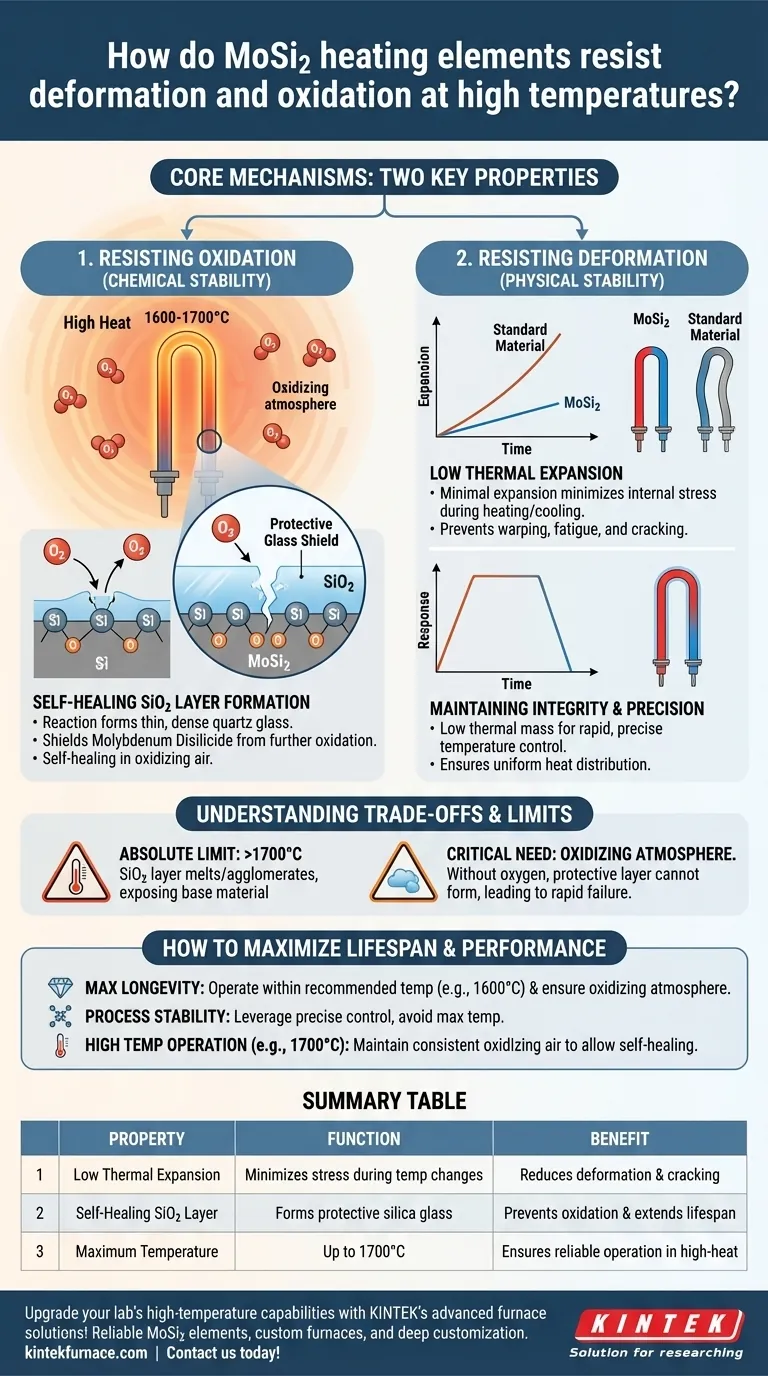
At its core, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements resist high-temperature failure through a combination of two key properties. Their low coefficient of thermal expansion minimizes physical stress and deformation during temperature changes, while the formation of a self-healing, glass-like protective layer on their surface chemically prevents them from burning up in oxidizing atmospheres.
The defining characteristic of MoSi2 is not just its heat resistance, but its ability to create its own protection. At high temperatures, the element undergoes a chemical reaction with oxygen to form a thin, durable layer of silica glass (SiO2), which shields it from further oxidation.

The Core Mechanism: Self-Healing Oxidation Resistance
The most critical property of a MoSi2 element is its ability to protect itself in the very environment where it operates. This process is dynamic and is what grants the material its exceptional lifespan at extreme temperatures.
The Formation of the SiO2 Layer
When a MoSi2 element is heated in an atmosphere containing oxygen, the silicon (Si) at the surface reacts with the oxygen. This reaction forms a thin, non-porous, and dense protective layer of quartz glass, also known as silica (SiO2).
This process is not a one-time event. The layer is self-forming and will regenerate if damaged, provided the element continues to operate in an oxidizing environment.
How This Layer Protects the Element
The SiO2 layer acts as a physical barrier. It effectively seals the underlying Molybdenum Disilicide material from the surrounding atmosphere, preventing oxygen from reaching it and causing further, destructive oxidation.
This protective "skin" is what allows the element to operate for thousands of hours at temperatures that would quickly destroy many other metals.
Resisting Physical Deformation
Beyond chemical stability, MoSi2 elements are engineered to resist the physical stresses of high-temperature work.
The Role of Low Thermal Expansion
MoSi2 has a very small thermal expansion coefficient. This means that as it heats up from room temperature to its operational temperature of 1600-1700°C, it expands very little.
This property is crucial because it minimizes internal stress. Materials that expand and contract significantly are prone to warping, fatigue, and cracking over repeated heating and cooling cycles. MoSi2's stability prevents this.
Maintaining Structural Integrity and Precision
The low thermal expansion ensures the element maintains its shape and position within a furnace. This is vital for uniform heat distribution and reliable temperature control.
Furthermore, the low thermal mass of these elements allows for rapid heating and cooling with minimal risk of thermal shock, enabling precise temperature control with less over- and undershooting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Limits
While incredibly robust, MoSi2 elements are not invincible. Their protective mechanism has specific requirements and limitations that you must understand for successful operation.
The Absolute Temperature Limit
The protective SiO2 layer is a form of glass, and it has a melting point. Above 1700°C (3092°F), this layer begins to soften, melt, and agglomerate into droplets due to surface tension.
When this happens, the layer loses its continuous, protective quality, exposing the base material to oxidation. This defines the upper operational boundary for these elements, as seen in models like the BR1800, which has a maximum working temperature of 1700°C.
The Critical Need for an Oxidizing Atmosphere
The self-healing mechanism is entirely dependent on the presence of oxygen. Using MoSi2 elements in a reducing, inert, or vacuum atmosphere at high temperatures is highly detrimental.
Without oxygen, the protective SiO2 layer cannot form or regenerate. Any existing layer can be stripped away, leading to rapid degradation and failure of the element.
How to Maximize Element Lifespan and Performance
Your operational strategy should be based on a clear understanding of the material's properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity: Operate the elements within their recommended working temperature (e.g., 1600°C for a BR1700 model) and always ensure an oxidizing atmosphere is present during high-temperature runs.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Leverage the low thermal mass and expansion for precise temperature control, but avoid pushing the elements to their absolute maximum temperature to maintain a buffer of safety.
- If you must operate near the maximum temperature (e.g., 1700°C): Be aware that you are near the SiO2 melting point. A consistent oxidizing atmosphere is non-negotiable to allow for rapid self-healing if the protective layer is compromised.
By understanding that MoSi2's strength lies in its dynamic, self-healing shield, you can create the ideal conditions for long-lasting and reliable performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Low Thermal Expansion | Minimizes stress during temperature changes | Reduces deformation and cracking |
| Self-Healing SiO2 Layer | Forms protective silica glass in oxidizing atmospheres | Prevents oxidation and extends lifespan |
| Maximum Temperature | Up to 1700°C | Ensures reliable operation in high-heat environments |
Upgrade your lab's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable MoSi2 heating elements and custom high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance performance and longevity in your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















