In short, the drying step is necessary to gently and controllably remove the solvent from the sample. This process is foundational to the entire analysis because it prevents the sample from spattering, which would lead to a catastrophic loss of precision and accuracy in your results.
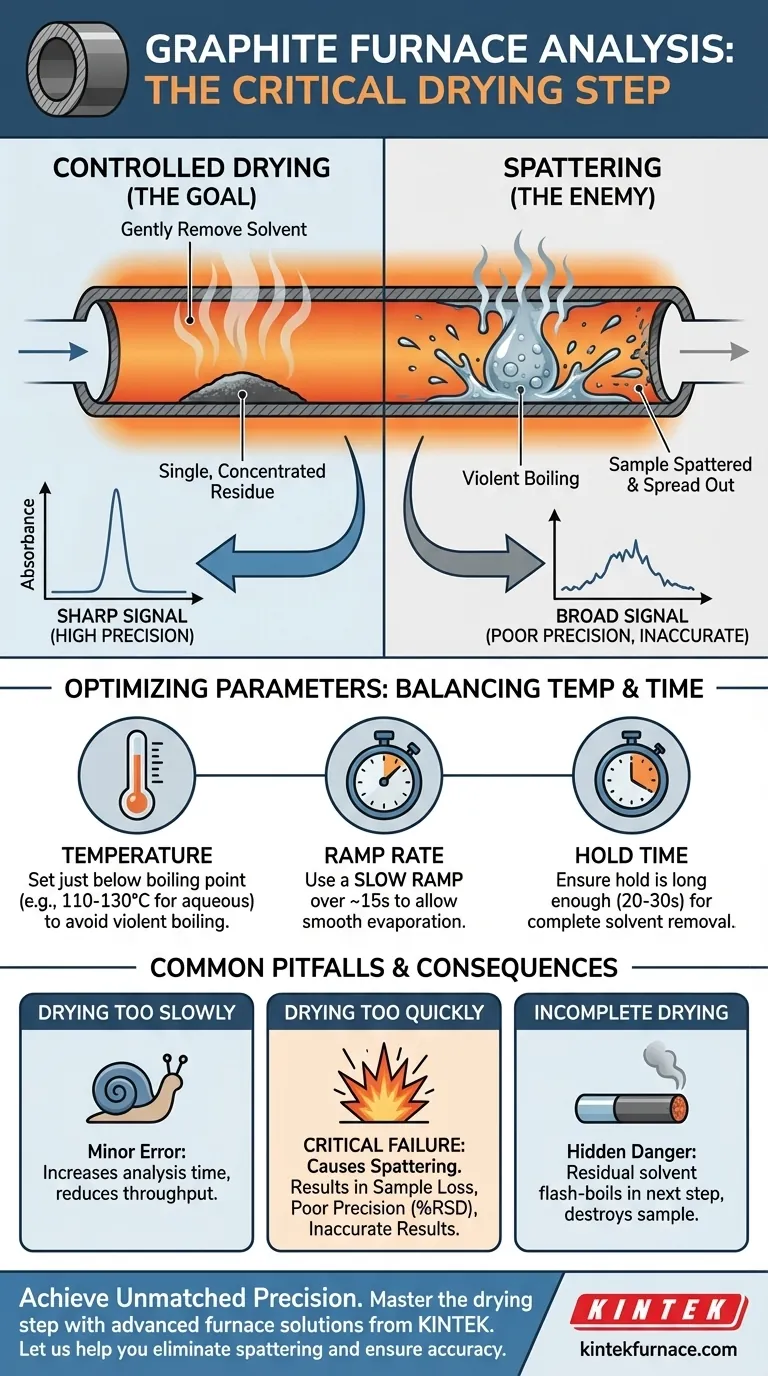
The core purpose of the drying step is not simply to dry the sample, but to do so in a way that leaves a single, concentrated, and undisturbed residue in the center of the graphite tube. This control is the prerequisite for reproducible and accurate atomization in the subsequent high-temperature steps.

The Goal: A Perfect Foundation for Atomization
The entire graphite furnace temperature program is a sequence designed to prepare your analyte for a single, explosive moment of measurement. The drying step is the critical first phase of this preparation.
From Liquid Droplet to Solid Residue
When you inject your sample, it is a small liquid droplet, typically 5 to 20 microliters. This droplet contains your analyte of interest dissolved or suspended in a solvent (like water or a weak acid).
The drying step's job is to apply gentle heat to evaporate this solvent, leaving behind only the solid components of the sample—the analyte and any matrix materials—as a tiny, solid crust.
The Enemy of Precision: Spattering
The temperature must be managed carefully. If it is raised too quickly or set too high (above the solvent's boiling point), the solvent will boil violently.
This boiling creates vapor bubbles that burst, splattering the sample across the inner surface of the graphite tube. Instead of one concentrated spot, your analyte is now spread out in an uncontrolled, non-uniform pattern.
How Spattering Destroys Your Signal
A graphite tube is not heated perfectly evenly during the final, high-temperature atomization step. The center is typically the hottest point.
If your sample is properly concentrated in the center, it all atomizes (turns into a gas of free atoms) at the same moment, producing a sharp, tall, and narrow absorbance peak. This is a good signal.
If the sample has spattered, different parts of the analyte will be in cooler regions of the tube. They will atomize later and less efficiently, resulting in a broad, short, and noisy peak. This signal is difficult to measure accurately and will not be reproducible from one injection to the next.
Understanding the Program Parameters
Optimizing the drying step involves balancing two key parameters: temperature and time.
Setting the Right Temperature
The ideal drying temperature is just below the boiling point of your solvent. This allows for rapid evaporation without causing the vigorous boiling that leads to spattering.
For aqueous samples (boiling point 100°C), a final drying temperature between 110°C and 130°C is common. This slight elevation helps drive off the final bound water molecules without causing explosive boiling.
The Importance of Ramp and Hold Times
The temperature is not instantly jumped to the final value. It is "ramped" up over a period of seconds.
A slow ramp rate is gentle and gives the solvent time to evaporate smoothly from the surface. A fast ramp can cause the sample to boil and spatter, even if the final temperature is set correctly.
The hold time is the duration the furnace stays at the final drying temperature. It must be long enough to ensure all solvent is gone before the program advances to the next stage.
Common Pitfalls and Consequences
Mishandling the drying step is one of the most common sources of error in GFAAS analysis.
The Cost of Drying Too Slowly
Setting the temperature too low or the ramp rate too slow is a minor error. It will not harm your analytical result, but it will significantly increase the time for each analysis, reducing sample throughput.
The Catastrophe of Drying Too Quickly
This is the most critical failure mode. A temperature or ramp rate that is too high will cause spattering. This directly leads to:
- Sample Loss: Part of your analyte is physically lost or spread out.
- Poor Precision: Your results will have a high percent relative standard deviation (%RSD) because the amount of sample atomized effectively will vary randomly with each run.
- Inaccurate Results: Your final calculated concentrations will be artificially low and unreliable.
The Hidden Danger of Incomplete Drying
If the hold time is too short, some solvent may remain when the program moves to the next high-temperature step (pyrolysis or charring). This residual solvent will then flash-boil explosively, completely destroying the sample and invalidating the measurement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Method
Use these guidelines to set the drying step based on your analytical goals and observations.
- If you are analyzing standard aqueous samples: Begin with a ramp to 120°C over 15 seconds and a hold time of 20-30 seconds as a robust starting point.
- If you observe poor precision (high %RSD): Your sample is almost certainly spattering. Slow down your temperature ramp, reduce the final drying temperature by 10°C, or both.
- If you are using a new matrix or organic solvent: Research the boiling point of that solvent and set your final drying temperature approximately 10-20°C below it.
- If you suspect incomplete drying: Watch the analysis through the injection hole with safety glasses. If you see a plume of vapor during the pyrolysis step, your drying hold time is too short.
Mastering the drying step is the first and most critical foundation for achieving precise and reliable graphite furnace results.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Purpose | Typical Setting (Aqueous Sample) |
|---|---|---|
| Final Temperature | Evaporate solvent gently, below boiling point | 110°C - 130°C |
| Ramp Rate | Control heating speed to prevent violent boiling | Slow ramp over ~15 seconds |
| Hold Time | Ensure complete solvent removal | 20-30 seconds |
| Key Risk | Spattering from rapid heating, leading to poor precision and inaccurate results | - |
Achieve Unmatched Precision in Your Graphite Furnace Analysis
Mastering the drying step is just the beginning. Consistent, reliable results depend on equipment that provides exceptional temperature control and uniformity.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let us help you eliminate spattering and achieve the accuracy your research demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your analytical capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















