In powder metallurgy, SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are the core components used inside sintering furnaces. They generate the high, consistently distributed heat required to transform compacted metal powders into dense, strong, and functional metal parts through a process known as solid-state diffusion.
The true value of SC Type SiC elements in powder metallurgy extends beyond simply getting hot. Their single-spiral design delivers exceptionally uniform heat, which is the most critical factor in preventing defects and ensuring consistent quality across every part you produce.
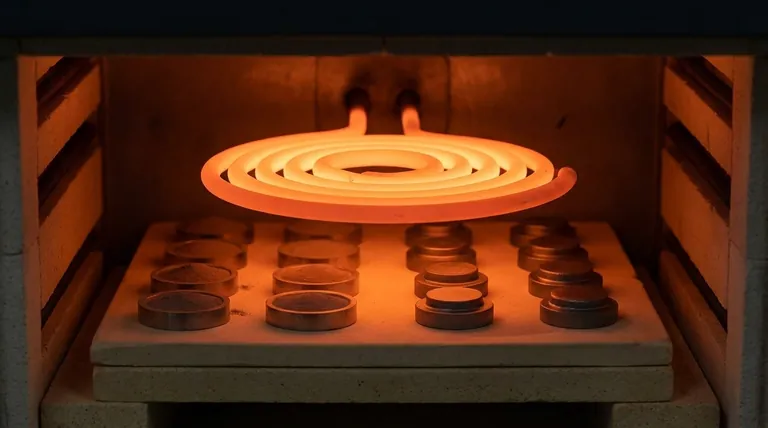

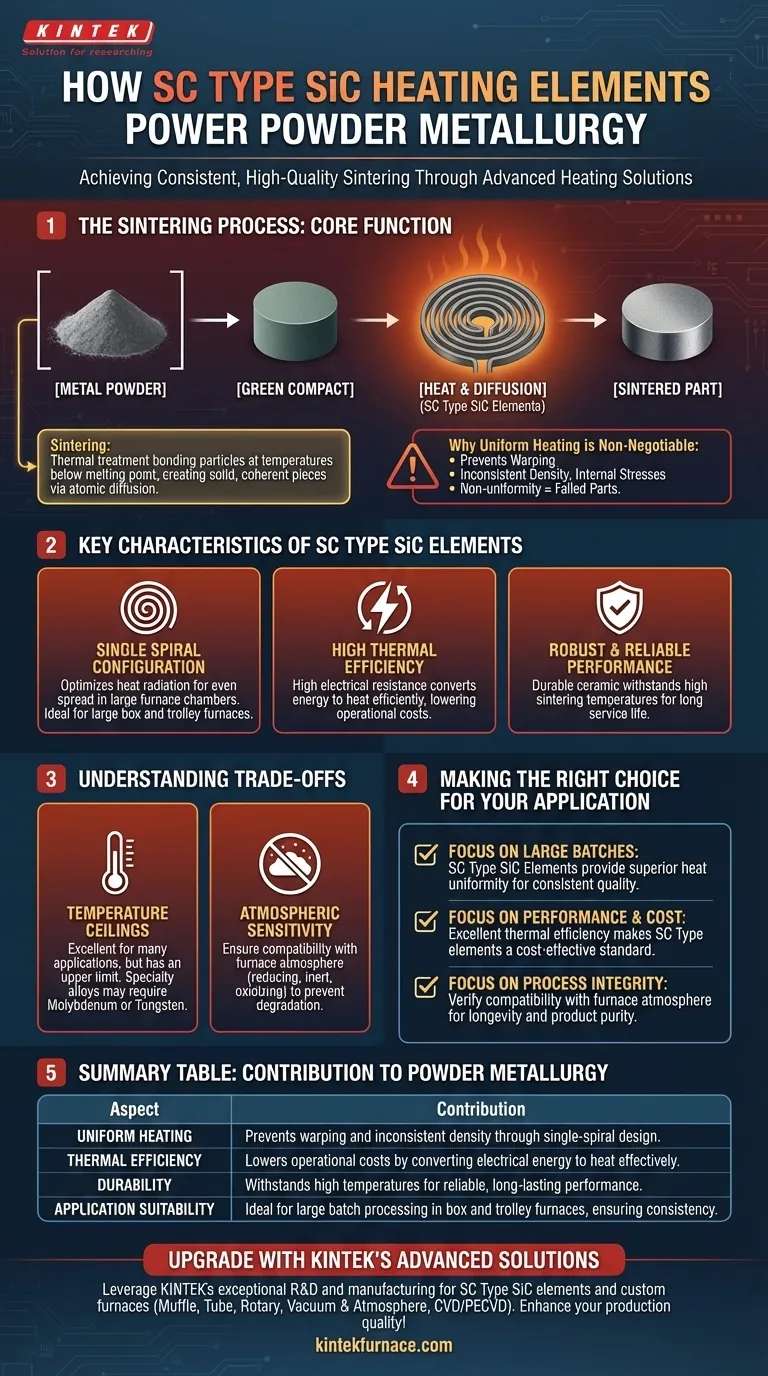
The Core Function: Enabling the Sintering Process
Sintering is a thermal treatment that bonds particles of a compressed powder together at a temperature below the material's melting point. The quality of the heating element directly dictates the success of this delicate process.
What is Sintering?
Sintering begins with metal powder that has been pressed into a desired shape, often called a "green compact." This compact is then heated in a controlled furnace environment.
The thermal energy from the heating elements allows atoms at the contact points of the powder particles to diffuse across boundaries, fusing the individual particles into a solid, coherent piece.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat acts as the catalyst for sintering. Without sufficient and sustained high temperatures, the atomic diffusion necessary to create strong metallic bonds simply will not occur, resulting in a weak and porous final part.
Why Uniform Heating is Non-Negotiable
This is the most critical factor for quality control. If one part of the furnace is hotter than another, the components will sinter unevenly.
This temperature variation leads to severe defects like warping, inconsistent density, and internal stresses. A non-uniform heating profile is a primary cause of failed parts and wasted material.
Key Characteristics of SC Type SiC Elements
The specific design of SC Type elements makes them particularly well-suited for the demands of powder metallurgy sintering.
The Single Spiral Configuration
The SC Type element features a single-spiral construction. This design optimizes the radiation of heat, ensuring it spreads evenly throughout a large furnace chamber.
This makes them highly effective in large box furnaces and trolley furnaces, where maintaining a consistent temperature zone is essential for processing large batches of components.
High Thermal Efficiency
The ceramic construction of these elements provides high electrical resistance, which allows them to convert electrical energy into heat very efficiently.
This high thermal efficiency means less wasted energy, leading to lower operational costs—a significant consideration in any industrial production environment.
Robust and Reliable Performance
Silicon carbide is a durable ceramic material capable of withstanding the high temperatures required for sintering most common metals. Its robust nature ensures a long service life and reliable performance cycle after cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single solution is perfect for every application. To be a true expert, you must understand the limitations and considerations of your equipment.
Temperature Ceilings
While SiC elements are excellent for many applications, they have an upper temperature limit. For ultra-high-temperature sintering of specialty alloys or ceramics, other materials like molybdenum or tungsten may be required.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
The atmosphere inside a sintering furnace (e.g., reducing, inert, or oxidizing) can impact the lifespan of SiC elements. It is critical to ensure the element is appropriate for the specific process gas being used to prevent premature degradation or contamination of the parts.
Cost vs. Specific Need
SC Type SiC elements represent a strong balance of performance, uniformity, and cost-effectiveness for a wide range of applications. However, for smaller-scale or less demanding processes, simpler and less expensive heating elements might be sufficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sintering Application
Selecting the right heating element is a foundational decision that impacts both product quality and operational efficiency.
- If your primary focus is producing large, consistent batches: The superior heat uniformity of SC Type SiC elements is ideal for large box or trolley furnaces, minimizing part-to-part variation.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and operational cost: SC Type elements provide excellent thermal efficiency, making them a cost-effective choice for many standard powder metallurgy applications.
- If your primary focus is process integrity: Always verify the compatibility of SiC elements with your furnace atmosphere to ensure element longevity and prevent product contamination.
By matching the heating element's characteristics to your specific process goals, you gain precise control over the final quality of your sintered products.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Contribution to Powder Metallurgy |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heating | Prevents warping and inconsistent density in sintered parts through single-spiral design. |
| Thermal Efficiency | Lowers operational costs by converting electrical energy to heat effectively. |
| Durability | Withstands high temperatures for reliable, long-lasting performance in sintering furnaces. |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for large batch processing in box and trolley furnaces, ensuring consistent quality. |
Upgrade your powder metallurgy process with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide SC Type SiC heating elements and custom furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems to ensure uniform sintering, reduce defects, and boost efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can meet your unique experimental needs and enhance your production quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















