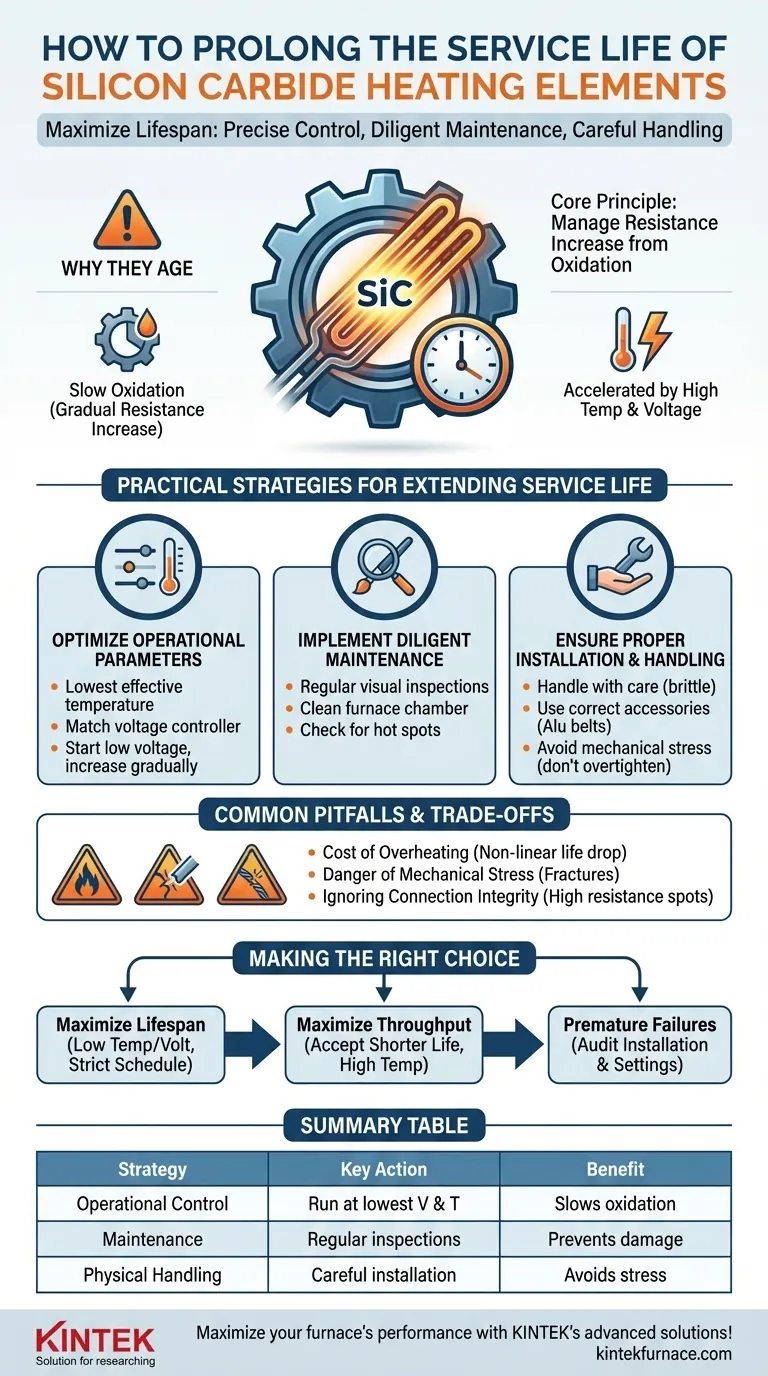
To maximize the lifespan of your silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements, you must focus on three key areas: precise operational control, diligent maintenance, and careful physical handling. The most critical operational factor is running the elements at the lowest possible voltage that still achieves your required furnace temperature, as this directly manages the element's aging process.
The service life of a SiC element is not a fixed duration; it is a direct result of its operating environment. The fundamental principle for extending its life is to manage the rate of resistance increase—caused by gradual oxidation—through meticulous control of temperature and voltage.
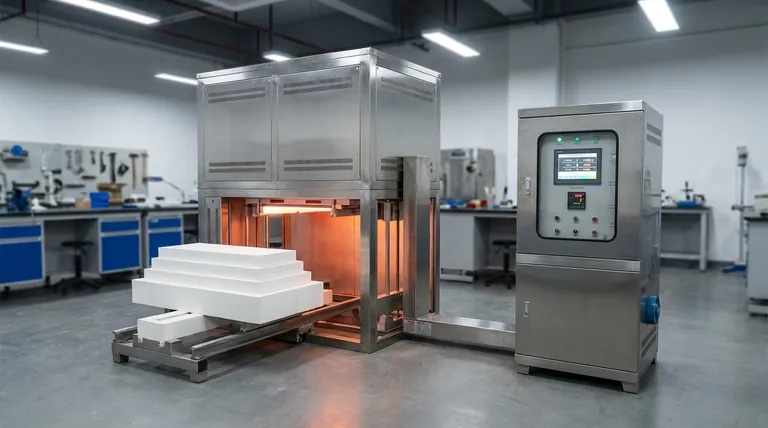

The Core Principle: Managing Resistance Over Time
Silicon carbide elements are known for their durability and resistance to thermal stress. However, they are not immune to aging. Understanding this process is the key to prolonging their use.
Why SiC Elements Age
The primary aging mechanism for a SiC element is slow oxidation. Over time and at high temperatures, the silicon carbide material reacts with the furnace atmosphere, which gradually increases the element's electrical resistance.
As resistance increases, the element requires more voltage to generate the same amount of heat (Power = Voltage² / Resistance). This aging process is gradual but inevitable.
The Critical Role of Voltage Control
Starting a new element at the lowest possible voltage is the single most effective strategy for extending its life. This provides maximum "headroom" on your power supply.
As the element ages and its resistance increases, you can gradually increase the voltage to maintain the required power output and temperature. An element is typically considered at the end of its life when the power supply can no longer provide enough voltage to compensate for the high resistance.
Temperature as an Accelerator
While SiC elements are designed for extremely high temperatures, heat acts as a powerful accelerator for oxidation. Running a furnace even slightly hotter than necessary will significantly speed up the resistance increase and shorten the element's life.
Practical Strategies for Extending Service Life
Applying the core principle involves specific, repeatable actions in your daily operations and maintenance schedules.
Optimize Your Operational Parameters
Always operate your furnace at the lowest effective temperature for your process. Avoid setting unnecessarily high temperature setpoints, as this provides no benefit and actively shortens element life.
Match your voltage controller to the needs of the element. Begin with low voltage and only increase it as required to maintain temperature over the element's lifespan.
Implement a Diligent Maintenance Routine
Regular furnace maintenance is not optional. Visually inspect elements for any signs of physical damage, cracking, or localized "hot spots" that might indicate an impending failure.
Ensure the furnace chamber is free of contaminants. Certain chemical vapors or deposits can react with the SiC material and accelerate degradation.
Ensure Proper Installation and Handling
SiC elements are robust under thermal load but can be brittle. They must be handled carefully to avoid being dropped or struck, which can cause micro-fractures that lead to failure.
Use the correct accessories, such as high-purity aluminum connecting belts, to ensure excellent electrical conductivity. Secure the elements with the proper fixing fixtures without overtightening, as this can introduce mechanical stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Avoiding common mistakes is as important as following best practices. Acknowledging the inherent trade-offs allows for more informed operational decisions.
The Cost of Overheating
The relationship between temperature and element life is not linear. A small increase in operating temperature can cause a disproportionately large decrease in service life. This is the primary trade-off between process speed and component replacement cost.
The Danger of Mechanical Stress
Never force an element into place. Overtightening clamps or failing to allow for thermal expansion can introduce mechanical stress that will cause the element to fracture and fail once it reaches operating temperature.
Ignoring Connection Integrity
A loose or corroded electrical connection creates a point of high resistance. This spot will overheat, potentially damaging the element's terminal end (the "cold end") and the connection hardware, leading to premature failure of the entire circuit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your operational strategy should align with your primary business goal, whether that is maximum component life or maximum production throughput.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Operate at the lowest effective temperature and voltage, and implement a strict inspection and maintenance schedule.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Accept a shorter element life as a necessary trade-off for running at higher temperatures, but still use the lowest voltage required for that temperature to avoid unnecessary stress.
- If you are experiencing frequent, premature failures: Immediately audit your installation procedures, power control settings, and handling protocols to identify sources of mechanical or electrical stress.
Proactive management of your heating elements transforms them from a simple consumable into a predictable and reliable asset.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Key Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Control | Run at lowest voltage and temperature | Slows oxidation, extends life |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections and clean furnace | Prevents damage and contamination |
| Physical Handling | Careful installation and use of proper accessories | Avoids mechanical stress and failures |
Maximize your furnace's performance with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















