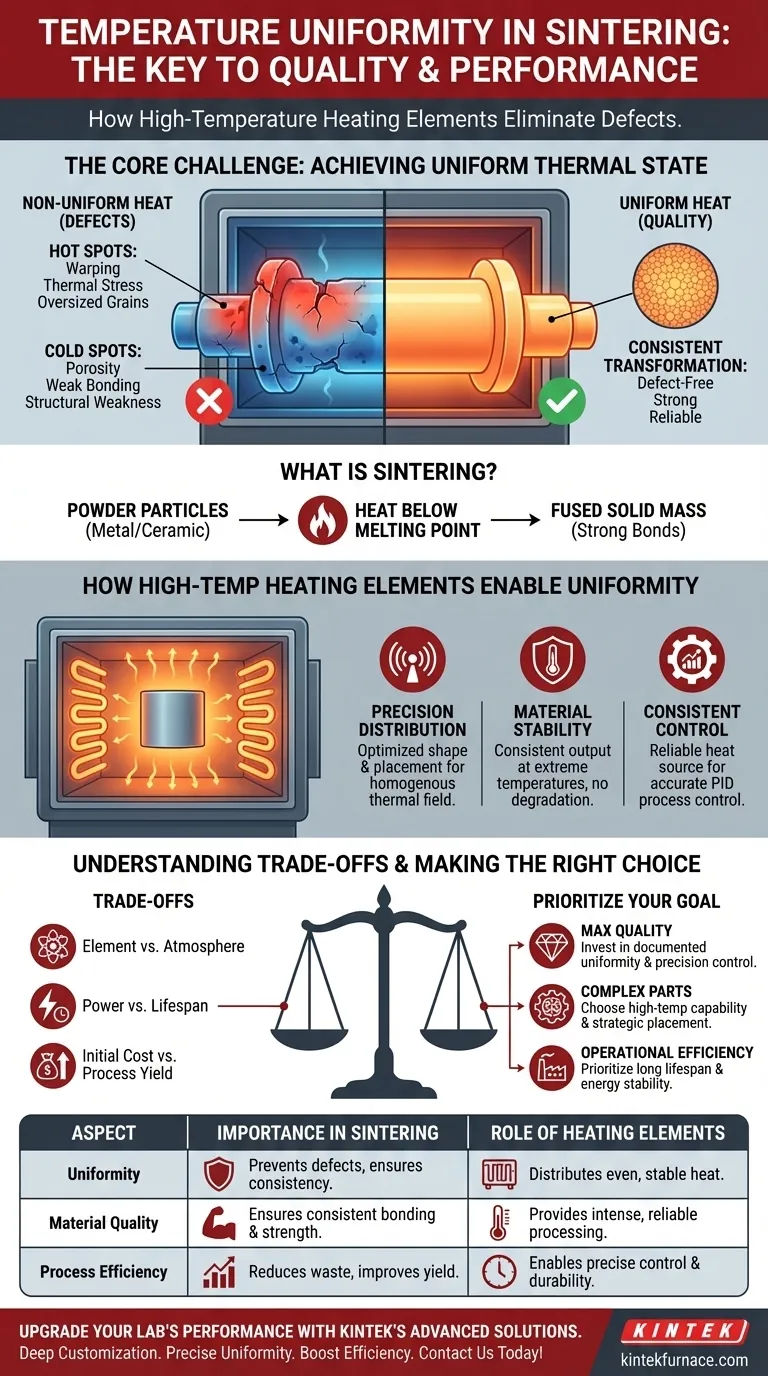
In short, temperature uniformity is critical in processes like sintering because it ensures every part of a material is transformed consistently, preventing structural defects that compromise quality and performance. High-temperature heating elements are the enabling technology, designed specifically to deliver the even, stable, and intense heat required to eliminate these destructive hot and cold spots.
The core challenge in high-temperature processing is not just reaching a target temperature, but achieving a uniform thermal state across the entire workpiece. Without this uniformity, you are manufacturing internal inconsistencies and weaknesses, leading directly to product failure and process inefficiency.

The Critical Role of Temperature Uniformity
To grasp why uniformity is non-negotiable, we must first understand the process it serves and the specific consequences of failure.
What is Sintering? A Quick Primer
Sintering is a thermal process for fusing particles of a material, such as a metal or ceramic powder, into a solid, coherent mass. This is achieved by applying heat below the material's melting point, causing the particles to bond at their contact points.
The Consequence of Hot Spots
If certain areas of the component become hotter than others, it can lead to thermal stress, warping, or excessive grain growth. These oversized grains create weak points in the material's microstructure, severely compromising its mechanical strength and integrity.
The Danger of Cold Spots
Conversely, areas that fail to reach the target sintering temperature will remain under-processed. These cold spots result in porous, poorly bonded regions that lack density and strength, effectively creating a structural defect from the inside out.
Beyond Sintering
This principle extends far beyond sintering. In semiconductor manufacturing, uniformity is essential for creating flawless wafers. In heat treatment, it ensures that a metal part achieves the desired hardness and durability consistently across its entire geometry.
How High-Temperature Heating Elements Enable Uniformity
High-temperature heating elements are not simply "heaters." They are precision-engineered components designed to solve the problem of thermal inconsistency.
Precision Heat Distribution
These elements are designed to radiate heat evenly throughout a furnace chamber. Their shape, placement, and material composition are all optimized to create a homogenous thermal field, eliminating the hot and cold spots that cause defects.
Material Stability at Extreme Temperatures
A key attribute of high-performance heating elements is their durability and stability at operating temperature. They maintain a consistent electrical resistance and do not degrade, ensuring that the heat output remains predictable and stable over countless process cycles.
Consistent Process Control
By providing reliable and even heating, these elements allow process control systems (like PID controllers) to work effectively. The system can accurately maintain the setpoint temperature across the entire chamber because the heat source itself is uniform and predictable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity involves balancing several engineering and economic factors. It is not as simple as installing the most powerful element.
Element Material vs. Atmosphere
The material of the heating element (e.g., Molybdenum Disilicide, Silicon Carbide) must be compatible with the furnace atmosphere. Using an element in the wrong atmosphere (e.g., an air-rated element in a vacuum) can lead to rapid oxidation and premature failure.
Power Density vs. Element Lifespan
Elements driven at their maximum power output will generate more heat but will also have a shorter operational lifespan. Designing a system involves a trade-off between throughput and the recurring cost of element replacement.
Initial Cost vs. Process Yield
Superior heating elements and furnace designs that provide exceptional uniformity come with a higher initial investment. This cost must be weighed against the long-term savings from reduced product rejection rates, improved quality, and higher process efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which factors to prioritize when designing or selecting a high-temperature system.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product quality: Invest in systems with documented thermal uniformity and pair them with high-precision control instrumentation.
- If your primary focus is processing complex or sensitive materials: Choose elements capable of reaching well above your target temperature and a furnace design that allows for strategic element placement to heat intricate geometries.
- If your primary focus is optimizing operational efficiency: Prioritize elements known for their long lifespan, energy efficiency, and stability to minimize downtime and replacement costs.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamentals of thermal uniformity transforms your approach from reactive problem-solving to proactive process control.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Importance in Sintering | Role of Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Uniformity | Prevents thermal stress, warping, and weak spots | Distributes heat evenly to eliminate hot/cold spots |
| Material Quality | Ensures consistent bonding and strength | Provides stable, intense heat for reliable processing |
| Process Efficiency | Reduces defects and improves yield | Enables precise control and long-term durability |
Upgrade your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Ensure precise temperature uniformity and boost your process efficiency—contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















