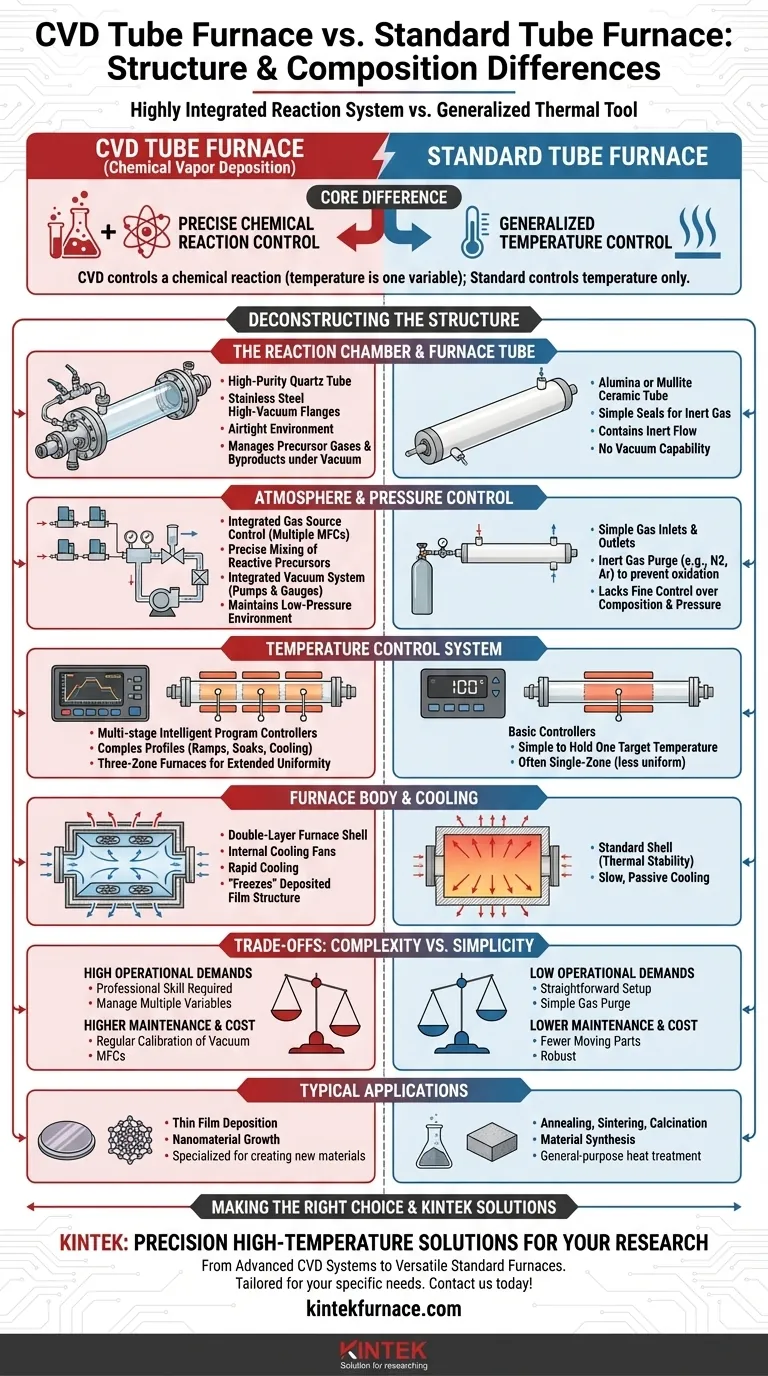
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) tube furnace is a highly integrated and precise system, whereas a standard tube furnace is a more generalized thermal processing tool. The CVD furnace's structure includes dedicated subsystems for gas delivery, vacuum control, and reactive chemistry, which are absent in simpler furnaces designed solely for heating a material in a controlled atmosphere.
The fundamental difference is not just in the components, but in the purpose. A standard tube furnace is designed to control temperature. A CVD tube furnace is designed to precisely control a chemical reaction, for which temperature is just one of several critical variables.

Deconstructing the Furnace: Key Structural Differences
The specialized requirements of the CVD process directly dictate its complex structure. Each component serves a specific function that goes far beyond simple heating.
The Reaction Chamber and Furnace Tube
A CVD system uses a high-purity furnace tube, often made of quartz, to ensure no contaminants interfere with the chemical deposition process.
These tubes are sealed on both ends with stainless steel high-vacuum flanges. This creates an airtight environment essential for managing precursor gases and removing byproducts under vacuum.
Standard tube furnaces typically use alumina or mullite ceramic tubes. Their seals are designed to simply contain an inert gas flow, not to hold a high vacuum.
Atmosphere and Pressure Control Systems
This is the most significant structural distinction. A CVD furnace incorporates a gas source control system, often with multiple mass flow controllers (MFCs), to precisely mix and inject reactive precursor gases.
It also includes an integrated vacuum control system, with pumps and gauges to maintain the specific low-pressure environment required for the deposition reaction to occur.
A standard furnace, by contrast, has simple gas inlets and outlets. It's designed to be purged with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation, but it lacks the fine control over gas composition and pressure.
The Temperature Control System
CVD furnaces utilize multi-stage intelligent program controllers. These allow for complex temperature profiles with precise ramps, soaks, and cooling rates, which are critical for controlling film growth and properties.
Many are also three-zone furnaces, with separate controllers for the center and ends of the tube. This creates an extended, highly uniform temperature zone essential for consistent deposition over a larger area, such as on a silicon wafer.
While multi-zone furnaces exist for non-CVD applications, basic tube furnaces often use a single heating zone and a simpler controller designed to hold one target temperature.
Furnace Body and Cooling
CVD furnaces often feature a double-layer furnace shell with internal cooling fans. This design allows for rapid cooling after a deposition run.
This rapid temperature change is a process requirement, helping to "freeze" the deposited film's structure and prevent unwanted phase changes or grain growth that could occur during slow cooling. Standard furnaces are designed for thermal stability and typically cool down slowly and passively.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Complexity vs. Simplicity
The advanced capabilities of a CVD furnace come with significant operational and maintenance considerations.
Operational Demands
Operating a CVD furnace requires professional knowledge and skill. The operator must manage gas flows, vacuum levels, and complex temperature programs simultaneously to achieve a successful deposition.
Standard tube furnaces are far simpler. Operation often involves little more than placing a sample, setting a target temperature, and initiating a gas purge.
Maintenance and Cost
The complexity of a CVD system leads to higher maintenance requirements and costs. Components like vacuum pumps, seals, and mass flow controllers require regular calibration and service to ensure repeatability.
A standard furnace has fewer moving parts and sensitive electronics, resulting in lower maintenance overhead and greater general robustness.
Application Specificity
A CVD furnace is a highly specialized tool, optimized exclusively for creating thin films and nanomaterials. Its complexity makes it less practical for general-purpose heat treatment.
A standard tube furnace is a versatile workhorse, suitable for a wide range of thermal processes like annealing, sintering, calcination, and material synthesis that do not involve a precursor gas reaction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing between a CVD system and a standard furnace depends entirely on the process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is depositing thin films or growing nanomaterials: You require a CVD furnace for its integrated gas delivery, vacuum capability, and precision process control.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment, annealing, or sintering: A standard single or multi-zone tube furnace offers the necessary temperature control in a simpler, more cost-effective, and robust package.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk powders with maximum thermal efficiency: You might even consider other specialized designs, like a fluidized bed furnace, which uses a different heat transfer mechanism altogether.
Understanding these fundamental design differences empowers you to select the right tool for your specific material synthesis or processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Tube Furnace | Standard Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Controls chemical reactions for thin film deposition | Controls temperature for general heat treatment |
| Gas Control | Multi-gas system with mass flow controllers for precise mixing | Simple gas inlets for inert atmosphere purging |
| Vacuum System | Integrated pumps and gauges for low-pressure environments | Lacks vacuum capability, focuses on atmospheric control |
| Temperature Control | Multi-zone with intelligent program controllers for complex profiles | Often single-zone with basic controllers for stable temperatures |
| Furnace Tube Material | High-purity quartz to prevent contamination | Alumina or mullite ceramic for general use |
| Cooling Mechanism | Double-layer shell with fans for rapid cooling | Passive cooling for slow temperature reduction |
| Operational Complexity | High, requires skilled handling of multiple variables | Low, straightforward setup and operation |
| Typical Applications | Thin film deposition, nanomaterial growth | Annealing, sintering, calcination, material synthesis |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with Precision High-Temperature Solutions from KINTEK
Are you working on advanced material synthesis, thin film deposition, or other specialized thermal processes? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need the integrated precision of a CVD furnace or the versatility of a standard tube furnace, we can tailor our offerings to enhance your efficiency and results.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our advanced furnace solutions can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision



















