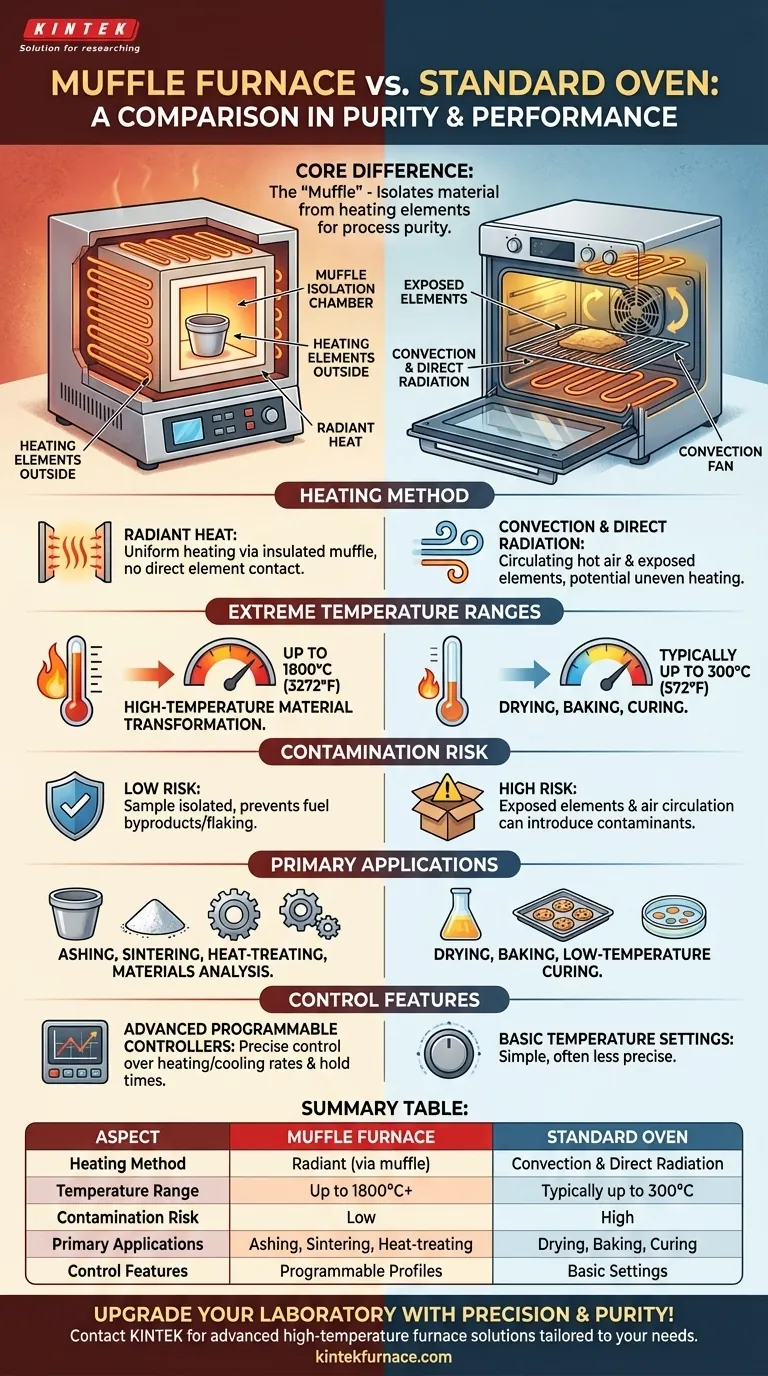
Fundamentally, a muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a specialized instrument designed for process purity. Its defining feature is an inner chamber, or "muffle," that isolates the material being heated from the heating elements and any potential contaminants. This, combined with its ability to reach far higher temperatures, distinguishes it completely from a standard oven.
The critical distinction is isolation. A standard oven heats both the air and the material directly, often with exposed elements. A muffle furnace uses a protective chamber to shield the material, enabling high-purity, high-temperature processes that are impossible in a conventional oven.
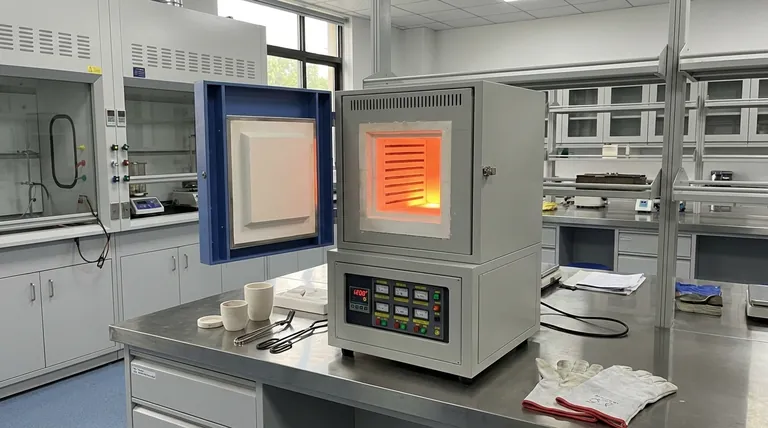

The Core Difference: The "Muffle"
The primary distinction comes from the furnace's namesake component, which dictates how heat is applied and what environment the sample is exposed to.
What is a Muffle?
A muffle is an insulating chamber, typically made of ceramic, that sits inside the furnace.
The material to be heated is placed inside this muffle. The heating elements are on the outside of the muffle, meaning they never come into direct contact with the sample or its immediate atmosphere.
The Impact on Heating Method
This design means a muffle furnace primarily heats via radiant heat. The elements heat the muffle, and the muffle then radiates that heat evenly onto the sample.
In contrast, a standard oven often uses convection (circulating hot air) and direct radiation from exposed heating elements, which can lead to uneven heating and contamination.
Preventing Process Contamination
Because the sample is isolated from the heating source, there is no risk of contamination from fuel byproducts (in a gas furnace) or flaking from the electric elements.
This makes muffle furnaces essential for sensitive applications like ashing, where the goal is to burn off organic material to determine the inorganic content, or sintering ceramic powders into a solid.
A Gulf in Performance and Control
Beyond the muffle itself, these furnaces are built for industrial and scientific applications, with performance capabilities that far exceed any standard oven.
Extreme Temperature Ranges
A standard kitchen or laboratory oven typically maxes out around 250-300°C (about 572°F).
Muffle furnaces, however, are designed for material transformation and can operate at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F) or even higher, depending on the model.
Precision Temperature Management
Muffle furnaces feature advanced, fully programmable controllers. This allows for precise control over heating rates, hold times at specific temperatures, and cooling rates.
This level of control is critical for materials science, metallurgy, and chemistry, where the thermal profile directly impacts the final properties of the material.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The enclosed muffle design inherently promotes highly uniform temperature throughout the chamber. This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, leading to consistent and repeatable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a muffle furnace and an oven requires understanding their specific roles and limitations.
Muffle Furnace vs. Convection Oven
A simple laboratory oven is for drying, baking, or low-temperature curing. A muffle furnace is for high-temperature material processing where purity is paramount. Using a muffle furnace for simple drying is inefficient and unnecessary.
Muffle Furnace vs. Vacuum Furnace
A muffle furnace provides a controlled atmosphere free from heating element contamination. It is ideal for most high-temperature lab work.
A vacuum furnace goes a step further by removing the atmosphere entirely. This is necessary only when the material itself is highly reactive with air (like titanium) or when even trace atmospheric gases could ruin the process.
Cost and Complexity
Muffle furnaces are robust, industrial-grade instruments built with premium components for reliability. They represent a significantly higher investment than standard ovens. Their operation also requires a greater understanding of the thermal process being performed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific temperature, purity, and control requirements of your task.
- If your primary focus is simple drying, baking, or low-temperature curing: A standard laboratory convection oven is the correct and most cost-effective tool.
- If your primary focus is ashing, sintering, heat-treating metals, or materials analysis: A muffle furnace is essential for its high temperatures and contamination-free environment.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive or atmosphere-sensitive materials: You may need to look beyond a muffle furnace to a more specialized vacuum furnace.
Choosing the right heating instrument is about matching the tool's core capabilities—isolation, temperature, and control—to your specific process requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Muffle Furnace | Standard Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Radiant heat via insulated muffle | Convection and direct radiation |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1800°C or higher | Typically up to 300°C |
| Contamination Risk | Low (sample isolated from elements) | High (exposed elements and air) |
| Primary Applications | Ashing, sintering, heat-treating | Drying, baking, low-temperature curing |
| Control Features | Programmable controllers for precise thermal profiles | Basic temperature settings |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision and purity! At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, metallurgy, or chemistry, our furnaces ensure contamination-free, high-temperature processing with reliable performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















