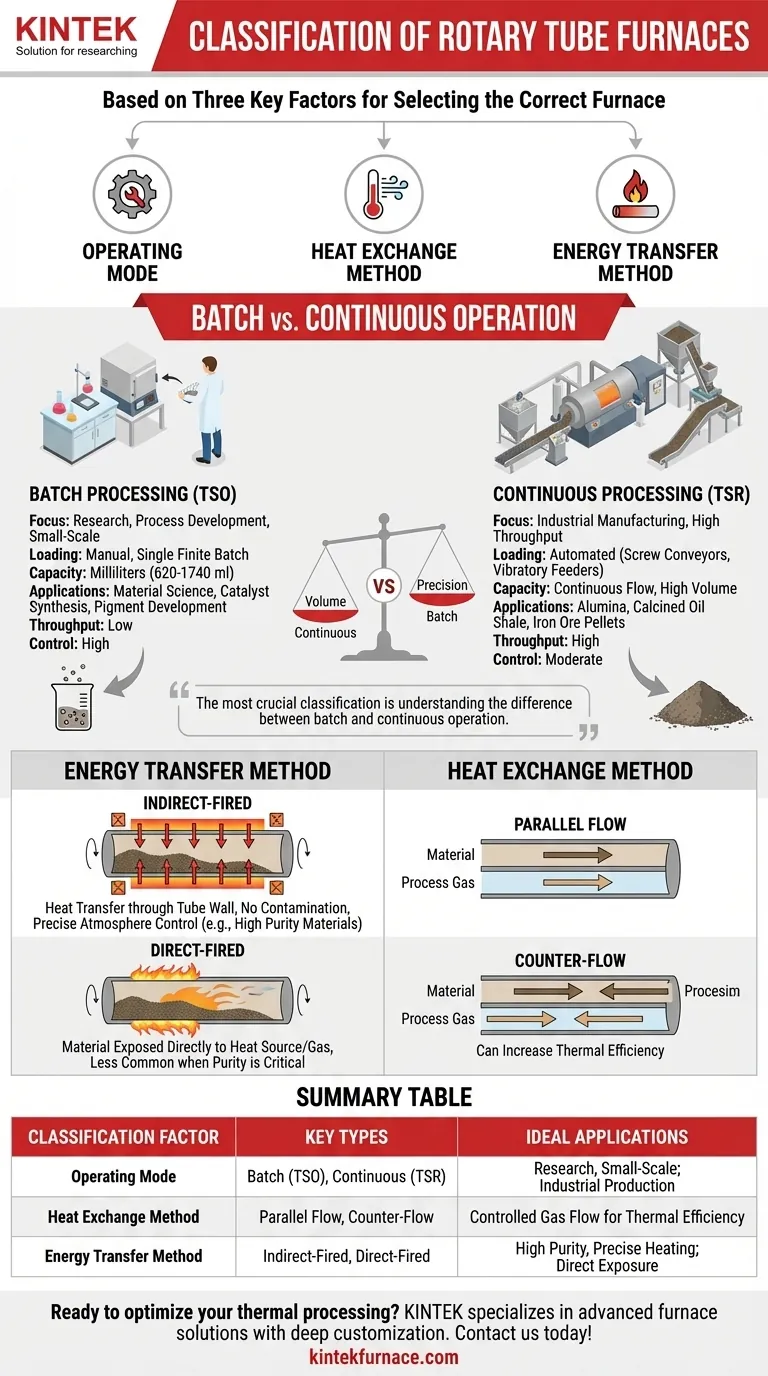
At their core, rotary tube furnaces are primarily classified by three key factors. These are their fundamental operating mode (batch or continuous), their heat exchange method (how process gas flows relative to the material), and their energy transfer method (how heat is applied to the material). Understanding these distinctions is critical to selecting the correct furnace for a specific application.
The most crucial classification for any user is understanding the difference between batch and continuous operation. This single choice dictates the furnace's suitability for either small-scale, precision-focused research or large-scale, high-throughput industrial production.
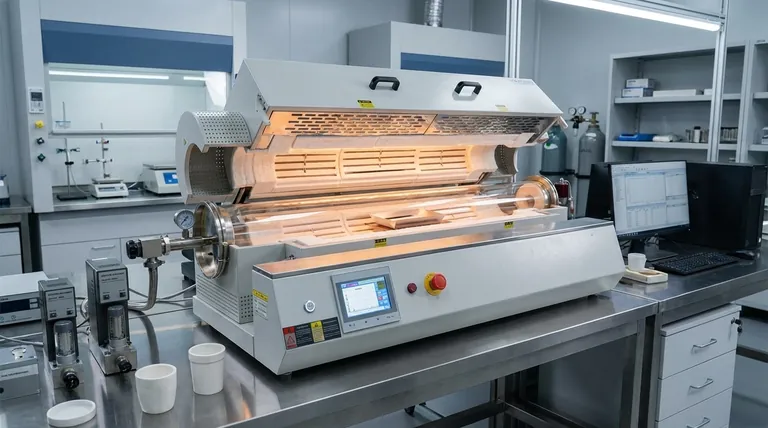

The Primary Classification: Batch vs. Continuous Operation
The first and most significant way to classify a rotary tube furnace is by its intended processing style. This determines its scale, feeding mechanism, and ideal use case.
Continuous Processing Furnaces (TSR)
Continuous furnaces are designed for industrial-scale manufacturing where a constant, uninterrupted flow of material is required. They are defined by high throughput.
Materials are fed into the furnace from a hopper using automated mechanisms like screw conveyors for fine powders or vibratory feeders for irregularly sized particles.
These systems are the standard for producing bulk materials like alumina, calcined oil shale, and iron ore pellets, where production volume is a key performance indicator.
Batch Processing Furnaces (TSO)
Batch furnaces are built for laboratory research, process development, and small-scale production runs. They process a finite amount of material at a time.
Loading is typically done manually for a single batch, with capacities often measured in milliliters (e.g., 620 to 1740 ml). This allows for precise control over a known quantity of material.
Their application is centered on material science research, catalyst synthesis, pigment development, and metallurgical analysis, where process precision outweighs the need for volume.
Understanding the Technical Classifications
Beyond the operating mode, two engineering principles define how the furnace heats the material and interacts with any process gases.
Energy Transfer Method: Direct vs. Indirect
The most common design is indirect firing. In this setup, heating elements are outside the rotating tube, and heat is transferred through the tube wall to the material inside. This prevents contamination and allows for precise atmosphere control.
A direct-fired furnace exposes the material directly to the heat source, such as hot combustion gas flowing through the tube. This is less common when material purity is a concern.
Some specialized designs may use a combined method to optimize heating for specific processes.
Heat Exchange Method: Airflow Direction
If a process gas is used, its flow direction is a key classifier. In a parallel flow design, the gas and the solid material travel through the tube in the same direction.
In a counter-flow (or reverse flow) design, the gas enters at the opposite end from the material and flows against it. This method can increase thermal efficiency by creating a more distributed temperature gradient.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Features
Choosing a rotary tube furnace involves balancing technical capabilities with your specific process requirements.
Throughput vs. Process Control
There is a direct trade-off between volume and precision. Continuous (TSR) furnaces are optimized for maximum throughput, while batch (TSO) furnaces are designed for maximum control over experimental variables.
Material Uniformity and Handling
The fundamental advantage of any rotary tube furnace is its ability to achieve uniform heating by tumbling the material. The continuous rotation ensures all particles are equally exposed to the heat source.
The choice of feeding mechanism is not trivial. An incorrect feeder can cause inconsistent processing in a continuous system. The feed system must match the material's properties (e.g., powder, granule, or irregular shape).
Atmosphere Control
Many rotary tube furnaces function as atmosphere furnaces, allowing for processes to occur in a tightly controlled gaseous environment. This is critical for applications like the gaseous reduction of ores, oxidation, or preventing unwanted reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your optimal furnace configuration depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is industrial production and high throughput: A continuous (TSR) model with an automated feeding system like a screw conveyor is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-scale testing: A batch (TSO) furnace provides the necessary process control and flexibility for experimental work.
- If your primary focus is material purity and precise heating: An indirect-fired furnace is essential to prevent contamination and allow for controlled atmospheres.
By aligning the furnace's classification with your operational needs, you ensure an efficient, reliable, and effective thermal processing solution.
Summary Table:
| Classification Factor | Key Types | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Mode | Batch (TSO), Continuous (TSR) | Research, small-scale; Industrial production |
| Heat Exchange Method | Parallel flow, Counter-flow | Controlled gas flow for thermal efficiency |
| Energy Transfer Method | Indirect-fired, Direct-fired | High purity, precise heating; Direct exposure |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today for a tailored solution that enhances efficiency and precision in your lab or facility!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















