In short, rotary tube furnaces enhance efficiency by combining continuous material processing with exceptionally uniform heating and precise environmental control. This design moves beyond the limitations of static batch furnaces, enabling higher throughput, superior product quality, and greater operational consistency for granular materials.
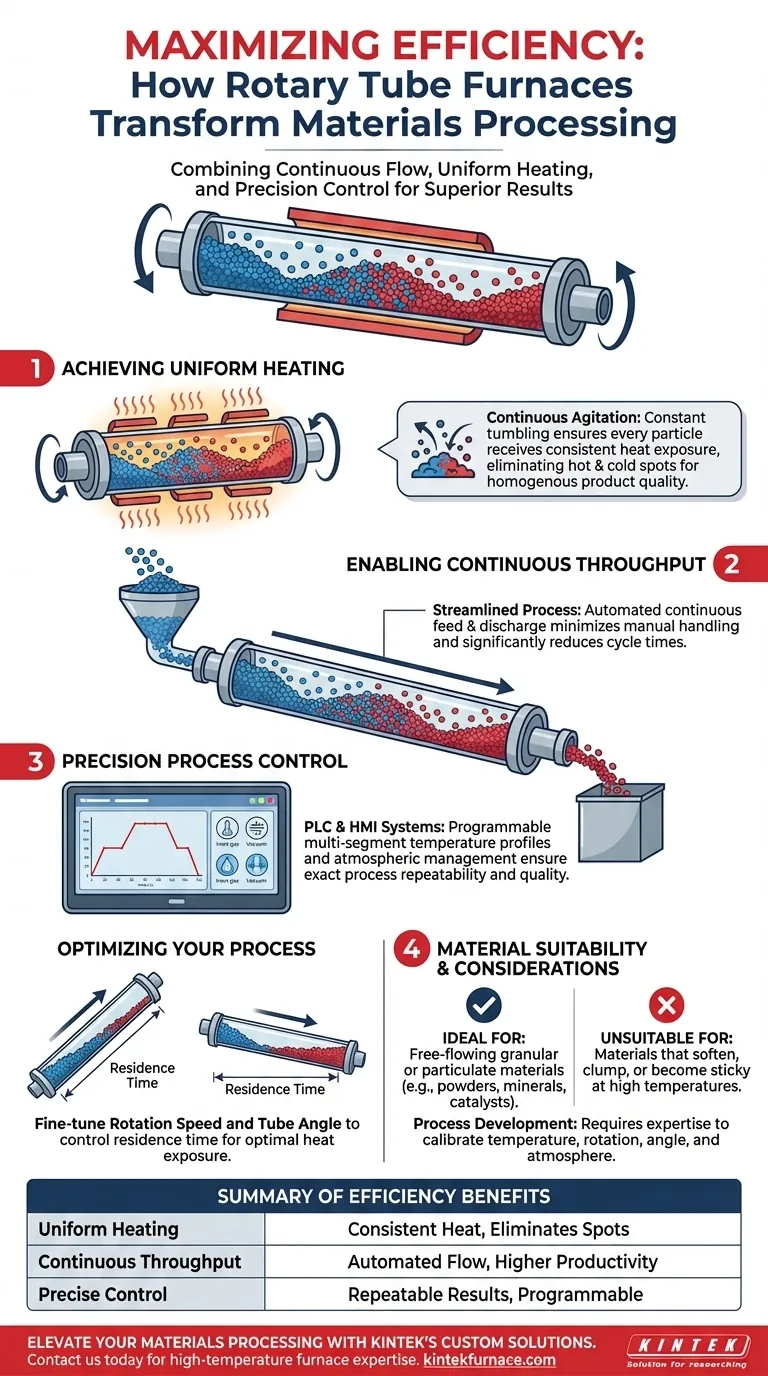
The core challenge in thermal processing is achieving uniform treatment for every particle in a batch. Rotary tube furnaces solve this by using constant rotation to agitate the material, ensuring consistent heat exposure while enabling a continuous, automated workflow.

The Core Mechanisms of Efficiency
The efficiency gains of a rotary tube furnace stem from three integrated design principles: continuous agitation, automated throughput, and precise atmospheric control.
Achieving Uniform Heating Through Agitation
The defining feature is the slow rotation of the furnace tube, typically between 3 and 7 RPM. This constant tumbling motion ensures that all material particles are repeatedly and uniformly exposed to the heat source.
This process eliminates hot spots and cold spots common in static furnaces, leading to a much more consistent and homogenous final product. The indirect-fired design heats the tube externally, which then transfers heat to the material, further guaranteeing even thermal distribution.
Enabling Continuous Throughput
Unlike traditional batch furnaces that require loading, heating, cooling, and unloading cycles, a rotary tube furnace operates continuously. Material is fed into one end of the inclined tube and gradually moves toward the discharge end as it rotates.
This continuous flow minimizes manual material handling, reduces cycle time, and dramatically increases overall productivity. It transforms a series of discrete steps into a single, streamlined process.
Precision Control Over the Process Environment
Modern rotary tube furnaces are equipped with sophisticated control systems. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) allow for the precise management of every critical variable.
Operators can program multi-segment temperature profiles for customized heating, holding, and cooling phases. This level of automation also extends to the furnace atmosphere, allowing for processing in air or a controlled inert environment to prevent unwanted chemical reactions and ensure process repeatability.
Optimizing Your Process
True efficiency is not just about the furnace's potential but about how you harness it. Fine-tuning the operational parameters is key to achieving optimal results for your specific material.
The Role of Rotation Speed and Tube Angle
The residence time—how long the material spends inside the furnace—is controlled by two main variables: the inclination angle of the tube and its rotation speed.
A steeper angle or faster rotation will move material through more quickly. A shallower angle or slower rotation increases residence time, allowing for longer heat exposure. Mastering the interplay between these two factors is critical for process optimization.
Managing Thermal Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a major component of overall cost-efficiency. These furnaces utilize high-quality ceramic fiber insulation and advanced heating elements to maximize heat transfer to the product and minimize energy loss to the environment.
Some models also incorporate air cooling systems, which can help balance the internal temperature field and improve thermal efficiency, further reducing operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly efficient, a rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Material Suitability is Non-Negotiable
These furnaces are specifically designed for granular or particulate materials that remain free-flowing at high processing temperatures. This includes many powders, minerals, and catalyst materials.
They are fundamentally unsuitable for materials that soften, clump, or become sticky when heated. Such materials will agglomerate and coat the inside of the furnace tube, halting the process and creating significant operational problems.
Process Development is Required
The high degree of control is also a source of complexity. Achieving optimal results for a new material requires a development phase to determine the ideal temperature profile, rotation speed, tube angle, and atmosphere. It is a precision instrument that requires expertise to calibrate correctly.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your primary objective will determine which features of a rotary tube furnace are most critical to your operation.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: Leverage the continuous feeding and discharging capability to integrate the furnace into an automated production line, drastically reducing manual handling and cycle times.
- If your primary focus is product quality and uniformity: Prioritize the combination of material agitation and multi-zone thermal control to eliminate inconsistencies and produce a highly homogenous final product.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Depend on the advanced PLC programming to automate complex heating profiles and ensure every batch is processed under identical conditions, guaranteeing consistent results.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively determine if a rotary tube furnace is the right tool to elevate the efficiency and quality of your materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Efficiency Benefit |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent heat exposure for all particles via rotation, eliminating hot/cold spots. |
| Continuous Throughput | Enables automated material flow, reducing cycle times and increasing productivity. |
| Precise Environmental Control | Allows programmable temperature and atmosphere management for repeatable results. |
| Material Suitability | Optimized for free-flowing granular materials like powders and catalysts. |
Ready to elevate your materials processing with a customized rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















