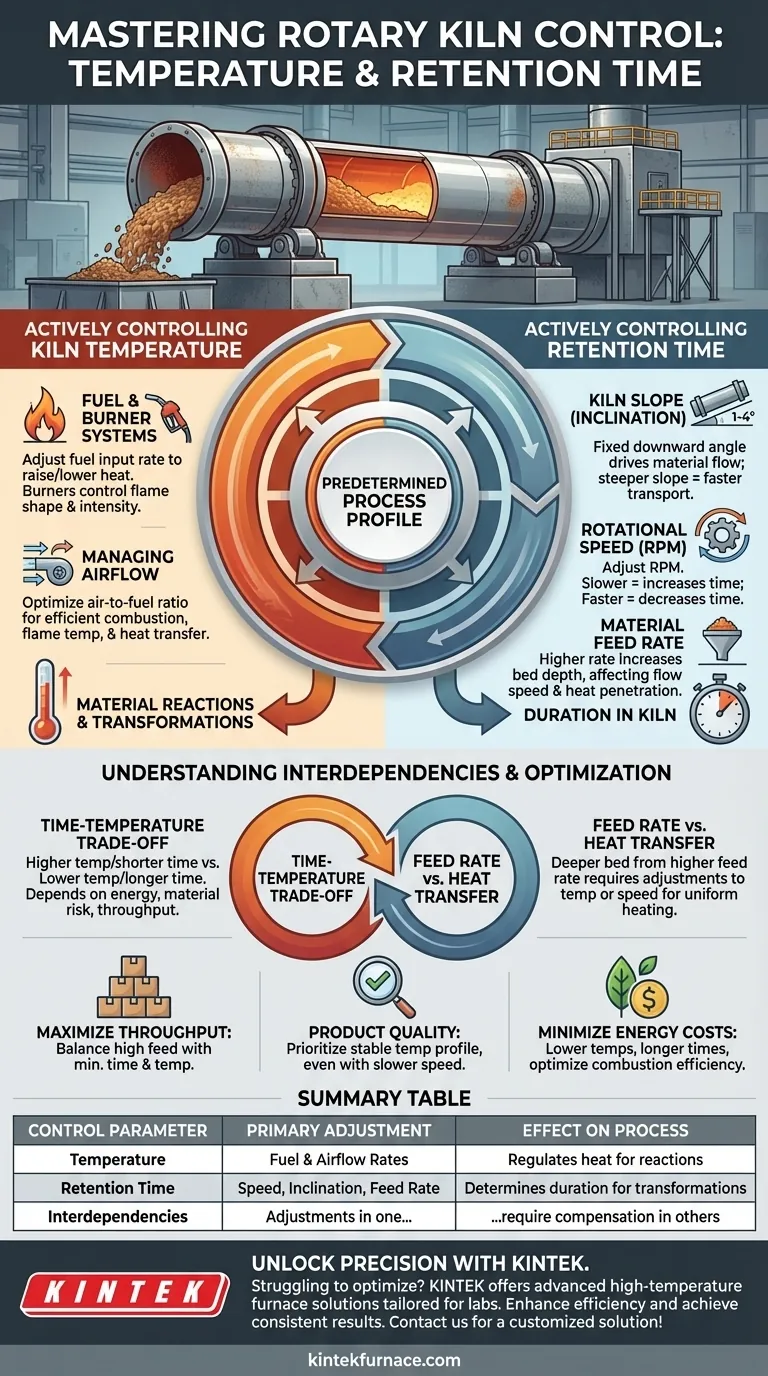
In a rotary kiln, temperature is primarily controlled by adjusting fuel and airflow rates, while retention time is governed by the kiln's rotational speed, its angle of inclination, and the material feed rate. These operational controls are implemented to match a predetermined processing profile that is carefully designed based on detailed thermal and chemical analysis of the material itself.
The core challenge of rotary kiln operation is not just manipulating controls, but understanding that active control (adjusting speed, fuel) is inseparable from process design (analyzing the material). True control is achieved when the kiln's mechanical and thermal parameters are precisely tuned to execute the specific chemical and physical transformations required by the material.

The Foundation: Designing the Process Profile
Before a kiln is ever started, the ideal time and temperature parameters must be established. This is a scientific process, not guesswork, designed to ensure the material undergoes the exact changes needed to create the final product.
Using Thermal Analysis to Map Temperatures
The first step is understanding how the material behaves when heated. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) is a key laboratory technique used for this purpose.
TGA precisely measures a material's mass as it is heated. This analysis identifies the exact temperature ranges where critical reactions—such as water evaporation or chemical decomposition—occur. For example, TGA can show that free water vaporizes around 100°C, while chemically bound water may only be released at temperatures up to 260°C.
This data is used to create a temperature profile, a roadmap that dictates the required temperature at each stage of the material's journey through the kiln.
Defining the Reaction Requirements
The ultimate goal is to trigger a specific chemical reaction or physical change. Retention time, also called residence time, is the duration the material must spend in the kiln to complete this transformation.
Based on the thermal analysis and desired outcome, engineers determine the necessary combination of time and temperature. This ensures the material is heated sufficiently and for the correct duration to form the desired product consistently.
Actively Controlling Kiln Temperature
Once the ideal temperature profile is known, operators use the kiln's combustion system to achieve and maintain it.
The Role of Fuel and Burner Systems
The primary lever for temperature control is the fuel input rate. By increasing or decreasing the flow of fuel (such as natural gas, pulverized coal, or oil) to the burner, operators can directly raise or lower the heat generated inside the kiln.
Sophisticated burner systems allow for precise control over the flame's shape and intensity, which is critical for distributing heat effectively to the material bed.
Managing Airflow for Efficient Combustion
Temperature is not just about fuel; it's about the efficiency of the burn. The amount of combustion air (both primary air mixed with fuel and secondary air drawn into the kiln) is a critical control parameter.
Adjusting airflow impacts flame temperature, flame length, and the transfer of heat to the material. An optimized air-to-fuel ratio ensures complete combustion, maximizing energy efficiency and providing stable, predictable heating.
Actively Controlling Retention Time
Retention time is governed by the mechanical properties and operating parameters of the kiln, which dictate how quickly material travels from the feed end to the discharge end.
Kiln Slope (Angle of Inclination)
A rotary kiln is installed at a slight downward angle, typically between 1 and 4 degrees. This slope is the primary driver of material flow.
A steeper slope results in faster material transport and a shorter retention time. While this angle is usually fixed after installation, it is the most fundamental design parameter for determining the kiln's baseline retention time.
Rotational Speed
The most common method for actively controlling retention time during operation is adjusting the kiln's rotational speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
Slowing the rotation causes the material to tumble in place for longer before advancing down the slope, thereby increasing retention time. Conversely, speeding up the rotation moves material through the kiln more quickly, decreasing retention time.
Material Feed Rate
The rate at which new material is introduced to the kiln also influences retention time. A higher feed rate can increase the "bed depth" of the material.
This can cause material to move through the kiln faster, but a deeper bed can also complicate heat transfer, requiring adjustments to temperature or rotational speed to ensure proper processing.
Understanding the Interdependencies
Temperature and retention time are not independent variables; they are deeply interconnected. Adjusting one almost always requires compensating with the other.
The Time-Temperature Trade-off
Often, a similar chemical transformation can be achieved with a higher temperature for a shorter time, or a lower temperature for a longer time. The optimal choice depends on factors like energy cost, risk of overheating the material, and desired throughput.
Feed Rate vs. Heat Transfer
Increasing the feed rate to boost production is a common goal, but it comes with a trade-off. A higher feed rate creates a deeper material bed, making it harder for heat from the flame and hot walls to penetrate to the bottom layers. This inefficiency may force you to increase the temperature or slow the kiln's rotation, negating some of the benefit of the higher feed rate.
Optimizing Control for Your Goal
Your control strategy should be dictated by your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Balance a high feed rate with the minimum retention time and temperature required to meet product specifications.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: Prioritize a stable and precise temperature profile, even if it requires a slower rotational speed and lower feed rate.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy costs: Explore process profiles that use lower temperatures and longer retention times, and meticulously optimize the air-to-fuel ratio for maximum combustion efficiency.
Mastering these interconnected controls is the key to moving from simply operating a kiln to truly commanding the material transformation process within it.
Summary Table:
| Control Parameter | Primary Adjustment | Effect on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Fuel and airflow rates | Regulates heat for material reactions |
| Retention Time | Rotational speed, inclination, feed rate | Determines duration for transformations |
| Interdependencies | Adjustments in one require compensation in others | Balances throughput, quality, and energy use |
Unlock Precision in Your Kiln Operations with KINTEK
Struggling to optimize temperature and retention time in your rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Enhance your material processing efficiency and achieve consistent results—contact us today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















