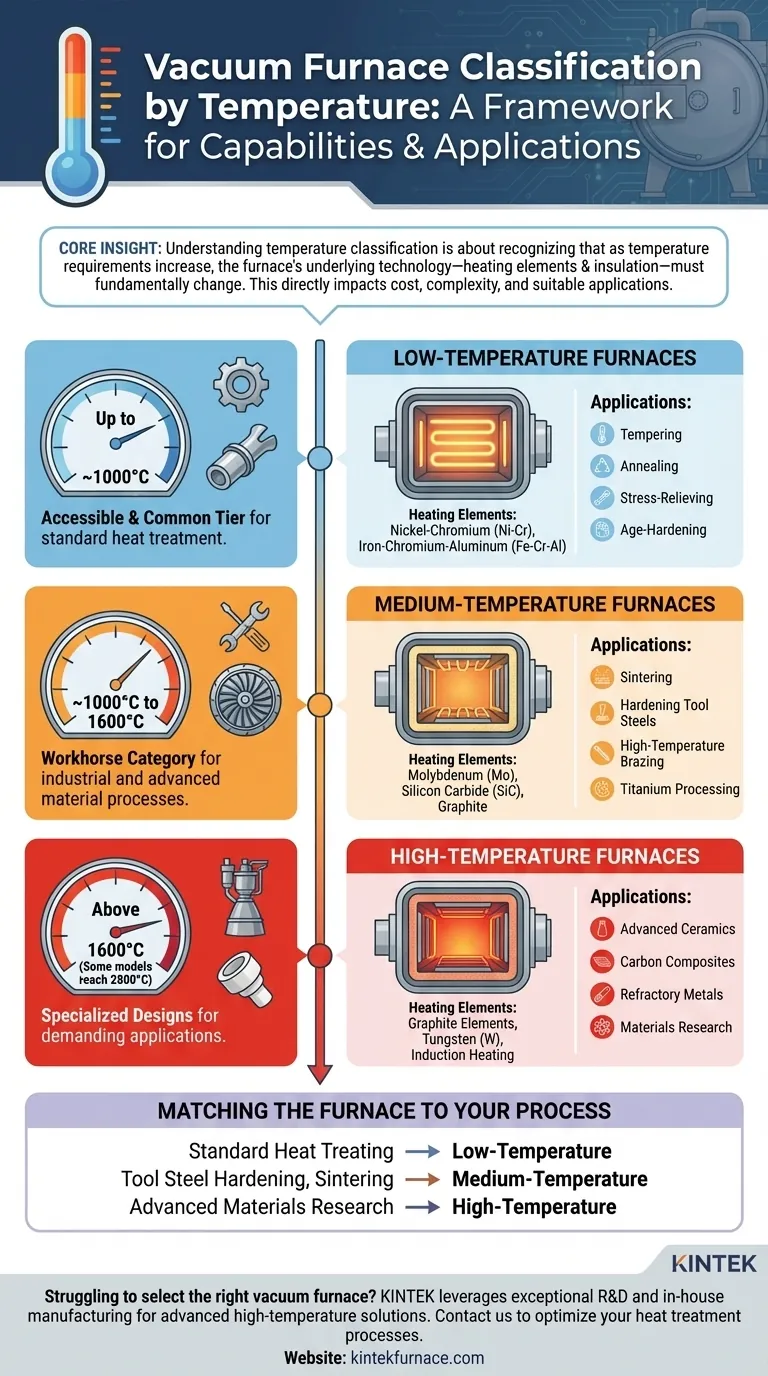
At its core, the classification of vacuum furnaces by temperature provides a framework for understanding their capabilities and intended applications. Furnaces are broadly grouped into three primary categories: low-temperature (up to approximately 1000°C), medium-temperature (up to 1600°C), and high-temperature (often exceeding 2000°C), with some specialized models reaching 2800°C. These ranges are not arbitrary; they are dictated by the fundamental materials used for heating elements and insulation.
Understanding temperature classification is less about memorizing specific numbers and more about recognizing that as temperature requirements increase, the furnace's underlying technology—from its heating elements to its insulation—must fundamentally change. This directly impacts its cost, complexity, and suitable applications.

The Primary Temperature Classifications
The most common way to categorize vacuum furnaces is by their maximum achievable operating temperature. This directly correlates to the types of materials and processes the furnace can handle.
Low-Temperature Furnaces (Up to ~1000°C)
These furnaces are designed for processes that do not require extreme heat. They represent the most accessible and common tier of vacuum heat treatment.
The heating elements are typically made from alloys like nickel-chromium (Ni-Cr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al), which offer reliable performance and longevity within this temperature range.
Common applications include tempering, annealing, stress-relieving, and age-hardening of various steels and non-ferrous alloys.
Medium-Temperature Furnaces (~1000°C to 1600°C)
This range is a workhorse category for many industrial and advanced material processes, requiring more robust construction and materials than low-temperature models.
Heating elements must be upgraded to materials like molybdenum (Mo), silicon carbide (SiC), or graphite. The insulation also becomes more critical, often using composite carbon or ceramic felts.
These furnaces are essential for sintering, hardening tool steels, high-temperature brazing, and processing titanium alloys. Some sources may subdivide this range, referring to 1200°C or 1400°C models for specific processes.
High-Temperature Furnaces (Above 1600°C)
Operating at these extreme temperatures requires highly specialized designs and materials capable of withstanding intense thermal stress in a vacuum.
Heating is typically achieved with high-purity graphite elements, tungsten (W), or through non-contact induction heating methods. Insulation is almost exclusively graphite-based felt.
These furnaces are used for the most demanding applications, such as processing advanced ceramics, carbon composite materials, refractory metals, and conducting advanced materials research. Models can reach temperatures of 2400°C or even 2800°C.
Understanding the Engineering Trade-offs
A furnace's temperature rating is not just a setting; it is a reflection of its fundamental engineering and material science limitations. Choosing the right one involves understanding these built-in trade-offs.
Heating Elements Dictate the Limit
You cannot simply run a low-temperature furnace at a high temperature. The heating elements and insulation define the operational ceiling.
An iron-chromium element designed for 800°C would rapidly degrade and fail if pushed to 1600°C. Likewise, the materials used in a high-temperature graphite furnace are often overkill and less efficient for low-temperature processes.
Application-Specific Naming
While the low, medium, and high-temperature framework is a useful guide, manufacturers often classify furnaces by their specific function, which has an implied temperature range.
For example, a "Vacuum Brazing Furnace" is typically a medium-temperature unit, while a "Vacuum Sintering Furnace" can be medium or high-temperature depending on the material being sintered.
Temperature is Only One Part of the Equation
A complete classification also considers other critical parameters. Furnaces are also categorized by their vacuum level (e.g., high vacuum vs. ultra-high vacuum) and their quenching method (e.g., gas quench vs. oil quench).
These factors, combined with temperature, determine the furnace's ultimate suitability for a specific material and desired outcome.
Matching the Furnace to Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace is a critical decision that impacts process quality, operational cost, and equipment longevity. Your primary application should be the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treating (tempering, annealing, stress relief): A low-temperature furnace (up to 1000°C) is the most cost-effective and appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is tool steel hardening, sintering, or brazing alloys: A medium-temperature furnace (~1600°C) provides the necessary capability and is a versatile standard for many industries.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or processing ceramics and refractory metals: A high-temperature furnace (above 1600°C) with graphite or tungsten elements is the only option that can meet these demands.
By understanding that temperature ranges are tied directly to material science and engineering, you can make a more informed technical and financial decision for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Heating Elements | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to ~1000°C | Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr), Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al) | Tempering, annealing, stress-relieving, age-hardening |
| ~1000°C to 1600°C | Molybdenum (Mo), Silicon Carbide (SiC), Graphite | Sintering, hardening tool steels, high-temperature brazing, titanium processing |
| Above 1600°C | Graphite, Tungsten (W), Induction Heating | Advanced ceramics, carbon composites, refractory metals, materials research |
Struggling to select the right vacuum furnace for your specific temperature and application needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















