To be clear, the performance of a Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating element is fundamentally determined by the atmosphere in which it operates. While they are renowned for their exceptional high-temperature capabilities in air, their maximum operating temperature and service life are significantly reduced in inert, reducing, or other reactive gas environments due to changes in their surface chemistry.
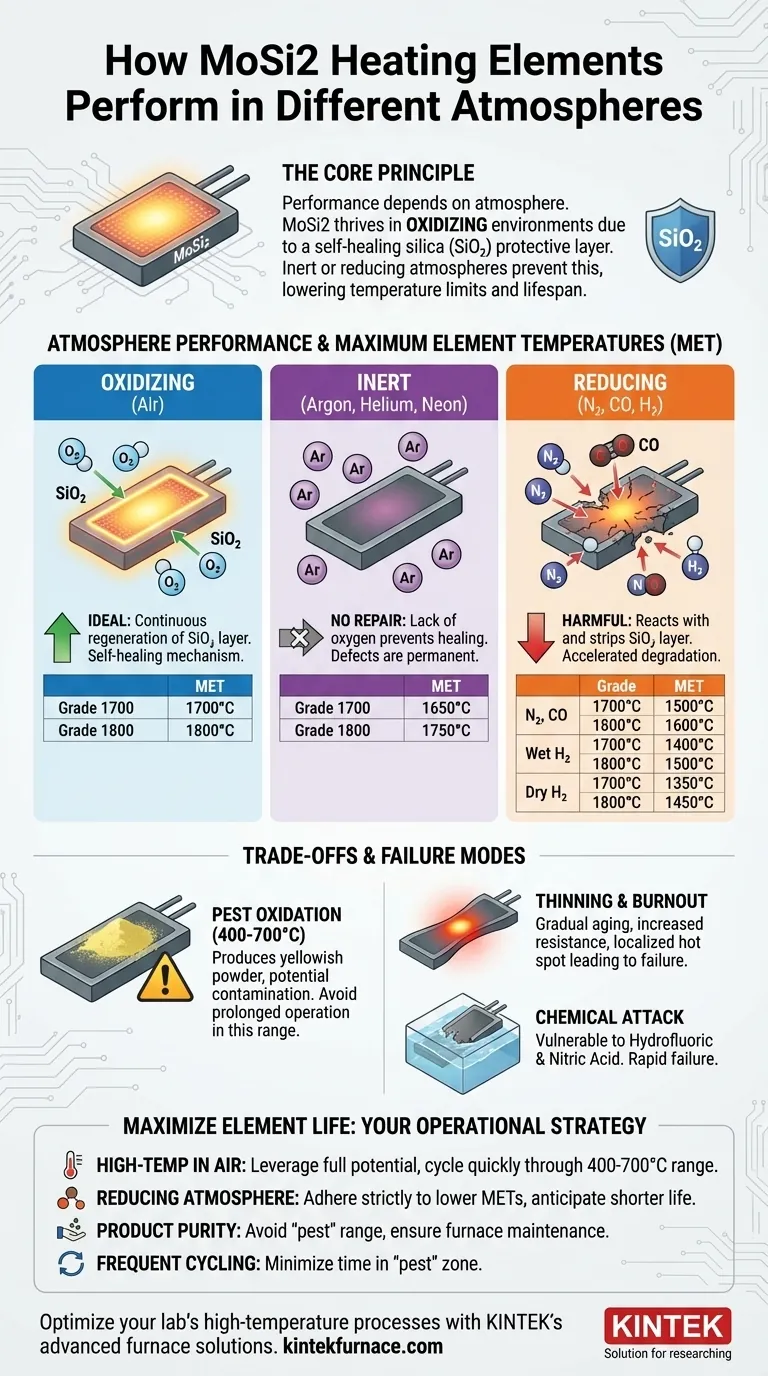
The core principle is simple: MoSi2 elements thrive in oxidizing atmospheres that allow them to form and regenerate a protective silica (glass) layer. In atmospheres lacking sufficient oxygen, this protective layer cannot be repaired, exposing the element to degradation and lowering its safe operating limits.

The Chemistry of MoSi2 Performance
MoSi2 heating elements do not simply resist heat; they leverage a chemical reaction with their environment to create a protective barrier. Understanding this mechanism is key to using them effectively.
The Protective Silica (SiO₂) Layer
At high temperatures in an oxidizing atmosphere like air, the surface of the MoSi2 element reacts with oxygen. This reaction forms a thin, non-porous layer of quartz glass (silica, or SiO₂).
This silica layer is the key to the element's performance. It acts as a durable chemical barrier, protecting the underlying molybdenum disilicide from further, more aggressive oxidation and degradation.
The Self-Healing Mechanism
The most critical feature of this silica layer is its ability to "self-heal." If a crack or flaw develops on the surface during operation, the newly exposed MoSi2 material immediately reacts with the surrounding oxygen, forming new silica and sealing the defect. This process is why MoSi2 elements can achieve such long service lives at extreme temperatures in air.
Performance in Different Atmospheres
The ability to form and maintain the protective SiO₂ layer dictates the element's maximum temperature. The lack of oxygen in other atmospheres prevents the self-healing process, making the element more vulnerable.
The following are typical maximum element temperatures (MET) for common MoSi2 grades (1700 and 1800).
Oxidizing Atmosphere (Air)
This is the ideal environment. The abundant oxygen allows for continuous regeneration of the protective silica layer.
- Grade 1700 MET: 1700°C
- Grade 1800 MET: 1800°C
Inert Atmospheres (Argon, Helium, Neon)
Inert gases do not react with the element, but they also provide no oxygen to repair the silica layer. Any existing defects will not be healed, creating points of failure.
- Grade 1700 MET: 1650°C
- Grade 1800 MET: 1750°C
Reducing Atmospheres (Nitrogen, CO, Hydrogen)
These atmospheres can be actively harmful. They not only lack oxygen for repairs but can also chemically react with and strip away the protective silica layer, leading to accelerated degradation.
- Nitrogen (N₂) or Carbon Monoxide (CO):
- Grade 1700 MET: 1500°C
- Grade 1800 MET: 1600°C
- Wet Hydrogen (H₂):
- Grade 1700 MET: 1400°C
- Grade 1800 MET: 1500°C
- Dry Hydrogen (H₂):
- Grade 1700 MET: 1350°C
- Grade 1800 MET: 1450°C
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
Beyond maximum temperature, certain conditions introduce unique risks that can lead to premature failure or process contamination.
The Risk of 'Pest' Oxidation
At lower temperatures, specifically between 400°C and 700°C, MoSi2 undergoes a different type of oxidation known as "pest." This process produces a yellowish powder on the element's surface.
While this oxidation does not damage the element's heating capability, the powder can flake off and contaminate the furnace and product. Therefore, prolonged operation within this temperature range should be strictly avoided.
End-of-Life Failure: Thinning and Burnout
The normal failure mode for a MoSi2 element is gradual aging. Over hundreds or thousands of hours, the element's surface slowly oxidizes and thins.
As the element thins, its electrical resistance increases. Eventually, it becomes too thin to handle the power load, causing a localized hot spot that leads to burnout. High-temperature grain growth, which can give the surface an "orange-peel" texture, also contributes to this thinning process.
Chemical Attack
While MoSi2 elements are resistant to most acids and alkaline solutions, they are vulnerable to direct chemical attack from hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid. These chemicals will dissolve the element and its protective layer, leading to rapid failure.
How to Maximize Element Life in Your Atmosphere
Your operational strategy must align with the atmosphere inside your furnace to ensure reliability and longevity.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in air: You can leverage the full potential of MoSi2, but ensure your furnace cycles quickly through the 400-700°C range to minimize pest oxidation.
- If your primary focus is processing in a reducing atmosphere (like H₂ or N₂): You must strictly adhere to the lower maximum element temperatures and anticipate a shorter overall service life compared to operation in air.
- If your primary focus is product purity: Be vigilant about avoiding the "pest" oxidation temperature range to prevent contamination and ensure proper furnace maintenance practices are followed.
- If your furnace cycles frequently: Your main goal is to minimize the total time the elements spend in the "pest" zone to protect both your elements and your products.
Ultimately, aligning your operating parameters with the element's known chemical behavior is the most effective way to ensure a reliable and long-lasting heating system.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Grade 1700 MET (°C) | Grade 1800 MET (°C) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidizing (Air) | 1700 | 1800 | Ideal for self-healing silica layer |
| Inert (Argon, etc.) | 1650 | 1750 | No oxygen for repair, higher failure risk |
| Reducing (N₂, CO) | 1500 | 1600 | Can strip silica layer, accelerates degradation |
| Wet Hydrogen (H₂) | 1400 | 1500 | Highly reactive, significant temperature drop |
| Dry Hydrogen (H₂) | 1350 | 1450 | Most aggressive, lowest temperature limits |
Optimize your lab's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















