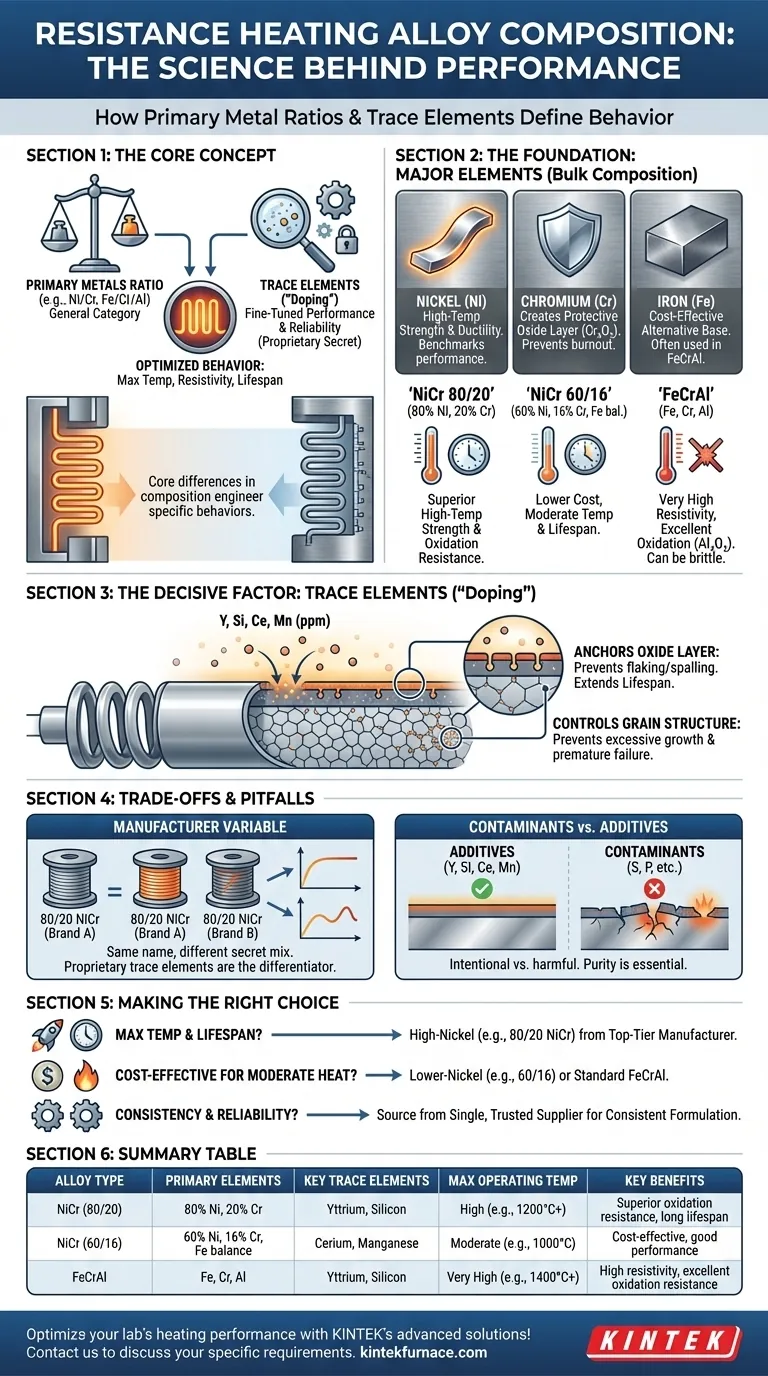
At its core, resistance heating alloys vary in two fundamental ways: the ratio of their primary constituent metals, such as nickel and chromium, and the precise, often minute, quantities of trace elements added to refine their performance. These major and minor compositional differences are not arbitrary; they are engineered to produce specific behaviors, directly influencing an alloy's maximum operating temperature, electrical resistivity, and operational lifespan.
The crucial insight is that while the ratio of primary metals defines an alloy's general category, it is the sophisticated control of trace elements—often a manufacturer's proprietary secret—that truly determines its high-temperature stability and ultimate reliability in a heating application.

The Foundation: Major Alloying Elements
The bulk composition of an alloy establishes its fundamental characteristics. The most common elements are Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr), and Iron (Fe), and their relative proportions are the first and most important specification.
The Role of Nickel (Ni) and Chromium (Cr)
Nickel is prized for its ductility and excellent strength at high temperatures. Chromium is the critical component for creating a protective oxide layer on the alloy's surface when heated.
This protective layer, typically chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃), is what prevents the underlying metal from burning out, acting as a stable, tenacious skin that resists further oxidation.
The Impact of Ratios (e.g., 80/20 vs. 60/16)
The ratio between nickel and chromium directly impacts performance. An 80 Ni, 20 Cr alloy (often called Nichrome 80/20) is the benchmark for high-performance heating elements. The high nickel content provides superior high-temperature strength and resistance to oxidation.
A 60 Ni, 16 Cr alloy (with the balance often being iron) offers a lower-cost alternative. While still highly effective, its lower nickel and chromium content typically results in a lower maximum operating temperature and a shorter service life compared to its 80/20 counterpart.
The Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alternative
Another major class of alloys replaces nickel with iron as the primary constituent, creating FeCrAl alloys. These are known for their very high resistivity and excellent oxidation resistance, thanks to the formation of an aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) layer.
While FeCrAl alloys can often reach higher temperatures than NiCr alloys, they can become brittle after thermal cycling. The choice between NiCr and FeCrAl depends on the specific demands of the heating application.
The Decisive Factor: Trace Elements
If major elements set the stage, trace elements direct the performance. These are tiny, intentional additions—sometimes measured in parts per million—that have a disproportionately large impact on the alloy's behavior.
Enhancing the Protective Oxide Layer
The single most important function of trace elements is to improve the adherence and integrity of the protective oxide scale. Additives like yttrium (Y), silicon (Si), cerium (Ce), and manganese (Mn) are "doped" into the alloy in precise amounts.
These elements migrate to the surface during heating and anchor the oxide layer to the base metal, preventing it from flaking or spalling off during thermal cycles. A more adherent oxide layer directly translates to a longer element lifespan.
Controlling Grain Structure and Stability
Trace elements also help control the alloy's grain structure at high temperatures. By pinning grain boundaries, they prevent excessive grain growth, which maintains the material's mechanical strength and prevents premature failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
An alloy's composition is a series of deliberate engineering compromises. Understanding these trade-offs is key to avoiding common failures.
The Manufacturer Variable
Two alloys sold under the same name (e.g., "80/20 NiCr") from different manufacturers are not necessarily identical. The proprietary mix of trace elements is a key differentiator and a primary reason for performance and price variations.
A premium alloy from a reputable manufacturer has undergone extensive research to optimize its trace element package for maximum life. A cheaper alternative may have the correct major element ratio but lack the refined "doping" needed for long-term stability.
Contaminants vs. Additives
There is a critical difference between intentional trace additives and unintentional contaminants. Elements like sulfur and phosphorus, even in minute quantities, can be highly detrimental.
These contaminants can disrupt the formation of a stable oxide layer and create weak points, leading to rapid, localized failure of the heating element. This is why sourcing high-purity, well-controlled alloys is essential for critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting an alloy is not just about matching a temperature rating; it's about matching the composition to your performance, reliability, and cost requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum operating temperature and lifespan: Choose a high-nickel alloy like 80/20 NiCr from a top-tier manufacturer known for its tight compositional control and optimized trace elements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for moderate heat: A lower-nickel alloy (e.g., 60/16 NiCrFe) or a standard FeCrAl alloy can provide excellent value and performance.
- If your primary focus is consistency and reliability: Source your alloy from a single, trusted supplier to ensure the proprietary trace element formulation, and therefore the performance, remains consistent from batch to batch.
Ultimately, understanding an alloy's composition transforms your selection process from a simple lookup on a data sheet to a strategic decision that ensures the long-term reliability of your design.
Summary Table:
| Alloy Type | Primary Elements | Key Trace Elements | Max Operating Temp | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiCr (80/20) | 80% Ni, 20% Cr | Yttrium, Silicon | High (e.g., 1200°C+) | Superior oxidation resistance, long lifespan |
| NiCr (60/16) | 60% Ni, 16% Cr, Fe balance | Cerium, Manganese | Moderate (e.g., 1000°C) | Cost-effective, good performance |
| FeCrAl | Fe, Cr, Al | Yttrium, Silicon | Very High (e.g., 1400°C+) | High resistivity, excellent oxidation resistance |
Optimize your lab's heating performance with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alloy selection for your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions


















