At their core, rotary kilns are considered environmentally friendly due to a combination of high thermal efficiency, advanced emissions control, and their unique ability to process and recover value from waste streams. Their design inherently minimizes energy waste and material loss, making them a sustainable choice for demanding industrial applications like cement production and hazardous waste treatment.
The environmental advantages of a rotary kiln are not a single feature, but an outcome of its fundamental design. By ensuring uniform heating, precise temperature control, and effective material containment, the system minimizes waste in every form—from lost energy and fugitive emissions to scrap product and raw materials.
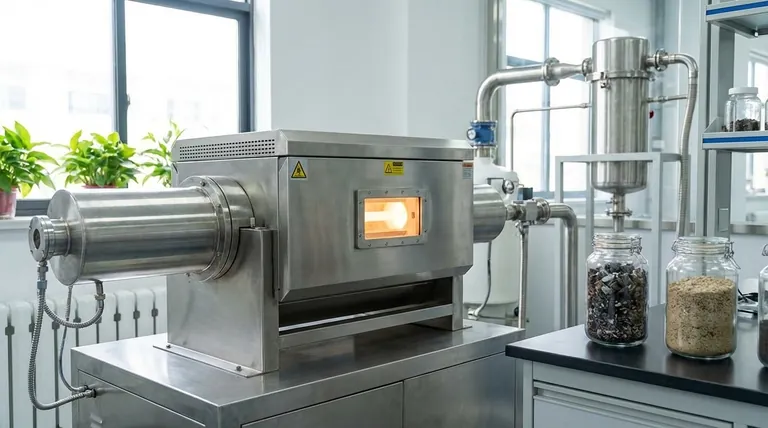

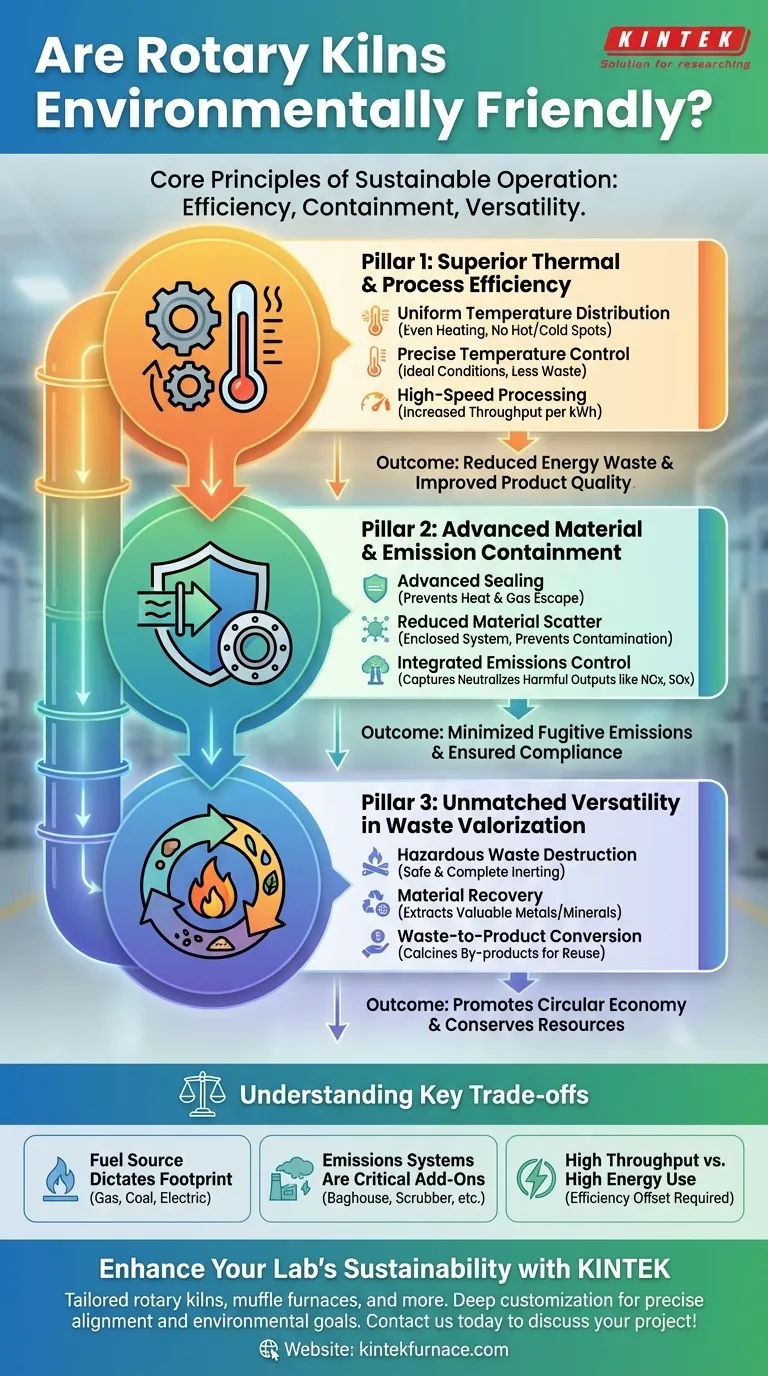
The Pillars of a Rotary Kiln's Environmental Performance
The sustainability of a rotary kiln is built on three key operational principles: efficiency, containment, and versatility. Each contributes directly to reducing a facility's overall environmental footprint.
Pillar 1: Superior Thermal and Process Efficiency
Inefficiency is a primary source of industrial waste. Rotary kilns are engineered to maximize the value extracted from every unit of energy consumed.
- Uniform Temperature Distribution: The rotating action constantly tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is heated evenly. This eliminates hot spots and cold spots, preventing wasted energy and ensuring consistent product quality.
- Precise Temperature Control: The ability to maintain a narrow and exact temperature range is crucial. It ensures the chemical reaction or physical change happens under ideal conditions, reducing the energy required and minimizing the creation of off-spec, wasted product.
- High-Speed Processing: Modern kilns often feature high-speed cycles, increasing throughput for a given amount of energy. This means more product is created per kilowatt-hour, directly improving energy efficiency.
Pillar 2: Advanced Material and Emission Containment
A key environmental benefit comes from the kiln's ability to keep materials and gases where they belong—inside the system.
- Advanced Sealing: State-of-the-art sealing devices at the inlet and outlet of the kiln are critical. They prevent heat from escaping (improving thermal efficiency) and stop process gases or fine dust particles from leaking into the atmosphere as fugitive emissions.
- Reduced Material Scatter: The enclosed, controlled nature of the kiln prevents raw materials from being scattered by wind or handling. This not only saves valuable input material but also prevents local land and air contamination.
- Integrated Emissions Control: Rotary kilns are designed to work with advanced emissions control systems. These systems capture and neutralize harmful outputs like NOx, SOx, and particulates before they are released, ensuring compliance with strict environmental regulations.
Pillar 3: Unmatched Versatility in Waste Valorization
Perhaps the most significant environmental contribution of rotary kilns is their ability to turn waste liabilities into assets, a core principle of the circular economy.
- Hazardous Waste Destruction: The extremely high temperatures achievable in a rotary kiln can safely and completely destroy hazardous organic compounds, rendering them inert. This makes the technology a cornerstone of environmental remediation.
- Material Recovery: Kilns are used to recover valuable metals and minerals from various waste streams. This reduces the need for virgin material extraction, which carries a much higher environmental cost.
- Waste-to-Product Conversion: They are highly effective at processing bulk materials like waste stones or other industrial by-products, calcining them into usable materials for construction and other industries.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While highly effective, a rotary kiln's environmental performance is not automatic. It depends entirely on its configuration, fuel source, and operational context.
The Fuel Source Dictates the Footprint
The label "environmentally friendly" is heavily dependent on how the kiln is heated. A kiln fired by natural gas has a different carbon footprint than one fired by coal, petroleum coke, or electricity. An electric kiln is only as "green" as the grid that powers it.
Emissions Systems Are a Critical Add-On
A basic rotary kiln is simply a rotating tube. The "advanced emissions control systems" that manage pollutants are separate, complex subsystems. Without a baghouse, scrubber, or other post-combustion treatment, the kiln's exhaust would be a significant source of pollution. These systems add capital cost, require energy to operate, and demand regular maintenance.
High Throughput vs. High Energy Use
The ability to achieve extremely high temperatures makes a rotary kiln versatile, but it also makes it energy-intensive. The environmental benefit is only realized when this high energy consumption is offset by high throughput, superior product quality (less waste), or the effective treatment of harmful waste that has no other viable solution.
How to Apply This to Your Project
When evaluating a rotary kiln, your decision should be guided by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization: A rotary kiln is an exceptional choice for safely destroying hazardous materials or recovering value from complex, mixed waste streams.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: The kiln's design offers excellent thermal control, but you must carefully model the total energy consumption against your required throughput and select the most sustainable fuel source available.
- If your primary focus is minimizing emissions: A kiln specified with modern, tight-tolerance seals and a comprehensive, properly sized emissions control system is essential for meeting stringent environmental standards.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can ensure your implementation of a rotary kiln genuinely contributes to your organization's sustainability goals.
Summary Table:
| Pillar | Key Features | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Superior Thermal and Process Efficiency | Uniform heating, precise temperature control, high-speed processing | Reduces energy waste, improves product quality, lowers carbon footprint |
| Advanced Material and Emission Containment | Advanced sealing, reduced material scatter, integrated emissions control | Minimizes fugitive emissions, prevents contamination, ensures regulatory compliance |
| Unmatched Versatility in Waste Valorization | Hazardous waste destruction, material recovery, waste-to-product conversion | Promotes circular economy, reduces landfill use, conserves natural resources |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide tailored rotary kilns, muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, and more. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior efficiency and environmental compliance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your project goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















