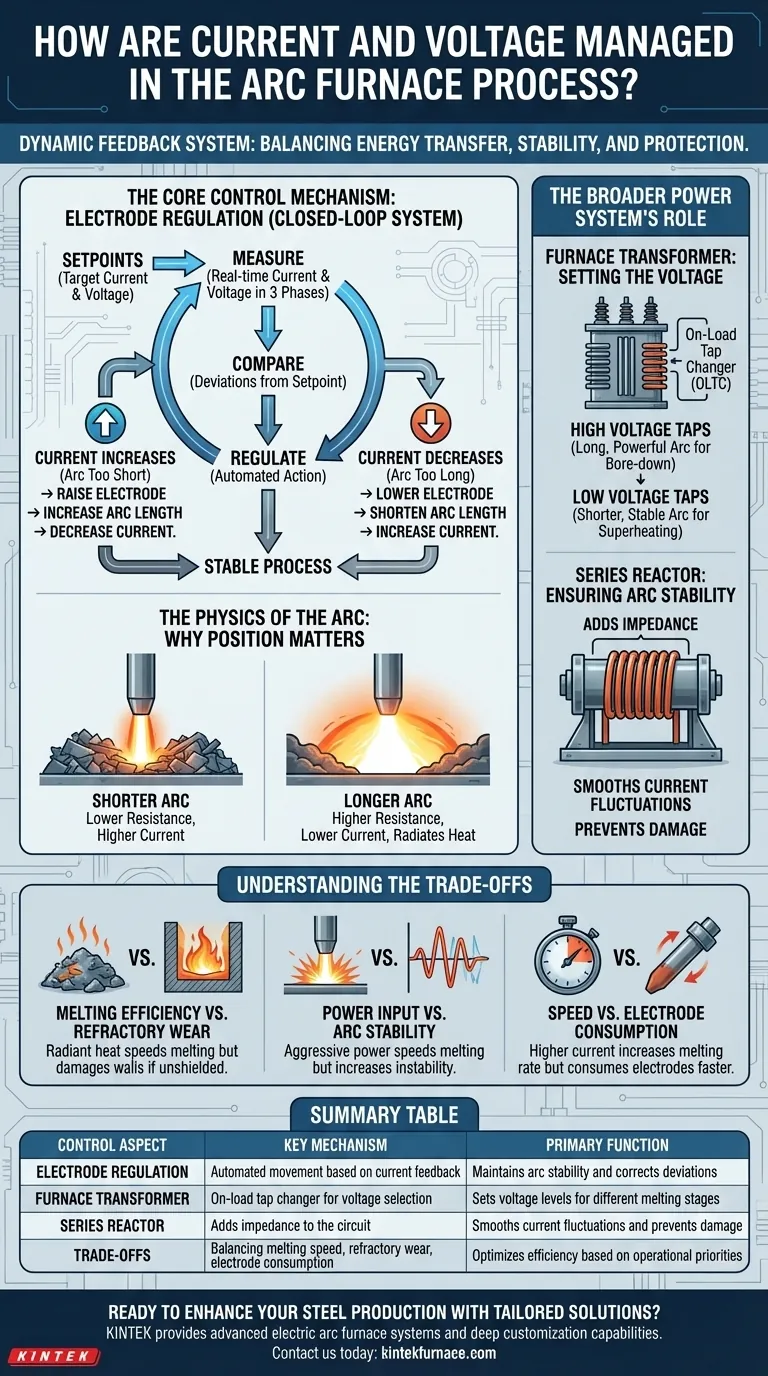
At its core, current and voltage in an electric arc furnace (EAF) are managed through a dynamic feedback system. The primary method is the precise physical movement of the graphite electrodes, which are automatically raised or lowered to maintain a target electrical current, combined with adjustments to the furnace transformer's voltage settings.
The challenge in EAF operation is not simply supplying power, but controlling it with precision. The management of current and voltage is a constant balancing act between maximizing energy transfer for efficient melting, maintaining arc stability, and protecting the furnace equipment from damage.
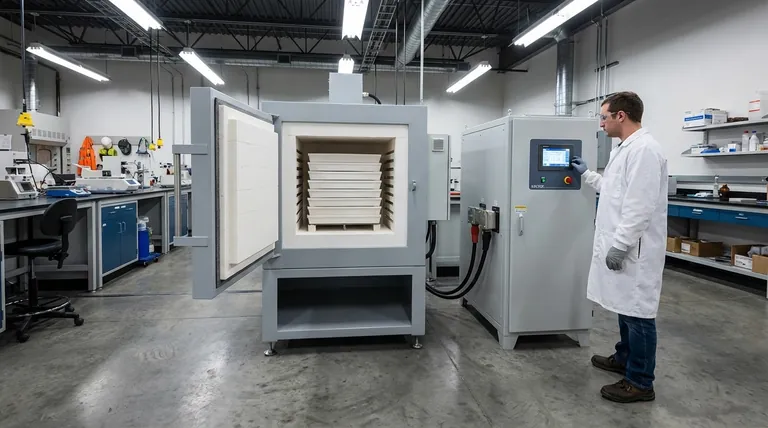

The Core Control Mechanism: Electrode Regulation
The heart of the EAF's power management is the electrode regulation system. This is an automated, closed-loop system that constantly works to keep the process stable and efficient.
Measuring and Comparing Setpoints
The system continuously measures the actual current and voltage in each of the three phases. These real-time values are compared against predetermined "setpoints" programmed by the furnace operators for the specific stage of the melt.
Electrode Movement as the Corrective Action
If the measured current deviates from the setpoint, the regulator takes immediate action. This action is the physical movement of the electrode mast.
If the current increases above the setpoint, it signifies that the arc length has become too short (lower resistance). The regulator raises the electrode to increase the arc length and bring the current back down.
Conversely, if the current decreases below the setpoint, the arc has become too long. The regulator lowers the electrode to shorten the gap and increase the current.
The Physics of the Arc: Why Position Matters
The distance between the electrode tip and the steel scrap (or molten bath) is the arc length. This distance directly governs the electrical characteristics of the arc.
A shorter arc has lower electrical resistance, which causes a higher current to flow for a given voltage.
A longer arc has higher resistance, which reduces the current. It also requires a higher voltage to be sustained and radiates more heat, which is useful for melting scrap from a distance.
The Broader Power System's Role
While electrode movement provides minute-to-minute control, the overall power profile is set by the main power supply components.
The Furnace Transformer: Setting the Voltage
The furnace transformer is the primary tool for managing voltage. It is equipped with an on-load tap changer (OLTC) that allows operators to select different voltage levels during the melting process.
Higher voltage taps are used to create a long, powerful arc for boring down into a pile of cold scrap. Lower voltage taps are used later in the process to create a shorter, more stable arc for heating the liquid bath.
The Series Reactor: Ensuring Arc Stability
A series reactor is essentially a large inductor placed in the circuit. Its purpose is to add impedance, which acts as a buffer or "shock absorber" for the electrical system.
This is critical during the initial bore-down phase when falling scrap can cause frequent short circuits. The reactor smooths out the wild current fluctuations, stabilizing the arc and preventing damage to the electrical supply system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Effective EAF control is about managing competing operational priorities. There is no single "perfect" setting.
Melting Efficiency vs. Refractory Wear
A long, radiant arc created by high voltage is very effective at transferring heat and melting scrap quickly. However, this same radiant energy can cause severe damage to the furnace's refractory-lined walls if it isn't shielded by scrap or a foamy slag.
Power Input vs. Arc Stability
During the initial meltdown, the process is inherently unstable. An aggressive, high-power program can speed up melting but may lead to more frequent arc extinctions or short circuits, which can reduce overall efficiency. A less aggressive program is more stable but slower.
Speed vs. Electrode Consumption
Operating at higher currents and power levels increases the rate of melting. However, it also increases the consumption of the expensive graphite electrodes through sublimation, adding to the operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The control strategy is adapted throughout the melt cycle based on the immediate goal.
- If your primary focus is the initial bore-down: Use a high voltage tap and a long arc program to radiate maximum energy into the cold scrap pile from above.
- If your primary focus is protecting the furnace walls: Use a shorter arc that is buried and shielded by a deep, foamy slag practice, which absorbs the radiant energy.
- If your primary focus is final superheating: Use a low voltage tap and a very short, stable arc to efficiently transfer energy directly into the molten steel bath with minimal radiation.
Ultimately, mastering the EAF process means using these electrical controls to manipulate the arc for the right purpose at the right time.
Summary Table:
| Control Aspect | Key Mechanism | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Regulation | Automated movement based on current feedback | Maintains arc stability and corrects deviations |
| Furnace Transformer | On-load tap changer for voltage selection | Sets voltage levels for different melting stages |
| Series Reactor | Adds impedance to the circuit | Smooths current fluctuations and prevents damage |
| Trade-offs | Balancing melting speed, refractory wear, and electrode consumption | Optimizes efficiency based on operational priorities |
Ready to enhance your steel production with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced electric arc furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental and production needs, boosting efficiency and reducing costs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















