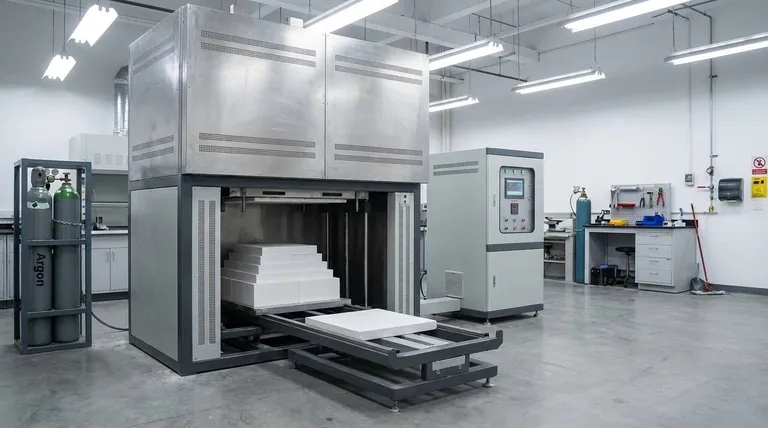
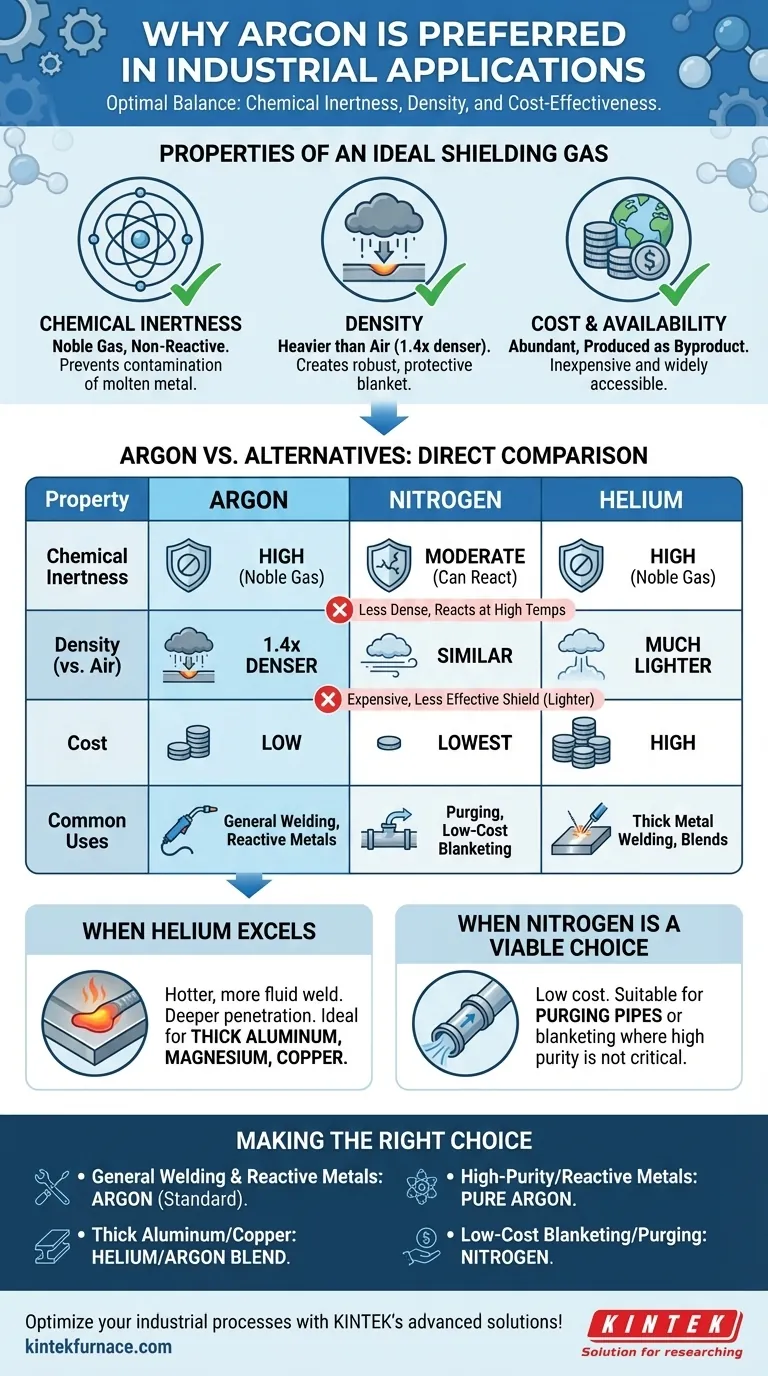
At its core, the preference for argon in many industrial applications stems from its optimal balance of three key factors: chemical inertness, density, and cost-effectiveness. While other gases may excel in one of these areas, argon provides the most versatile and reliable performance for common processes like welding and metal fabrication without the significant drawbacks of its alternatives.
The central decision in choosing an industrial gas is not about finding a "perfect" gas, but about selecting the one that offers the right properties for a specific process at an acceptable cost. Argon consistently hits this sweet spot for a wide range of critical applications.

The Properties of an Ideal Shielding Gas
To understand why argon is so widely used, we must first define what makes an industrial gas effective, particularly in its role as a shielding gas in welding and manufacturing.
Chemical Inertness: Preventing Contamination
The primary function of a shielding gas is to protect a process, like a molten weld pool, from atmospheric gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor.
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it has a full outer shell of electrons. This makes it extremely non-reactive, ensuring it will not chemically combine with the molten metal and introduce defects.
Density: Creating a Protective Blanket
An effective shielding gas must be able to physically displace the surrounding air.
Argon is approximately 1.4 times denser than air and nitrogen. This superior density allows it to form a stable, heavy "blanket" over the work area, providing more robust protection with lower gas flow rates compared to lighter alternatives.
Cost and Availability: The Practical Constraint
Performance means little if the material is prohibitively expensive or difficult to obtain.
Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere. It is commercially produced as a byproduct of cryogenic air separation (the same process that produces liquid oxygen and nitrogen), making it relatively inexpensive and widely available.
Argon vs. The Alternatives: A Direct Comparison
While other inert gases exist, they each have characteristics that make them less suitable than argon for general-purpose applications.
Why Not Nitrogen?
Nitrogen is very abundant and the cheapest inert gas available. However, it has two key limitations.
First, it is less dense than argon, making it a less effective shield. More gas is required to displace the air, which can offset some of its cost advantage.
Second, while largely inert, nitrogen can react with certain metals at high temperatures (like those in a welding arc) to form brittle compounds called nitrides, compromising the integrity of the material.
Why Not Helium?
Helium is also a noble gas and is completely inert. Its primary drawbacks are cost and physical properties.
Helium is significantly more expensive and less available than argon, as it is extracted from natural gas deposits rather than the atmosphere.
It is also extremely light—much less dense than air. This means it rises quickly and provides a less effective shield, requiring much higher flow rates to achieve the same coverage as argon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single gas is the universal best choice. The selection always depends on the specific material, process, and desired outcome. Understanding the limitations of argon is key to making an informed decision.
When Helium Excels
While argon is excellent for general use, helium's physical properties give it an advantage in specific welding scenarios.
Helium produces a hotter, more fluid weld puddle with deeper penetration. This is highly desirable when welding thick sections of conductive metals like aluminum, magnesium, or copper. For these applications, a blend of argon and helium is often used to balance arc stability and heat input.
When Nitrogen is a Viable Choice
Despite its potential for reactivity, nitrogen's low cost makes it suitable for specific uses.
It is often used for purging pipes and as a blanketing gas in applications where high purity is not the primary concern. In some cases, it is intentionally added in small amounts to argon when welding certain stainless steels to improve mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your choice of gas must be driven by your specific technical requirements and budget.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose welding of steel and non-reactive metals: Argon is the industry standard due to its excellent shielding, stable arc, and low cost.
- If your primary focus is welding thick aluminum or copper: A helium/argon mixture is superior for achieving the necessary heat input and weld penetration.
- If your primary focus is high-purity manufacturing or welding reactive metals like titanium: Pure argon is non-negotiable to prevent any form of contamination.
- If your primary focus is low-cost blanketing or purging where slight reactivity is acceptable: Nitrogen offers the most economical solution.
Choosing the right gas is a critical process variable that directly impacts the quality, efficiency, and cost of your work.
Summary Table:
| Property | Argon | Nitrogen | Helium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | High (noble gas) | Moderate (can react) | High (noble gas) |
| Density (vs. Air) | 1.4x denser | Similar | Much lighter |
| Cost | Low | Lowest | High |
| Common Uses | General welding, reactive metals | Purging, low-cost blanketing | Thick metal welding, blends |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs—contact us today to enhance efficiency and quality in your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















