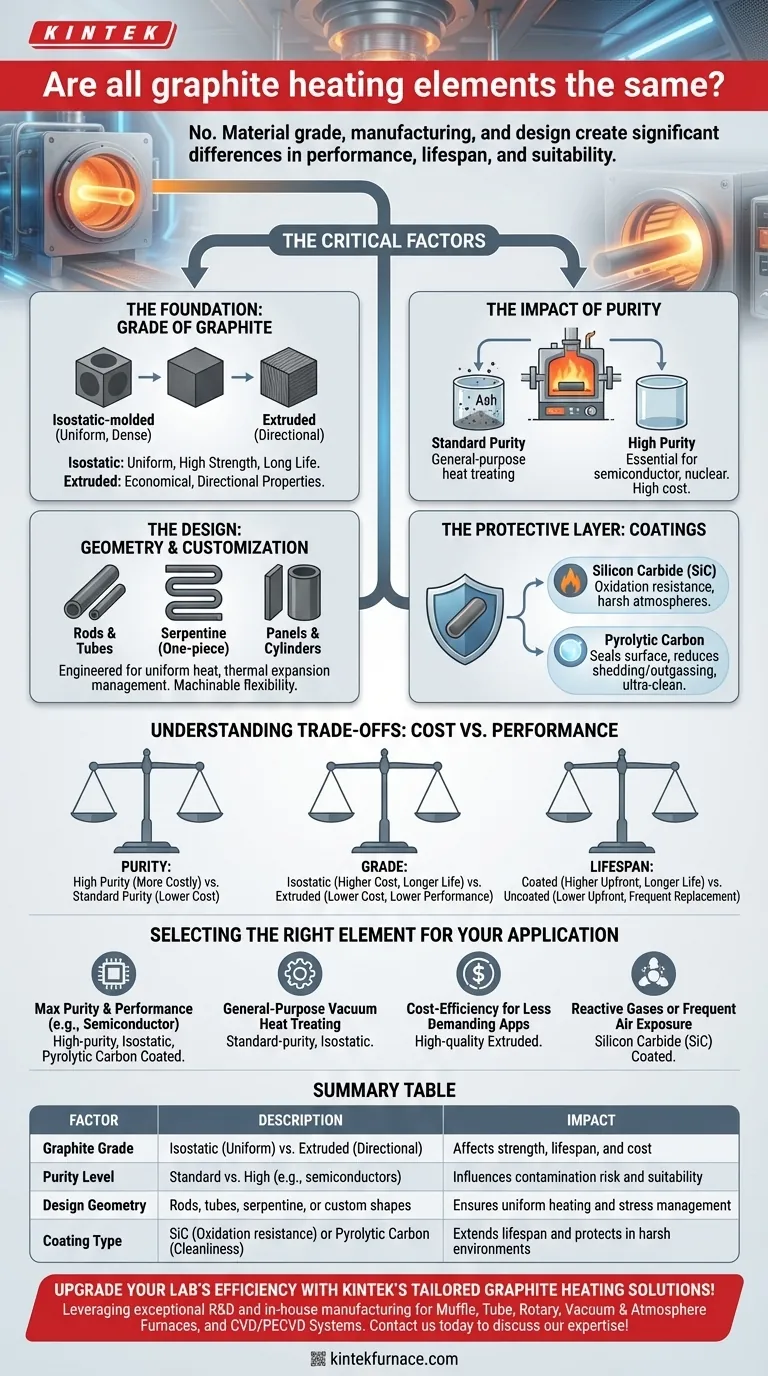
No, not all graphite heating elements are the same. While they are all made from graphite, the specific grade of the material, its manufacturing process, and its final design create significant differences in performance, lifespan, and application suitability. These distinctions are critical for ensuring efficiency and reliability in high-temperature environments like vacuum furnaces.
The selection of a graphite heating element is not about a generic component, but about a precise engineering choice. The right element must match the material's properties—such as purity and density—and its physical design to the specific temperature, atmosphere, and process requirements of your application.

The Critical Factors That Differentiate Graphite Elements
Understanding what makes one graphite element different from another comes down to a few key variables in its material science and physical construction. These factors directly impact electrical resistivity, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance.
The Foundation: Grade of Graphite
The base material itself is the first point of differentiation. Graphite is generally categorized into two primary grades for this purpose.
Isostatically-molded graphite is created by pressing graphite powder uniformly from all directions. This results in a highly consistent, dense material with uniform properties, excellent strength, and a long service life, making it ideal for the most demanding applications.
Extruded graphite is formed by pushing a graphite paste through a die. This process is more economical but results in a material with directional grain properties, meaning its strength and electrical conductivity can vary depending on the orientation.
The Impact of Purity
Graphite for heating elements undergoes a high-temperature purification process to remove impurities like ash. The level of purity is a critical specification.
Standard purity grades are suitable for many general-purpose heat treating and sintering applications.
High-purity grades are essential for industries like semiconductor manufacturing or nuclear applications, where even trace contaminants from the heating element could ruin the product or process.
The Design: Geometry and Customization
As a machinable material, graphite offers immense design flexibility. Elements can be crafted into a wide variety of shapes to optimize performance for a specific furnace hot zone.
Common designs include simple rods or tubes, complex serpentine (one-piece) elements, and multi-part panel or cylinder arrangements. The geometry is engineered to ensure uniform heat distribution and accommodate thermal expansion without causing mechanical stress.
The Protective Layer: Coatings
To enhance performance and lifespan, graphite elements can be coated with other materials. This is especially important for protecting against oxidation and chemical attack.
A Silicon Carbide (SiC) coating is a common choice that dramatically increases the element's resistance to oxidation, allowing it to operate in less-than-perfect vacuums or atmospheres containing reactive gases.
A Pyrolytic Carbon coating can also be applied to seal the graphite's surface porosity. This reduces particle shedding and outgassing, which is critical for ultra-clean environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
Choosing the right heating element involves balancing your technical requirements with your budget. The ideal choice for one application may be unnecessarily expensive or perform poorly in another.
Purity Comes at a Price
The intensive furnace process required to achieve high and ultra-high purity levels adds significant cost. An element for semiconductor processing can be substantially more expensive than one used for general metal heat treating.
Isostatic vs. Extruded Graphite
Isostatic graphite offers superior performance, uniformity, and a longer lifespan, but it comes at a higher initial cost. For less critical applications or those with tighter budgets, extruded graphite can provide an effective and economical solution if its directional properties are accounted for in the design.
The Lifespan Dilemma: Coated vs. Uncoated
Coated elements offer a clear advantage in longevity, especially in environments where perfect vacuum is not always maintained. However, this added protection comes with an increased upfront cost. Uncoated elements are simpler and less expensive but may require more frequent replacement if subjected to oxidizing conditions.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by the specific demands of your process. There is no single "best" element, only the one that is best suited for your goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance (e.g., semiconductor processing): You require a high-purity, isostatically-molded graphite element, often with a pyrolytic carbon coating to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating in a vacuum: A standard-purity, isostatically-molded element provides an excellent balance of long life and reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a less demanding application: A high-quality extruded graphite element can offer the most economical solution without a significant compromise in function.
- If your process involves reactive gases or frequent air exposure: A Silicon Carbide (SiC) coated element is not optional; it is essential for preventing rapid degradation and ensuring an acceptable service life.
Understanding these distinctions transforms the selection process from a simple purchase into a strategic engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite Grade | Isostatic (uniform) vs. Extruded (directional) | Affects strength, lifespan, and cost |
| Purity Level | Standard vs. High (e.g., for semiconductors) | Influences contamination risk and suitability |
| Design Geometry | Rods, tubes, serpentine, or custom shapes | Ensures uniform heating and stress management |
| Coating Type | SiC (oxidation resistance) or Pyrolytic Carbon (cleanliness) | Extends lifespan and protects in harsh environments |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's tailored graphite heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise matching to your unique experimental needs, whether for semiconductor processing or general heat treating. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your application's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability



















