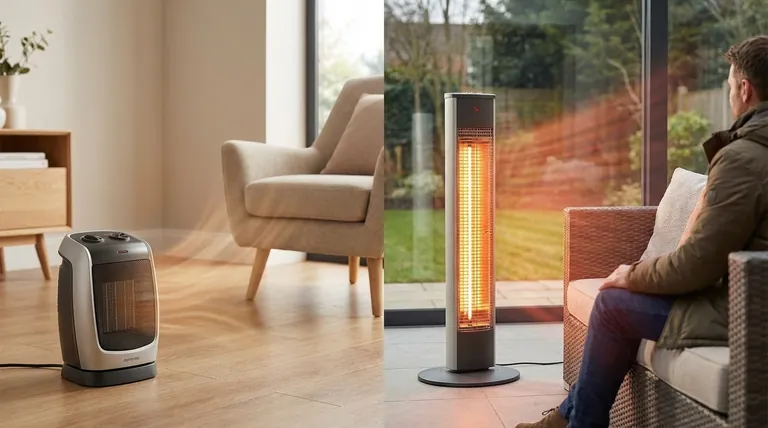
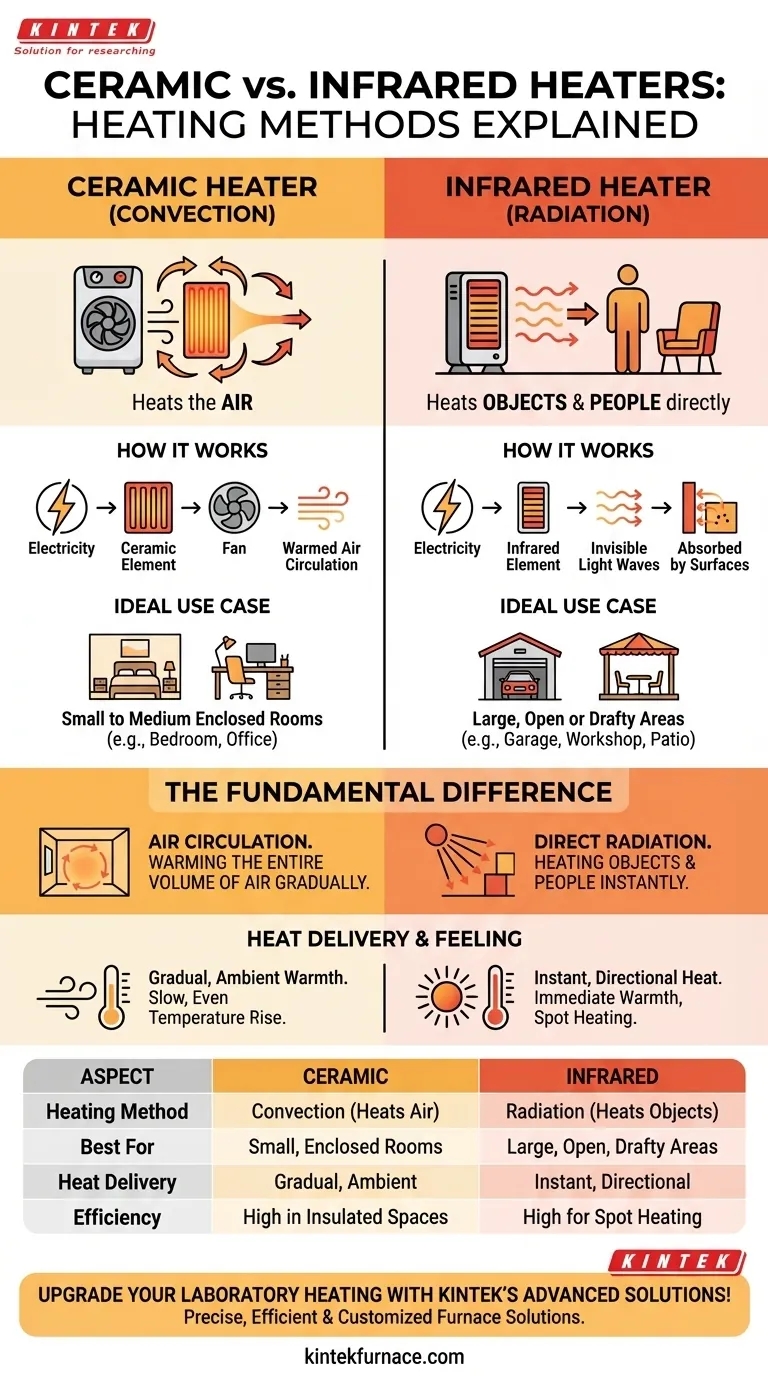
At their core, ceramic and infrared heaters operate on two fundamentally different principles of physics. A ceramic heater uses convection, passing air over a heated ceramic element to warm the entire room's air volume over time. In contrast, an infrared heater uses radiation, emitting invisible light waves that directly heat the objects and people in their path, much like the sun.
The choice between them is not about which is "better," but about what you intend to heat. A ceramic heater warms the air in an enclosed space, while an infrared heater warms you directly, regardless of the surrounding air temperature.

The Fundamental Difference: Air vs. Objects
To select the right heater, you must first understand how each one transfers thermal energy into your environment. They accomplish the same goal—providing warmth—through entirely different mechanisms.
How Ceramic Heaters Work (Convection)
A standard ceramic heater is essentially a contained, self-regulating furnace for a single room. Electricity passes through a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic plate, causing it to heat up rapidly.
A built-in fan then draws in cool ambient air and pushes it across the hot ceramic element. This heated air is then circulated throughout the room, gradually raising the overall temperature.
This method, known as convection, is designed to heat the entire volume of air within a defined space. It creates a gentle, pervasive warmth.
How Infrared Heaters Work (Radiation)
An infrared heater functions like a miniature sun. It converts electricity into infrared radiation, a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in a straight line until it hits an object.
When these waves strike you, your clothes, or a piece of furniture, the energy is absorbed and converted into heat. The air between the heater and the object remains largely unheated.
This is why you can feel the warmth of an infrared heater instantly, even in a cold, large, or drafty space. The heat is delivered directly to you, not wasted on the surrounding air.
Where Each Technology Excels
The differing heating methods make each type of heater uniquely suited for specific applications and environments. Matching the technology to the space is the key to efficient heating.
The Ideal Use Case for Ceramic Heaters
Ceramic heaters are the superior choice for small to medium-sized, enclosed rooms with good insulation, such as a bedroom, a home office, or a den.
Their purpose is to raise the ambient temperature of the entire space, creating a uniformly comfortable environment. Because they rely on heating the air, they are most effective when that heated air can be contained.
The Ideal Use Case for Infrared Heaters
Infrared heaters excel at spot heating in large, open, or drafty areas. Think of a garage, a workshop, an open-concept living room, or even a semi-enclosed patio.
In these scenarios, trying to heat the entire volume of air with convection would be incredibly inefficient. An infrared heater bypasses this by delivering radiant heat directly to you, creating a bubble of comfort without needing to warm the entire space.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior. Your satisfaction will depend on managing the inherent limitations of each heating method.
The Efficiency Question
While both types of heaters are nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity into heat, their application efficiency is what truly matters.
A ceramic heater becomes highly inefficient in a drafty room, as the warm air it produces is immediately lost. Conversely, an infrared heater is an inefficient choice for warming up an entire closed room, as it only heats the surfaces it can "see."
The Feeling of Heat
The subjective experience of warmth differs greatly. Ceramic heaters provide a gentle, circulating heat that raises the room's temperature slowly and evenly.
Infrared heaters provide an intense, directional heat that is felt instantly. This can be pleasant if you are cold, but some may find the direct radiation less comfortable than the ambient warmth of a convection heater.
A Note on "Ceramic Infrared" Heaters
You may encounter products marketed as "ceramic infrared" heaters. This term typically refers to an infrared heater that uses a ceramic plate as its radiating element.
Do not let this confuse the core principle. If the heater's primary function is to send out waves of heat that warm you directly, it is an infrared heater, regardless of the material used for its heating element. The method of heat transfer is what defines it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Space
To select the most effective and efficient heater, base your decision on the environment you need to heat, not on a generic claim of superiority.
- If your primary focus is heating a small, enclosed room like an office or bedroom: A ceramic heater is your most effective choice for raising the overall ambient temperature.
- If your primary focus is providing targeted warmth in a large, drafty area like a garage or open-concept room: An infrared heater will deliver heat directly to you far more efficiently.
- If your primary focus is instant, direct heat for a specific spot or outdoor patio: An infrared heater provides immediate warmth without needing to heat the surrounding air.
Ultimately, understanding the physics of heat transfer—convection versus radiation—is the key to choosing the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Ceramic Heater | Infrared Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Convection (heats air) | Radiation (heats objects directly) |
| Best For | Small, enclosed rooms | Large, open, or drafty areas |
| Heat Delivery | Gradual, ambient warmth | Instant, directional heat |
| Efficiency | High in insulated spaces | High for spot heating |
Upgrade Your Laboratory Heating with KINTEK's Advanced Solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need precise temperature control for material testing or efficient heating for specialized processes, we can help optimize your setup. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your lab's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More



















