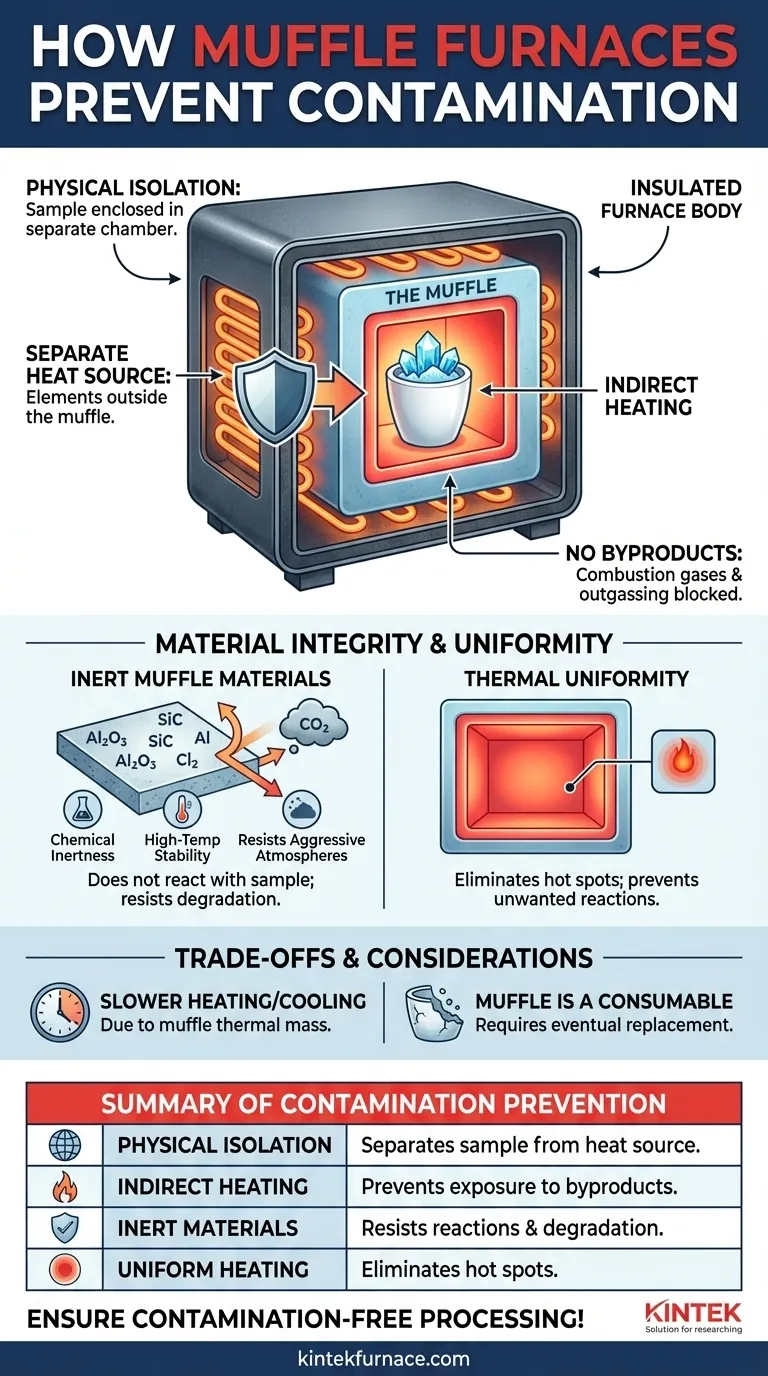
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is its use of physical isolation to prevent contamination. It achieves this by enclosing the material in a separate, insulated inner chamber—the "muffle"—which is then heated from the outside. This design ensures that the sample is never exposed to the byproducts of combustion or direct radiation from heating elements, guaranteeing a clean processing environment.
A muffle furnace is not just a hot box; it is an engineered system for thermal processing where sample integrity is paramount. Its core value lies in creating a chemically isolated environment by physically separating the material being heated from the source of the heat itself.

The Core Principle: A Chamber Within a Chamber
The entire design of a muffle furnace revolves around a simple but highly effective concept: indirect heating. This prevents contaminants from the heat source from ever reaching the sample.
The Role of the Muffle
The "muffle" is the heart of the furnace. It is an enclosed chamber, typically made of a high-temperature ceramic or metal alloy, that houses the material or sample.
This chamber acts as a complete barrier, isolating its internal atmosphere from the rest of the furnace where the heating occurs.
Separating the Heat Source
Whether the furnace uses electric resistance coils or gas burners, the heat source is located outside the muffle.
The heat is transferred through the muffle's walls to the interior via conduction and radiation. The sample is heated by the hot walls of the muffle, not by the heating elements directly.
Eliminating Byproducts and Outgassing
In gas-fired furnaces, this design keeps combustion byproducts like soot and reactive gases away from the sample.
In electric furnaces, it prevents any particles or gases released from the heating elements at extreme temperatures (a process known as outgassing) from contaminating the material.
Material Integrity: Beyond Simple Separation
The choice of material for the muffle itself is a second critical layer of contamination control. It ensures the chamber does not become a source of contamination.
The Importance of Inert Materials
Muffles are constructed from materials chosen for their chemical inertness and high-temperature stability, such as dense ceramics or specialized metal alloys.
These materials are designed not to react with the sample being heated, even at extreme temperatures, thus preserving the sample's original composition.
Resistance to Aggressive Atmospheres
Many thermal processes release aggressive gases or vapors from the sample itself. The muffle's material is selected to resist chemical attack from these substances.
This resilience prevents the muffle from degrading and releasing its own constituent materials into the chamber, which would contaminate the sample and future batches.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
A secondary benefit of the muffle is that it promotes uniform heating. The chamber walls absorb and radiate heat evenly, surrounding the sample with a consistent temperature.
This eliminates hot spots that could cause unwanted side reactions, phase changes, or degradation of the sample, further protecting its integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective for purity, the muffle furnace design comes with inherent trade-offs that are important to understand for process control.
Slower Heating and Cooling Rates
The muffle has significant thermal mass. It must first absorb heat before it can transfer it to the sample, resulting in slower heat-up times compared to direct-heating furnaces.
Similarly, it cools down slowly, which can extend the total processing time. This is a trade-off for the superior temperature uniformity and purity it provides.
Muffle Material as a Consumable
Over time, repeated thermal cycling and exposure to reactive chemicals will eventually degrade even the most robust muffle.
The muffle should be considered a long-term consumable component that may require inspection and eventual replacement to maintain a contamination-free environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the principles of a muffle furnace allows you to select the right tool for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is absolute sample purity: A muffle furnace is the industry standard, as its indirect heating mechanism is specifically designed to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive materials: Carefully select the muffle material (e.g., high-purity ceramic vs. a specific alloy) to ensure it is chemically compatible with your process atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and high throughput: A direct-fired furnace may be faster, but you must be certain that direct exposure to combustion byproducts will not compromise your material.
By leveraging the physical isolation of a muffle furnace, you ensure the integrity of your materials is governed by your process, not by your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Contamination Prevention |
|---|---|
| Physical Isolation | Separates sample from heat source via muffle chamber |
| Indirect Heating | Prevents exposure to combustion byproducts and outgassing |
| Inert Muffle Materials | Resists chemical reactions and degradation |
| Uniform Heating | Eliminates hot spots that cause unwanted reactions |
Ensure contamination-free thermal processing for your lab! KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to learn how our furnaces can protect your materials and enhance your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















