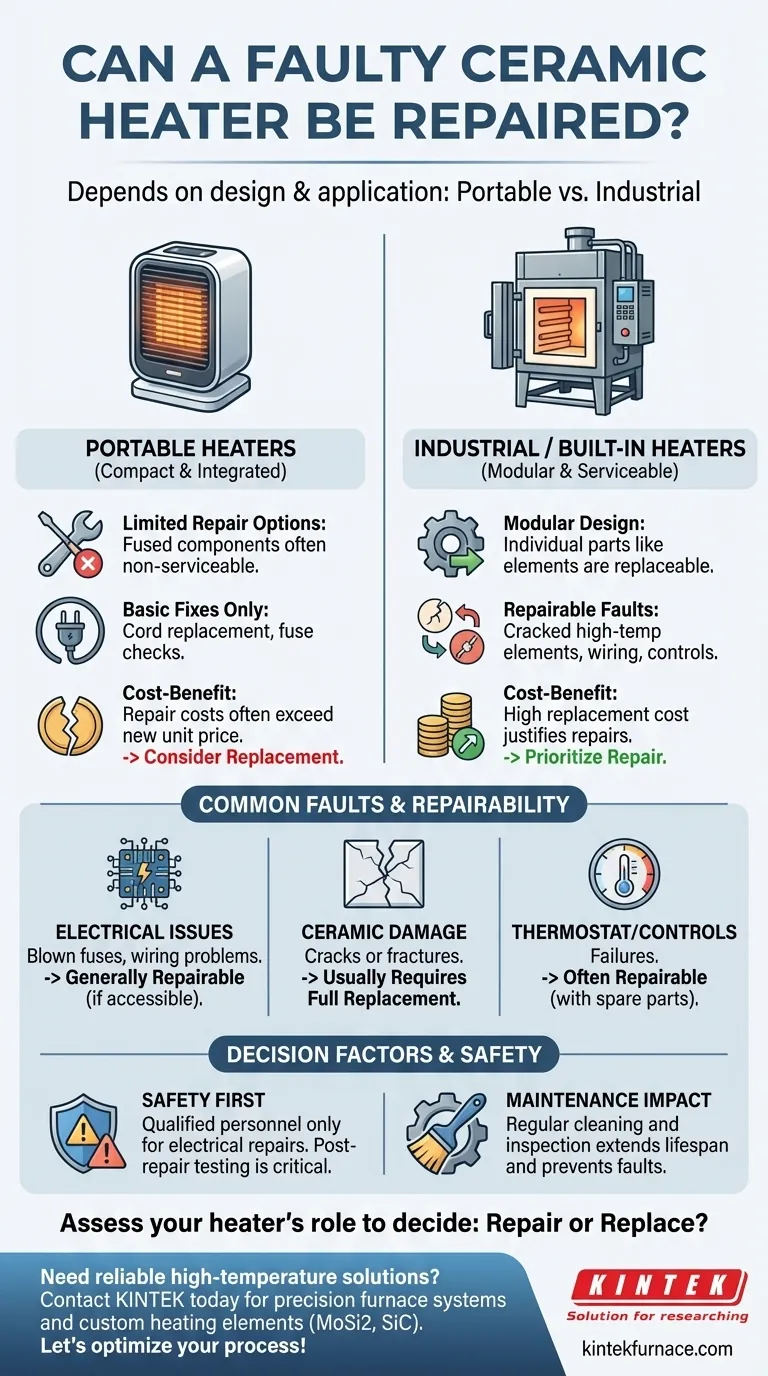
The repairability of a faulty ceramic heater depends largely on its design and application. Portable ceramic heaters often have limited repair options due to their compact, integrated construction, while larger industrial or built-in units with replaceable high temperature heating elements can typically be serviced. Factors like heater type, damage severity, and availability of replacement parts determine whether repair is feasible or cost-effective compared to replacement.

Key Points Explained:
-
Portable vs. Built-In Heaters
- Portable models: Often designed as single units with non-serviceable components. Repair options are limited to basic fixes like cord replacement or fuse checks.
- Built-in/industrial heaters: Feature modular designs where ceramic heating elements or other parts can be individually replaced. For example, a cracked high temperature heating element in a kiln can often be swapped out.
-
Common Faults and Repairability
- Electrical issues: Blown fuses or wiring problems are generally repairable if accessible.
- Ceramic element damage: Cracks or fractures in the ceramic component may require full replacement, especially in portable units where the element is fused to the housing.
- Thermostat/control failures: Often repairable if replacement parts are available.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- For inexpensive portable heaters, repair costs may exceed the price of a new unit.
- Industrial heaters (e.g., those in rotary kilns or furnaces) justify repairs due to higher replacement costs and downtime implications.
-
Safety Considerations
- DIY repairs on electrical components should only be attempted by qualified personnel to avoid hazards like short circuits or improper insulation.
- Post-repair testing is critical to ensure the heater operates within safe temperature ranges.
-
Maintenance Impact
- Regular cleaning of ceramic elements and vents can prevent faults caused by dust buildup or overheating.
- Proactive inspection of wiring and connections extends lifespan, as noted in the reference about alumina ceramic furnace tubes.
-
When to Replace
- Irreparable physical damage to the ceramic core or housing.
- Obsolete models with unavailable parts.
Have you assessed whether your heater’s fault aligns with repairable categories? Understanding the heater’s role—whether it’s warming a small room or enabling industrial processes—helps prioritize repair or replacement decisions.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Repairability |
|---|---|
| Portable Heaters | Limited; often non-serviceable (e.g., fused ceramic elements). |
| Industrial Heaters | Modular; replaceable parts (e.g., heating elements, wiring). |
| Electrical Issues | Repairable if accessible (e.g., fuses, wiring). |
| Ceramic Damage | Usually requires full replacement (cracks/fractures). |
| Cost vs. Replacement | Portable: Often cheaper to replace. Industrial: Repair preferred for cost/downtime. |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab or industrial process? Contact KINTEK today! Our expertise in high-temperature furnace systems—including custom heating elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC)—ensures precision, durability, and tailored performance for your unique requirements. Let’s optimize your thermal processes together!
Products You Might Be Looking For:
Explore durable heating elements for electric furnaces Upgrade to high-performance SiC heating elements Shop vacuum-compatible observation windows Discover precision vacuum feedthroughs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















