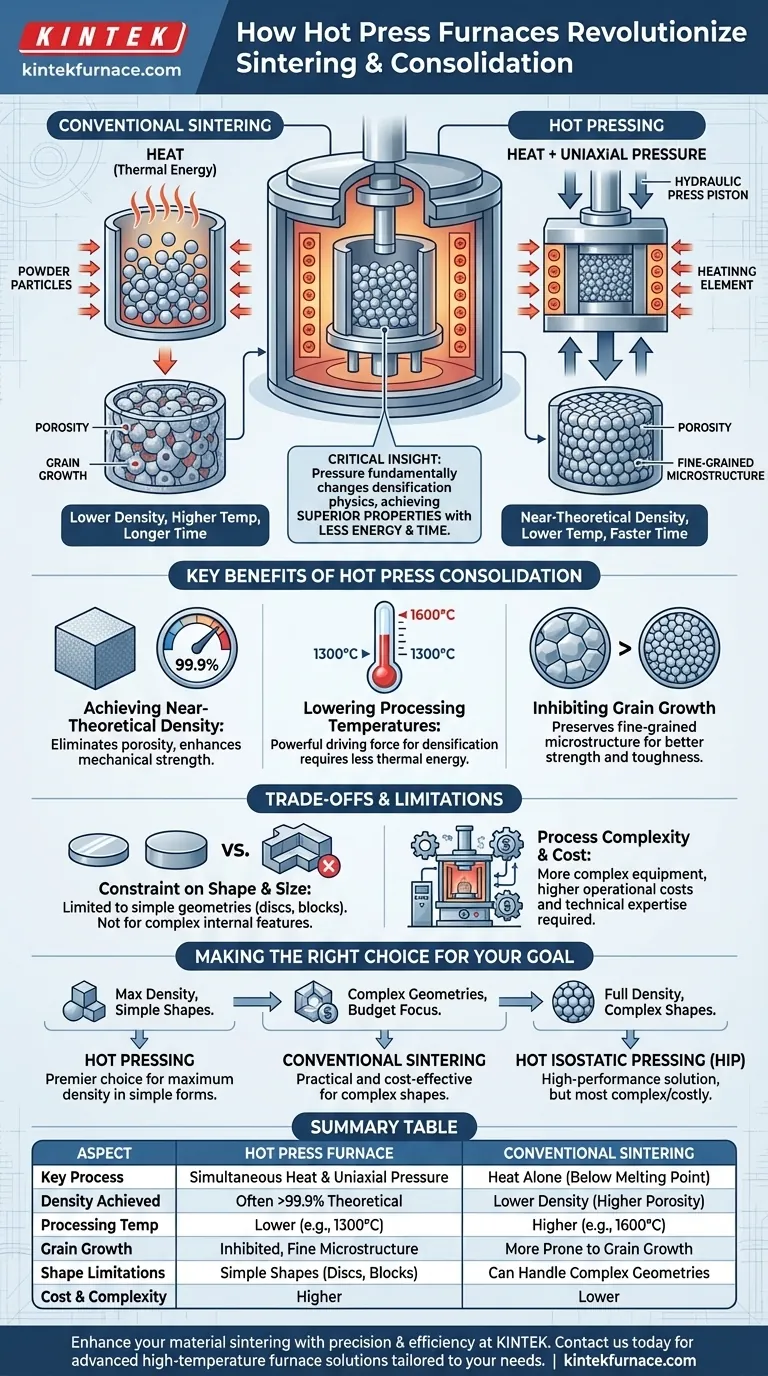
At its core, a hot press furnace is used to simultaneously apply high temperature and immense mechanical pressure to a powdered material. This dual action forces the individual particles to fuse together, dramatically increasing the material's density and strength in a process known as sintering or consolidation.
The critical insight is that adding pressure to the sintering process does more than just squeeze particles together. It fundamentally changes the physics of densification, allowing you to achieve superior material properties at lower temperatures and in less time than with heat alone.

The Principle: Heat vs. Heat and Pressure
To understand the value of a hot press, we must first distinguish between standard sintering and hot pressing.
What is Conventional Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process for making a solid object from a powder. By heating the material below its melting point, you give the atoms enough energy to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, causing them to fuse.
This process reduces the empty space, or porosity, between particles. For example, dental zirconia is sintered at high temperatures (up to 1600°C) to achieve its final hardness and strength.
The Hot Press Advantage: Adding Uniaxial Pressure
A hot press furnace adds a second, critical variable: uniaxial pressure. While the furnace heats the material, a hydraulic press applies a strong, directional force to the powder held within a die.
This mechanical force physically pushes the powder particles into intimate contact. This enhances the diffusion process and actively helps collapse the pores within the material.
Key Benefits of Hot Press Consolidation
The combination of heat and pressure offers significant advantages over processes that rely solely on heat.
Achieving Near-Theoretical Density
The primary goal of consolidation is to eliminate porosity. Hot pressing is exceptionally effective at this, often producing materials that are over 99.9% of their theoretical maximum density. This lack of voids directly translates to superior mechanical properties.
Lowering Processing Temperatures
Because pressure provides a powerful driving force for densification, less thermal energy is required. A material that might need 1600°C for conventional sintering could potentially be hot-pressed at 1300°C.
Inhibiting Grain Growth
In many advanced materials, smaller microscopic grains lead to better strength and fracture toughness. The lower temperatures and shorter times used in hot pressing help prevent grain growth, preserving a fine-grained microstructure and, therefore, superior performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Constraint on Shape and Size
The use of a die and a uniaxial press means that hot pressing is typically limited to producing simple geometric shapes, such as discs, pucks, or rectangular blocks. It is not suitable for manufacturing parts with complex internal features or curved surfaces.
Process Complexity and Cost
Hot press furnaces are more complex and expensive than conventional sintering furnaces. The requirement for robust dies, precision pressure control, and specialized furnace atmospheres adds to the operational cost and technical expertise needed.
Hot Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a related technology that applies pressure using a hot, inert gas from all directions simultaneously. HIP can consolidate complex shapes to full density but is generally an even more expensive and complex process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct consolidation method depends entirely on your end goal, balancing performance requirements with manufacturing constraints.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties for simple shapes: Hot pressing is the premier technology for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is producing parts with complex geometries on a budget: Conventional pressureless sintering is often the more practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving full density in a part with a complex shape: You should investigate Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) as the appropriate high-performance solution.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal processing technique is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts the final performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Press Furnace | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Key Process | Simultaneous high temperature and uniaxial pressure application | Heating below melting point for particle fusion |
| Density Achieved | Often over 99.9% of theoretical density | Lower density due to reliance on heat alone |
| Processing Temperature | Lower temperatures (e.g., 1300°C vs. 1600°C) | Higher temperatures required |
| Grain Growth | Inhibited, preserving fine microstructure | More prone to grain growth |
| Shape Limitations | Limited to simple shapes like discs or blocks | Can handle more complex geometries |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher due to pressure systems and dies | Lower cost and simpler operation |
Ready to enhance your material sintering with precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're consolidating powders or optimizing material properties, our hot press furnaces can help you achieve superior results with lower temperatures and faster processing times. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your research and development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density



















