In short, electromagnetic induction rotary kilns simplify maintenance by fundamentally changing how heat is generated and controlled. They replace complex, high-wear mechanical and combustion components with a non-contact, solid-state heating system, which drastically reduces the number of potential failure points and mitigates the primary causes of kiln degradation.
The core reason for simplified maintenance is a shift in technology: moving from failure-prone mechanical and fuel-based systems to a more reliable electromagnetic one. This design inherently prevents the thermal stress and wear that plague traditional kilns, leading to longer component life and less required intervention.

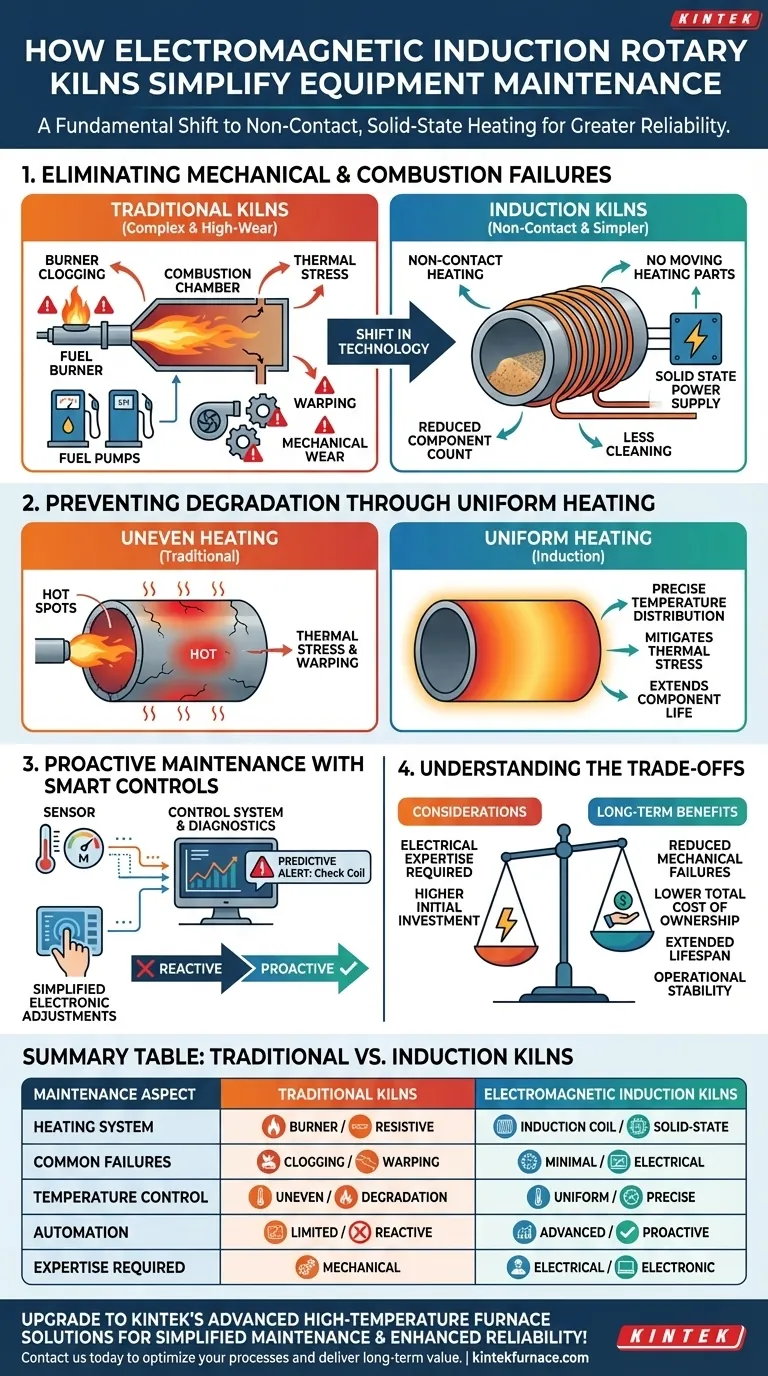
The Core Principle: Eliminating Mechanical and Combustion Failures
The most significant maintenance advantage comes from removing the components that historically cause the most problems in fuel-fired or resistive heating kilns.
Non-Contact Heating Reduces Wear
Traditional kilns rely on fuel burners, combustion chambers, or resistive elements that are subject to intense heat, corrosion, and mechanical stress.
Electromagnetic induction heating is non-contact. An induction coil generates a magnetic field that heats the kiln drum directly, without any moving parts in the heating system itself. This eliminates a wide range of common maintenance tasks, such as cleaning fuel nozzles, replacing burners, or repairing combustion chambers.
A Radically Simpler Design
By design, an induction kiln has fewer components that can break down. The heating system consists of a durable induction coil and a solid-state power supply.
This contrasts sharply with traditional systems that involve fuel pumps, blowers, ignition systems, and complex refractory arrangements around the burner, all of which require regular inspection, servicing, and eventual replacement.
How Uniform Heating Prevents Degradation
Uneven heating is a primary driver of maintenance costs and catastrophic failure in conventional rotary kilns. Electromagnetic induction directly addresses this issue.
Mitigating Thermal Stress and Warping
Fuel-fired kilns often create intense "hot spots" where the flame directly impinges on the kiln shell. This uneven temperature distribution causes the metal tube to warp, deform, and crack over time.
Induction heating provides exceptionally uniform and precise temperature distribution around the entire circumference of the kiln. This prevents localized overheating, drastically reducing thermal stress and preserving the structural integrity of the kiln shell for a much longer lifespan.
Extending Refractory and Component Life
The precise temperature control also reduces wear on the internal refractory lining and other components. By avoiding temperature spikes and rapid fluctuations, the system minimizes the thermal cycling that causes materials to expand and contract, which eventually leads to cracking and spalling.
The Role of Automation and Smart Controls
Modern induction kilns integrate advanced control systems that shift maintenance from a reactive to a proactive model.
Automated Monitoring and Diagnostics
Sensors continuously monitor critical parameters like temperature and power output. The control system can automatically adjust heating to maintain perfect consistency.
More importantly, these systems can flag performance deviations that may indicate an impending issue, allowing maintenance teams to address a problem before it leads to a shutdown.
Simplified Adjustments
Adjusting the heat profile in an induction kiln is an electronic process managed through a control panel. There is no need for a technician to physically access and manually adjust a burner or fuel valve. This makes fine-tuning the process faster, safer, and more precise.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While maintenance is simplified, it is not eliminated. The nature of the required expertise simply changes.
The Need for Electrical Expertise
Mechanical maintenance is significantly reduced, but troubleshooting the system now requires a different skill set. A failure in the power supply or control system necessitates expertise in industrial electronics and power systems. Maintenance teams accustomed to purely mechanical systems may require additional training.
Higher Initial Investment
Electromagnetic induction systems typically carry a higher upfront capital cost than traditional fuel-fired kilns. While they deliver a lower total cost of ownership through reduced maintenance and energy savings, this initial investment is a critical factor for consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to adopt an induction rotary kiln depends on your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: The significant reduction in mechanical failure points makes an induction kiln an extremely reliable choice for continuous processes.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term costs: The extended lifespan of the kiln shell and lower need for replacement parts deliver substantial savings on operational expenditures over the equipment's life.
- If your primary focus is process purity and quality: The closed, non-contact heating system prevents product contamination from combustion byproducts, simplifying maintenance related to system cleaning.
Ultimately, choosing an electromagnetic induction kiln is an investment in operational stability and long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Aspect | Traditional Kilns | Electromagnetic Induction Kilns |
|---|---|---|
| Heating System | Fuel burners, resistive elements prone to wear | Non-contact induction, solid-state, minimal wear |
| Common Failures | Burner clogging, thermal stress, warping | Reduced; focuses on electrical components |
| Temperature Control | Uneven, causes degradation | Uniform, precise, prevents thermal stress |
| Automation | Limited, reactive maintenance | Advanced sensors, proactive diagnostics |
| Expertise Required | Mechanical | Electrical and electronic |
Upgrade to KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for simplified maintenance and enhanced reliability! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with electromagnetic induction rotary kilns and other products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, reducing downtime and operational costs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and deliver long-term value!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















