, but few can perform under the conditions that silicon carbide excels in. The material's specific properties are what make it a superior choice for high-temperature work.
Extreme Temperature Stability
The primary advantage of SiC is its ability to operate at very high temperatures, often exceeding 1400°C (2550°F), where many conventional metallic elements would simply melt or rapidly oxidize and fail.
High Mechanical Strength
As noted, silicon carbide is a hard, rigid material. Critically, it does not deform or sag under its own weight at high temperatures, ensuring it maintains its position and heating integrity within a furnace structure.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Industrial processes often require rapid heating and cooling cycles. SiC elements are highly resistant to the stress of this thermal shock, giving them a long and reliable service life in demanding cyclic applications.
Predictable and Uniform Heating
The uniform composition of SiC elements ensures that heat is generated evenly along their length. This leads to a small temperature difference across the heated zone and highly accurate temperature control, which is critical for sensitive processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. To be a true expert, you must understand the limitations and operational considerations of SiC technology.
The Challenge of Brittleness
While hard and rigid, SiC elements are also brittle. They are susceptible to fracture from mechanical impact or shock. Careful handling during installation and maintenance is essential to prevent damage.
Resistance Change Over Time (Aging)
A crucial operational characteristic of SiC is that its electrical resistance gradually increases with use and time at temperature. This phenomenon is known as aging.
This is not a defect but a predictable property. Your power supply system must be capable of increasing its voltage output over time to push the same current through the higher-resistance element, thereby maintaining constant power and temperature.
Atmosphere Sensitivity
While generally robust, the lifespan of a SiC element can be affected by the furnace atmosphere. Certain reactive gases can accelerate aging or cause degradation, a factor that must be considered during process design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of heating element technology must align with your specific process goals. Use these points as a guide for your decision.
- If your primary focus is achieving very high process temperatures (above 1200°C): SiC is an exceptional choice due to its superior thermal stability compared to most metallic elements.
- If your primary focus is process control and uniformity: The stable and predictable nature of SiC heating makes it ideal for applications requiring consistent thermal output and high accuracy.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational cost: You must account for the gradual aging of SiC elements and ensure your power control system can adapt to their changing resistance over their service life.
By understanding these core principles and material properties, you can effectively leverage silicon carbide heating elements to achieve reliable and precise high-temperature performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Joule heating via electrical resistance in SiC material |
| Key Advantages | Operates up to 1400°C, high mechanical strength, thermal shock resistance, uniform heating |
| Limitations | Brittleness, resistance increases with age (aging), sensitive to certain atmospheres |
| Ideal Applications | High-temperature processes (>1200°C), precise temperature control, cyclic heating environments |
Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Are you struggling with maintaining consistent temperatures in demanding industrial applications? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures that we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our silicon carbide heating elements and other solutions can elevate your lab's performance and reduce operational costs. Let's achieve superior heat treatment together!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















