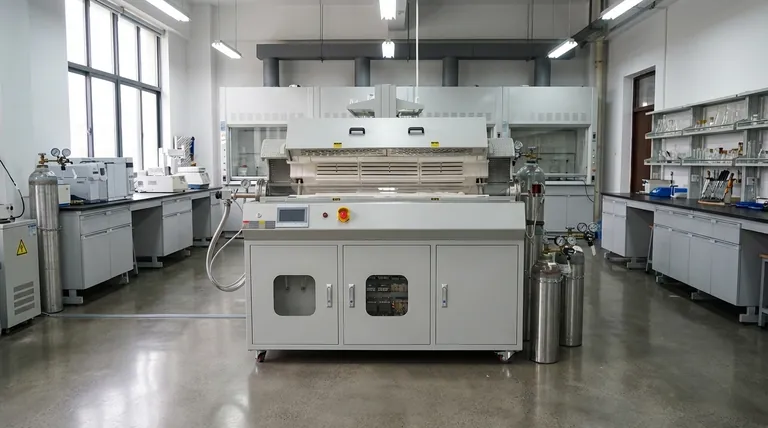
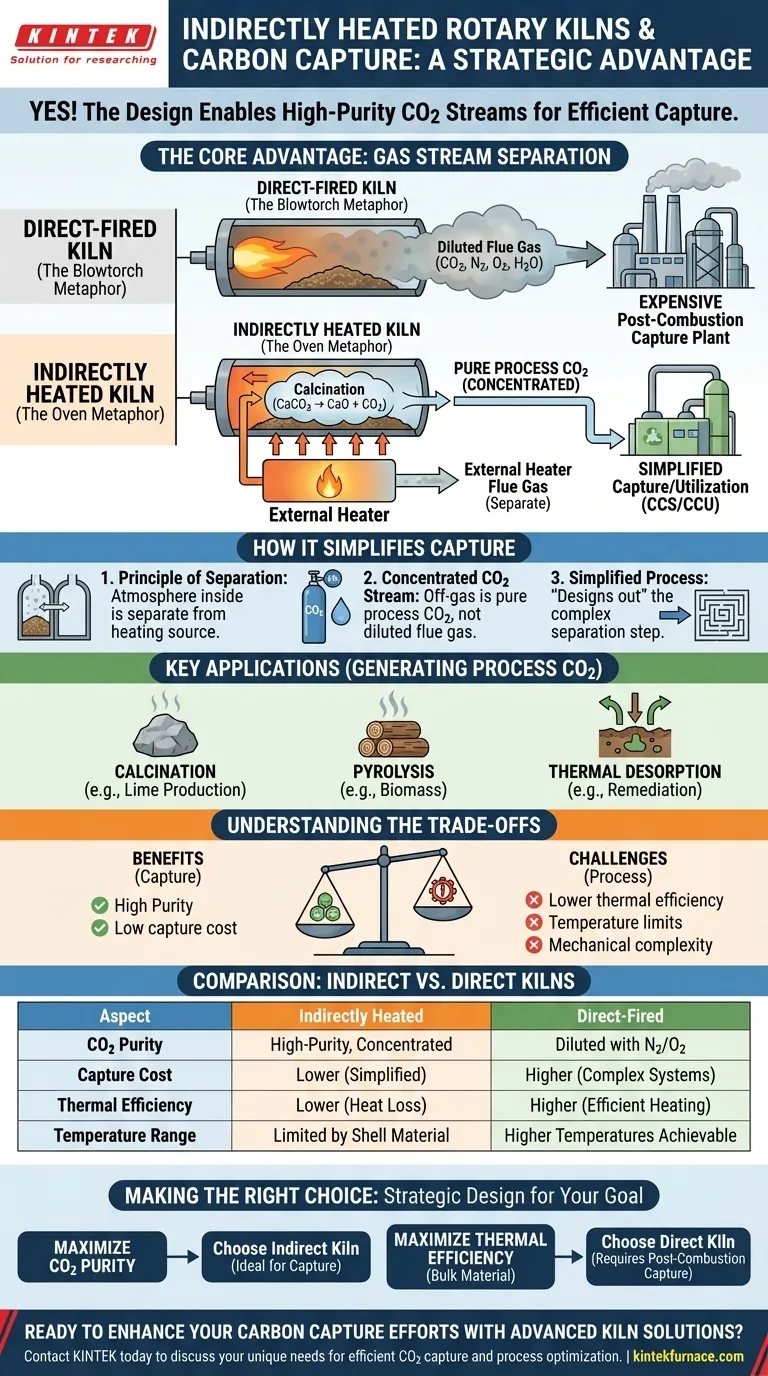
Yes, indirectly heated rotary kilns are exceptionally well-suited for carbon capture. Their fundamental design is what makes them so effective. Unlike direct-fired kilns where combustion gases mix with the material being processed, an indirect kiln heats the material from the outside. This keeps the CO2 released from the process (e.g., from calcination or pyrolysis) separate and undiluted, creating a concentrated stream that is significantly easier and cheaper to capture.
The core advantage is not that the kiln itself captures carbon, but that its design produces a high-purity stream of process CO2. This elegantly sidesteps the most expensive part of many carbon capture efforts: separating CO2 from the nitrogen and excess oxygen in typical flue gas.

How Indirect Kilns Enable Carbon Capture
To understand their value, you must first grasp the fundamental difference in how direct and indirect kilns operate. This distinction is the key to their role in decarbonization.
The Principle of Gas Stream Separation
A direct-fired kiln works like a massive blowtorch, with the flame and hot combustion gases flowing directly over and through the material. This is very efficient for heat transfer, but it mixes the process off-gas with the products of combustion (CO2, water vapor, and, most importantly, large volumes of nitrogen from the air).
An indirectly heated rotary kiln, by contrast, functions more like an oven. The rotating shell is heated externally, and that heat transfers through the metal wall to the material tumbling inside. The atmosphere inside the kiln is completely separate from the heating source.
Producing a Concentrated CO2 Stream
This separation is critical. When a process like calcination occurs inside an indirect kiln (e.g., heating limestone, CaCO₃), the reaction releases CO₂.
Because no combustion gas enters the kiln's interior, the resulting off-gas is almost pure process CO₂, not a diluted flue gas. This high-purity stream can be piped directly to a compression, utilization, or sequestration unit.
Simplifying the Entire Capture Process
In a conventional setup with a direct-fired kiln, carbon capture requires a large, expensive "post-combustion" chemical absorption plant to isolate the CO₂ from the massive volume of nitrogen.
By using an indirect kiln, you essentially design the separation problem out of the system from the start. This makes the overall carbon capture and storage (CCS) or utilization (CCU) process vastly simpler and more economically viable.
Key Applications That Generate Process CO2
Indirect kilns are deployed in various industries where capturing process emissions is a primary goal. Their precise temperature control makes them ideal for these applications.
Calcination of Minerals
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process. It's used to produce lime from limestone (CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂) and in other mineral processing steps that release CO₂ as a direct result of a chemical change, not from burning fuel.
Pyrolysis and Carbonization
When heating organic materials like biomass, waste wood, or sewage sludge in the absence of oxygen (pyrolysis), an indirect kiln drives off volatile compounds. The resulting gas stream is often rich in CO₂ and other hydrocarbons, which can be captured or refined.
Thermal Desorption and Remediation
Indirect kilns are used to clean contaminated soil or industrial waste. Heating the material drives off pollutants for collection and treatment. The controlled atmosphere prevents unwanted combustion and simplifies the management of the off-gas stream, allowing for CO₂ capture if carbonaceous materials are present.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ideal for carbon capture, indirect kilns are not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding their limitations.
Thermal Efficiency
Because heat must be conducted through the heavy steel shell of the kiln, indirect heating is generally less thermally efficient than direct heating. More energy can be lost to the surrounding environment, potentially increasing fuel consumption for the external burners.
Temperature Limitations
The maximum achievable temperature inside an indirect kiln is limited by the material science of the kiln shell itself. High-performance alloys are required for high-temperature applications, which increases cost. Direct-fired kilns can often achieve higher process temperatures more easily.
Mechanical Complexity and Scale
The design of an indirect kiln, with its sealed atmosphere and external heating jacket, is more complex than a simple direct-fired tube. Ensuring a perfect seal to prevent air leakage—which would dilute the CO₂ stream—is a critical and ongoing maintenance consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right kiln technology depends entirely on your primary objective, as the optimal choice involves balancing efficiency, cost, and decarbonization impact.
- If your primary focus is maximizing CO2 purity for capture: An indirectly heated kiln is the superior choice because it inherently produces a concentrated CO2 stream, dramatically reducing downstream separation costs.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency for a bulk material: A direct-fired kiln may be more economical, provided you are prepared to invest in a separate, large-scale post-combustion capture system to handle the diluted flue gas.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive materials: An indirect kiln offers gentle, uniform heating without flame impingement, making it the ideal solution for quality control, with the benefit of being capture-ready.
Ultimately, leveraging an indirectly heated rotary kiln is a strategic design choice that proactively engineers a solution for carbon capture right at the source.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Indirectly Heated Kilns | Direct-Fired Kilns |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Purity | High-purity, concentrated stream | Diluted with nitrogen and oxygen |
| Capture Cost | Lower due to simplified separation | Higher, requires post-combustion systems |
| Applications | Calcination, pyrolysis, thermal desorption | Bulk material processing |
| Thermal Efficiency | Lower, more heat loss | Higher, more efficient heating |
| Temperature Range | Limited by shell materials | Can achieve higher temperatures |
Ready to enhance your carbon capture efforts with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve efficient CO2 capture and process optimization. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your laboratory or industrial process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















