In electronic material processing, muffle furnaces are critical for thermally treating materials to achieve specific electrical, optical, and structural properties. They are used for a range of tasks including growing thin films, annealing semiconductor wafers, sintering ceramic substrates, and heat-treating metallic components, all of which depend on precise temperature and atmospheric control.
The core value of a muffle furnace in electronics is its ability to provide two non-negotiable conditions: exceptionally uniform temperature and a contaminant-free, highly controlled atmosphere. These two capabilities are essential for manufacturing high-performance electronic materials and devices.
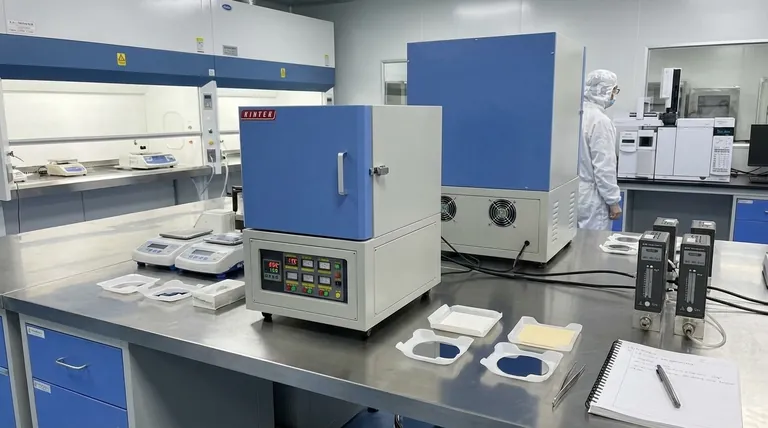

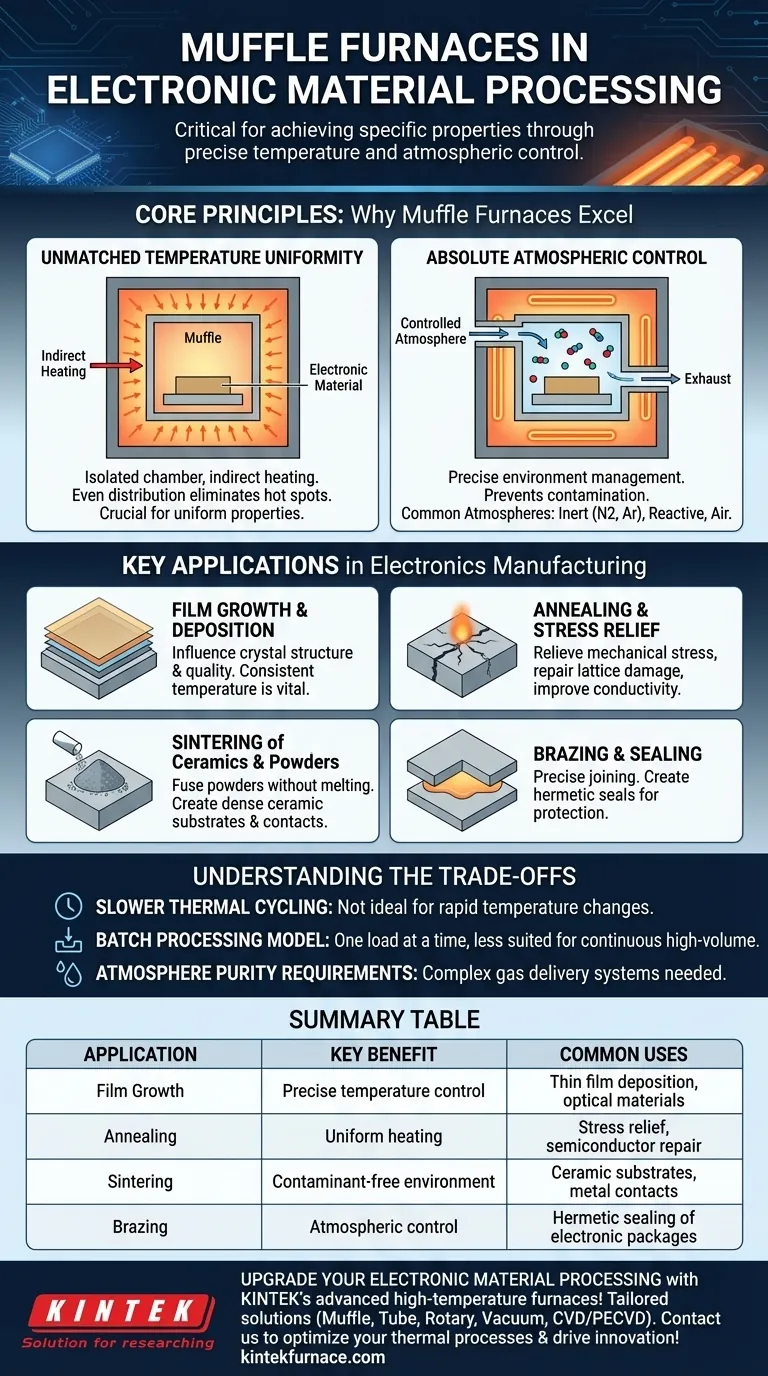
The Core Principles: Why Muffle Furnaces Excel
A muffle furnace's design is deceptively simple but uniquely effective. The "muffle" is a sealed inner chamber that isolates the material being processed from the external heating elements. This separation is the key to its advantages.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The isolated chamber is heated primarily through radiation and convection, not direct contact with heating coils. This indirect heating method distributes energy evenly throughout the chamber, eliminating hot spots and ensuring the entire workpiece experiences the same temperature.
This uniformity is critical for processes like annealing, where even slight temperature variations across a silicon wafer can introduce defects and compromise device performance.
Absolute Atmospheric Control
Because the workpiece is sealed within the muffle, the atmosphere inside can be precisely managed. This isolation prevents contamination from fuel byproducts or degrading heating elements, which would be disastrous for sensitive electronic materials.
This allows processing to occur in specific environments:
- Inert Gas (Nitrogen, Argon): Prevents oxidation of materials like copper interconnects or other sensitive metals during heat treatment.
- Reactive Gas: Used for specific chemical reactions on a material's surface, such as in some forms of film growth.
- Air: For processes where oxidation is desired or not a concern, like ashing photoresist.
Key Applications in Electronics Manufacturing
The unique capabilities of muffle furnaces make them indispensable for several high-precision manufacturing steps.
Film Growth and Deposition
For thin films and optical materials, the furnace's controlled temperature and atmosphere directly influence crystal structure, growth rate, and final quality. Consistent temperature is vital for achieving the desired material phase and properties.
Annealing and Stress Relief
Annealing involves heating a material and then slowly cooling it. In electronics, this is done to relieve mechanical stress induced during manufacturing, repair crystal lattice damage in semiconductors after ion implantation, and improve the electrical conductivity of metal contacts.
Sintering of Ceramics and Powders
Sintering is the process of fusing powders together using heat, without melting them. Muffle furnaces are used to create dense, durable ceramic substrates for integrated circuits or to form electrical contacts from powdered metals.
Brazing and Sealing
Precise temperature control is essential for joining components using a filler metal (brazing). A common use is creating hermetic seals on electronic packages to protect sensitive internal circuitry from moisture and other environmental factors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, muffle furnaces are not the solution for every thermal processing need. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Slower Thermal Cycling
The same insulation and thermal mass that provide excellent temperature stability also mean muffle furnaces heat up and cool down relatively slowly. They are not ideal for applications requiring rapid temperature changes.
Batch Processing Model
Most muffle furnaces are designed for batch processing, where one load is treated at a time. While industrial-scale versions exist, they are generally less suited for continuous, high-volume assembly lines compared to other furnace types like conveyor belt furnaces.
Atmosphere Purity Requirements
Achieving and maintaining a high-purity inert atmosphere requires a furnace with excellent seals, a reliable gas delivery system, and proper purging protocols. This can add to the system's complexity and operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on the material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize a furnace with the most precise temperature controller and versatile options for managing different atmospheres (e.g., inert gas, vacuum).
- If your primary focus is processing oxidation-sensitive materials: Ensure the furnace has excellent seals and a robust system for purging and maintaining an inert gas environment.
- If your primary focus is repeatable component treatment like annealing: Look for a model with a programmable controller that can reliably execute multi-step heating, soaking, and cooling profiles.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace's value lies in its ability to create a perfectly controlled, high-temperature environment, making the ideal properties of electronic materials not just possible, but repeatable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Film Growth | Precise temperature control | Thin film deposition, optical materials |
| Annealing | Uniform heating | Stress relief, semiconductor repair |
| Sintering | Contaminant-free environment | Ceramic substrates, metal contacts |
| Brazing | Atmospheric control | Hermetic sealing of electronic packages |
Upgrade your electronic material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your thermal processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















