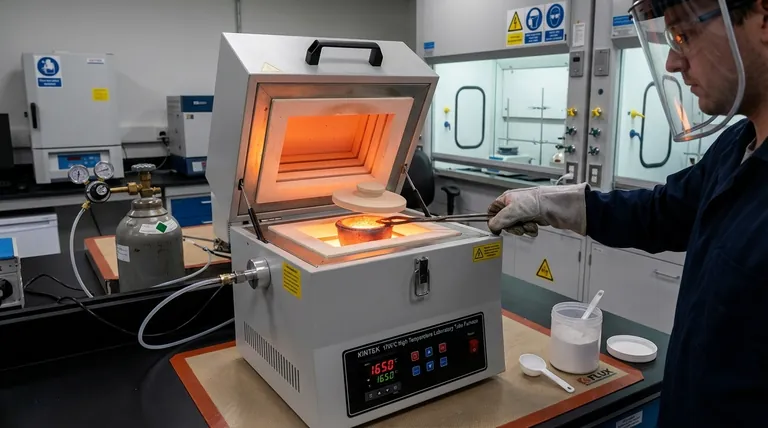
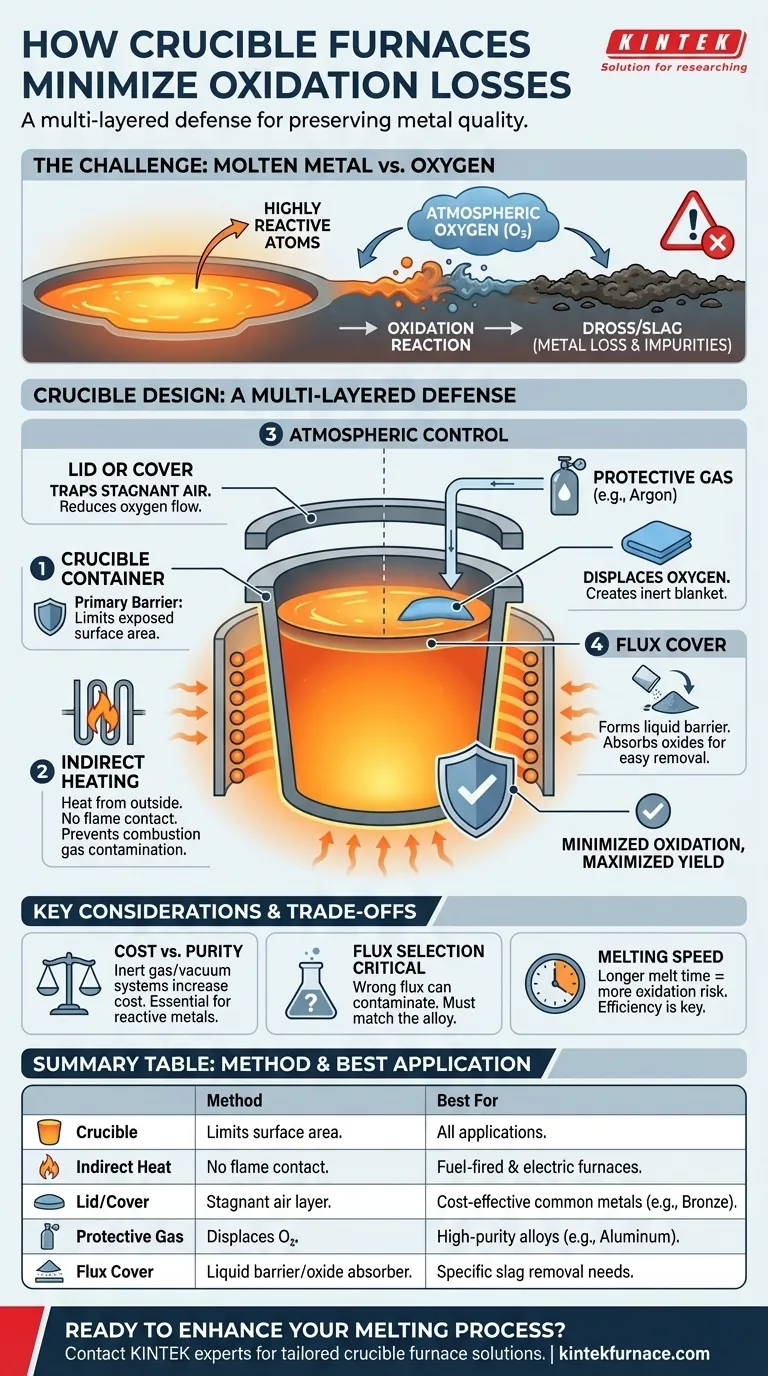
At its core, a crucible furnace minimizes oxidation by creating multiple layers of separation between the molten metal and atmospheric oxygen. The design relies on physical containment within the crucible, indirect heating methods that prevent contact with combustion gases, and the ability to control the atmosphere directly above the melt using covers, fluxes, or protective gases.
The key takeaway is that crucible furnaces don't use a single trick to prevent oxidation. Instead, they employ a combination of physical barriers and atmospheric control, making them a highly effective and adaptable solution for preserving metal quality during melting.

The Fundamental Challenge: Molten Metal vs. Oxygen
When metal is heated to its melting point, its atoms become highly energized and mobile. This makes the liquid metal extremely reactive with oxygen in the surrounding air.
The Problem of Oxidation
This reaction, known as oxidation, forms metallic oxides. These oxides manifest as dross or slag, which represents a direct loss of valuable metal, reduces the overall yield, and can introduce impurities that degrade the quality of the final casting.
The Goal of Furnace Design
Therefore, a primary goal of any effective melting furnace is to either limit the amount of oxygen that can reach the metal or reduce the time the metal is exposed to it.
How Crucible Design Provides a Multi-Layered Defense
Crucible furnaces are effective because they inherently incorporate several design principles that work together to combat oxidation.
The Crucible as a Primary Barrier
The most basic defense is the crucible itself. By containing the metal, it naturally limits the surface area of the melt that is exposed to the atmosphere. Unlike a large, open-hearth furnace, the melt's surface area is restricted to the crucible's diameter.
Indirect Heating: Keeping Contaminants Away
A critical design feature is indirect heating. In both fuel-fired and electric resistance models, the heat source is applied to the outside of the crucible.
The molten metal never comes into direct contact with the flame or heating elements. This prevents contaminants from the combustion process (in fuel-fired furnaces) from being introduced into the melt and reacting with the metal.
Atmospheric Control: Displacing Oxygen
The most active method for preventing oxidation is managing the atmosphere directly above the melt.
A simple lid or cover placed over the crucible traps heat and creates a more stable, stagnant layer of air, reducing the free flow of oxygen to the metal's surface.
For more sensitive alloys, a protective or inert gas (such as argon or nitrogen) can be pumped into the space above the melt. This physically displaces the oxygen, creating a blanket of non-reactive gas that protects the metal.
The Role of Protective Fluxes
A flux cover is another powerful tool. A layer of a specific chemical compound, or flux, is added to the top of the molten metal.
This flux melts to form a liquid blanket that acts as a physical barrier to oxygen. It also serves a secondary purpose by reacting with and absorbing any oxides or impurities that do form, allowing them to be skimmed off easily.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, these protection methods come with their own set of considerations.
Cost vs. Purity
Implementing a full inert gas or vacuum system significantly increases the furnace's cost and operational complexity. This is typically reserved for applications involving highly reactive metals (like aluminum or titanium) or where absolute purity is non-negotiable.
Flux Selection is Critical
Using the wrong flux can be worse than using no flux at all. An improperly selected flux can fail to protect the metal, or it could even introduce unwanted chemical elements into the melt, contaminating the alloy.
Speed of Melting
The longer the metal is molten, the more opportunity it has to oxidize. An undersized or inefficient furnace that takes too long to melt the charge will increase the risk of oxidation, even with other protective measures in place.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The method you choose depends entirely on the metal you are melting and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for common metals like bronze: A well-fitting lid and a properly selected flux cover provide excellent protection.
- If your primary focus is high-purity aluminum alloys: An electric furnace combined with an argon gas cover is the industry-standard approach.
- If your primary focus is small-batch melting of precious metals: A sealed induction or electric resistance crucible furnace offers the cleanest and most controlled environment.
By understanding these layers of defense, you can select the right combination of tools to ensure maximum yield and quality from your melt.
Summary Table:
| Method | How It Minimizes Oxidation | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible Container | Limits exposed surface area of the melt. | All applications. |
| Indirect Heating | Prevents contact with flame/combustion gases. | Fuel-fired and electric furnaces. |
| Lid or Cover | Creates a stagnant air layer, reducing oxygen flow. | Cost-effective melting of common metals. |
| Protective Gas | Displaces oxygen with an inert blanket (e.g., Argon). | High-purity alloys, reactive metals like aluminum. |
| Flux Cover | Forms a liquid barrier that absorbs oxides. | Applications where specific slag removal is needed. |
Maximize your metal yield and achieve superior purity with a furnace tailored to your specific alloy and process needs.
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Crucible, Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental or production requirements.
Ready to minimize oxidation losses and enhance your melting process? Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the ideal crucible furnace solution for your lab or foundry.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















