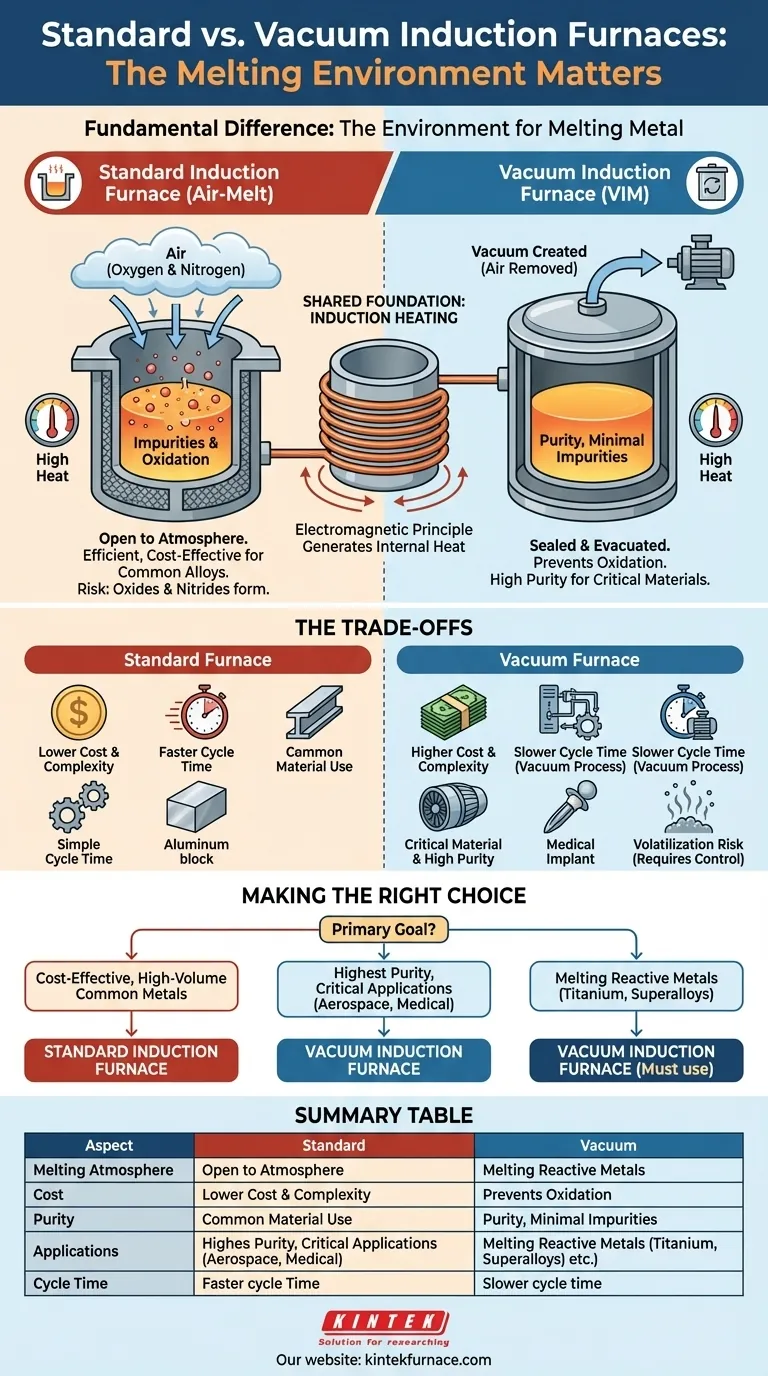
The fundamental difference between a vacuum induction furnace and a standard induction furnace is the environment in which the metal is melted. A standard furnace heats metal in the open air, whereas a vacuum induction furnace performs this process inside a sealed chamber where the air has been removed. This single distinction is the source of all major differences in cost, complexity, and final product quality.
While both furnaces use the same electromagnetic principle to generate heat, the choice between them is a choice between process control and cost. A standard furnace is a workhorse for common metals; a vacuum furnace is a precision instrument for creating high-purity, performance-critical materials.

The Shared Foundation: Induction Heating
All induction furnaces, whether standard or vacuum, operate on the same core principle of physics. Understanding this shared foundation is key to seeing why the melting atmosphere is such a critical differentiator.
How Induction Works
An induction furnace uses a powerful alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the metal charge placed inside the coil.
This magnetic field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal itself. The metal’s natural electrical resistance causes these currents to generate immense heat, melting the material from the inside out without any external flame or heating element.
The Critical Distinction: The Melting Atmosphere
The environment surrounding the molten metal dictates the final chemistry and integrity of the product. This is where standard and vacuum furnaces diverge completely.
Standard Furnaces: The "Air-Melt" Process
A standard induction furnace is open to the atmosphere. This simple, robust design makes it efficient and cost-effective for melting a wide range of common alloys like iron, steel, and aluminum.
The Problem with Air
Air is approximately 21% oxygen and 78% nitrogen. At high temperatures, these gases readily react with molten metal. This creates undesirable oxides and nitrides, which form impurities (slag) and can get trapped in the final casting, creating defects and weakening the material.
Vacuum Furnaces: The Solution for Purity
A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace encases the entire process in a sealed, robust chamber. Powerful pumps remove the air before melting begins, creating a vacuum.
By eliminating oxygen and nitrogen, the VIM process prevents these unwanted chemical reactions. This results in a cleaner, purer metal with significantly fewer gas-related impurities and defects.
Beyond Vacuum: Controlled Atmospheres
After creating a vacuum, the furnace chamber can be backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, such as argon. This creates a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere that still prevents oxidation while also helping to suppress the vaporization of certain valuable elements in the alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a vacuum induction furnace is a decision driven by necessity, not preference. The benefits of purity come with significant operational trade-offs.
Cost and Complexity
VIM systems are an order of magnitude more expensive than standard air-melt furnaces. The vacuum chamber, pumping systems, and sophisticated controls required for operation add substantial capital and maintenance costs.
Cycle Time
The process of pumping down the chamber to create a vacuum adds significant time to each melt cycle. This reduces overall throughput compared to the faster, more continuous operation of a standard furnace.
Material Constraints
For most common metals where standard levels of purity are acceptable, the cost and complexity of a VIM system are unnecessary and uneconomical.
Volatilization Risk
Under a hard vacuum, some elements with high vapor pressure (like manganese or zinc) can "boil off" from the molten bath. This requires careful process control and is one reason why inert gas backfills are often used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material requirements and application directly determine the correct furnace technology. The choice is rarely ambiguous.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume melting of common metals like iron, carbon steel, or aluminum: A standard air-melt induction furnace is the most logical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is producing materials with the highest possible purity for critical applications like aerospace or medical implants: A vacuum induction furnace is not just an option, but a requirement.
- If your primary focus is melting reactive metals like titanium or superalloys that cannot be exposed to air: You must use a vacuum induction furnace to prevent severe oxidation and ensure material integrity.
Ultimately, matching the furnace technology to the material's needs is the first step in successful and efficient manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Standard Induction Furnace | Vacuum Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Atmosphere | Open air | Sealed vacuum or inert gas |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Purity | Lower, with impurities | Higher, minimal impurities |
| Applications | Common metals (e.g., iron, steel) | Critical applications (e.g., aerospace, medical) |
| Cycle Time | Faster | Slower due to vacuum process |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material processing efficiency and purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















