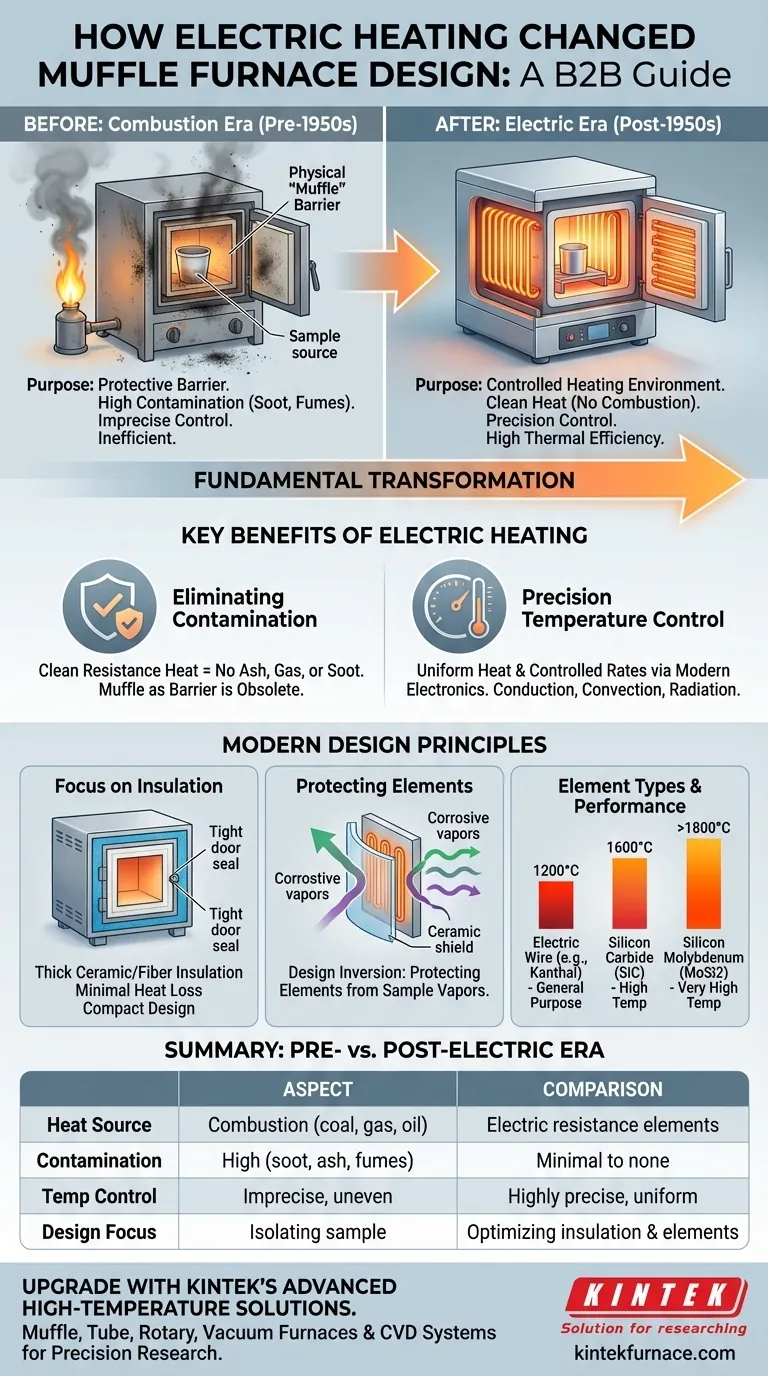
Fundamentally, the introduction of electric heating elements in the 1950s transformed the muffle furnace from a protective chamber into a highly controlled heating environment. By eliminating the flame, ash, and soot associated with fuel-based combustion, electric elements removed the primary source of contamination. This shift allowed furnace design to focus on precision temperature control and thermal efficiency rather than simply isolating the sample from a dirty heat source.
The core change was a shift in purpose: the "muffle" was no longer a physical barrier against combustion by-products. Instead, the entire furnace chamber evolved to optimize the clean, uniform heat provided by electrical resistance.

The Original Design Challenge: Combustion and Contamination
Before electric heating became viable, muffle furnaces were a clever solution to a difficult problem: how to heat a material without letting it touch the flame and its contaminants.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The original design featured a "muffle," which was an inner chamber or box made of a refractory material. This muffle held the sample.
The heat source—typically burning coal, gas, or oil—would heat the outside of the muffle. The muffle then transferred heat to the sample inside, protecting it from direct contact with the flames, soot, and chemical by-products of combustion.
Inherent Limitations of Combustion
This design, while functional, had significant drawbacks. Temperature control was imprecise, and achieving uniform heat throughout the muffle was a constant challenge. The process was often inefficient, with a great deal of heat lost to the surrounding environment.
The Electric Revolution of the 1950s
The development of high-temperature electric heating elements marked a turning point, leading nearly all manufacturers to convert to the new technology.
Eliminating Combustion By-products
The most significant change was the move to a clean heat source. Electric elements generate heat through resistance, producing no ash, gas fumes, or soot.
This instantly eliminated the primary reason for having a separate, sealed muffle. The risk of contaminating the sample from the heat source was gone.
Achieving Precision Temperature Control
Electric elements provide far superior temperature control through modern electronics. Heat can be applied evenly and regulated with high precision via conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation.
This allows for controlled heating rates and consistent, uniform temperatures throughout the chamber, which is critical for sensitive applications in materials science, chemistry, and metallurgy.
The Muffle Becomes the Chamber
With the elimination of combustion, the term "muffle" became largely synonymous with "heating chamber." The design focus shifted from isolation to optimization.
Today's muffle furnaces are essentially highly insulated boxes with carefully placed electric heating elements designed for maximum thermal performance. The legacy name "muffle furnace" persists, but its design philosophy has been completely redefined.
Modern Design Principles Driven by Electric Heat
The shift to electric power created a new set of design considerations focused on efficiency, element longevity, and performance.
Focus on Insulation and Efficiency
Modern muffle furnaces use thick, fireproof ceramic and fiber insulation to maintain high temperatures with minimal energy loss. The compact design and well-sealed doors are possible because the heat source is contained and predictable.
Protecting the Heating Elements
The design challenge has inverted. Instead of protecting the sample from the heat source, modern designs often focus on protecting the heating elements from vapors and gases released by the sample during heating.
Placing elements outside the direct path of corrosive fumes is a key design feature that extends their operational lifespan.
Element Types and Performance
The choice of heating element now defines the furnace's capabilities. Different materials are used to achieve specific temperature ranges and heating characteristics.
- Electric Furnace Wire (e.g., Kanthal): Common for general-purpose applications up to around 1200°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: Used for higher temperatures, typically up to 1600°C.
- Silicon Molybdenum (MoSi2) Rods: Employed for very high-temperature applications, often exceeding 1800°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While superior, electric muffle furnaces are not without their own set of operational trade-offs that stem directly from their design.
Element Lifespan and Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the chamber, created by the material being heated, can dramatically affect the heating elements. Corrosive vapors can cause the elements to degrade prematurely, requiring careful consideration of process compatibility.
Heating Rate vs. Uniformity
While highly controllable, there is often a trade-off between the speed of heating and temperature uniformity. A very rapid heating rate may create temporary hot or cold spots within the chamber before the temperature can stabilize.
Cost and Temperature Range
The maximum operating temperature of a furnace is dictated by its heating elements, which directly impacts cost. Furnaces with Silicon Molybdenum rods capable of extreme temperatures are significantly more expensive than standard wire-element models.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the evolution of the muffle furnace clarifies what to look for when selecting one. Your choice should be dictated by your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is general lab work below 1200°C: A standard furnace with electric wire elements offers the best balance of cost and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material processing (1200°C-1600°C): A furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements is necessary to reliably reach and maintain these temperatures.
- If your primary focus is research with potentially corrosive materials: Prioritize a furnace designed with protected elements to ensure reliability and longevity.
By appreciating how electric elements redefined the muffle furnace, you can select and operate your equipment with greater precision and confidence.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pre-Electric Era | Post-Electric Era |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Combustion (coal, gas, oil) | Electric resistance elements |
| Contamination | High (soot, ash, fumes) | Minimal to none |
| Temperature Control | Imprecise and uneven | Highly precise and uniform |
| Design Focus | Isolating sample with muffle | Optimizing insulation and element protection |
| Common Applications | Basic heating with contamination risks | Materials science, chemistry, metallurgy |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision-engineered products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for clean, efficient heating. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your research and processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















