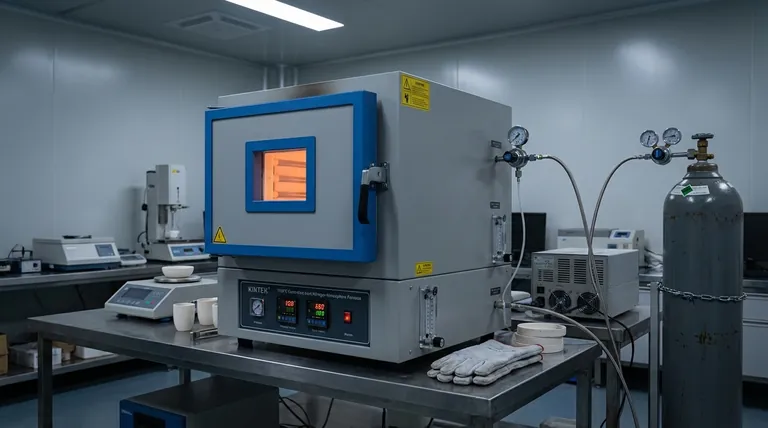
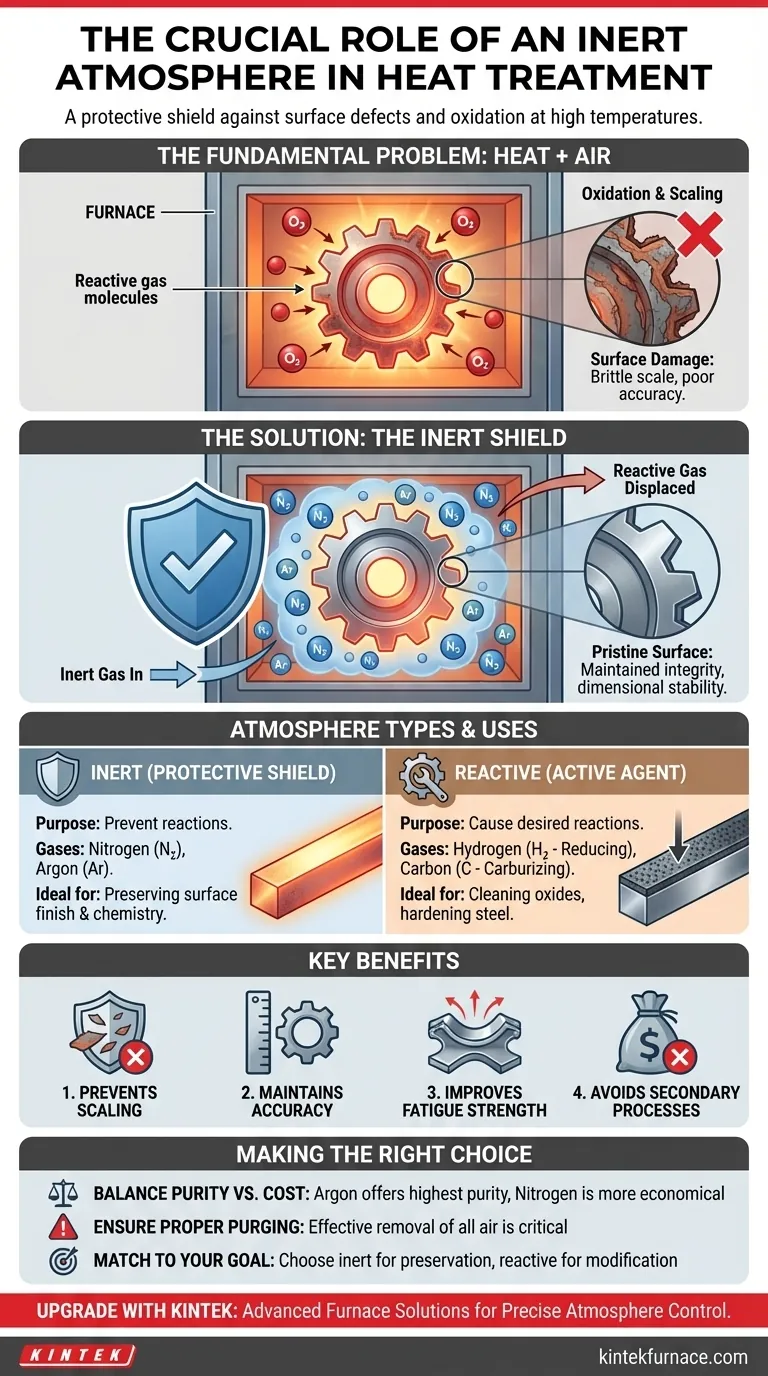
In heat treatment, an inert atmosphere is critical for protecting a material's integrity at high temperatures. It functions as a protective shield, displacing the reactive gases in the air—primarily oxygen—that would otherwise chemically attack the hot surface of the metal, leading to defects and component failure.
The core challenge of heat treatment is that high temperatures, while necessary for altering a material's internal structure, also dramatically accelerate destructive surface reactions with the surrounding air. An inert atmosphere solves this by replacing the air with a non-reactive gas, ensuring the heat treatment process modifies only the intended properties without causing surface damage.

The Fundamental Problem: Heat, Metal, and Air
At room temperature, most metals are relatively stable in air. However, introducing the intense heat required for processes like annealing, brazing, or sintering fundamentally changes this relationship.
Why Heat Is a Catalyst for Damage
Heat acts as an accelerant for chemical reactions. For every incremental increase in temperature, the rate at which metal atoms react with atmospheric gases increases exponentially. This makes the controlled environment of the furnace the most critical factor.
The Primary Culprit: Oxidation
The most common and damaging reaction is oxidation, where the metal surface reacts with oxygen from the air. This chemical change is often irreversible and compromises the part.
The visible result of severe oxidation is scaling, which is the formation of a brittle, flaky layer of oxide on the material's surface. This scale must often be removed through costly and time-consuming secondary processes like sandblasting or acid pickling.
The Impact on Performance and Quality
Surface oxidation is not just a cosmetic issue. It can lead to a loss of dimensional accuracy, reduced fatigue strength, and poor conductivity. For high-precision components, even a microscopic layer of oxide can render a part useless, leading to high rejection rates.
The Furnace Atmosphere as a Process Tool
The gas inside a furnace is not merely a background condition; it is an active tool that dictates the outcome of the heat treatment. Atmospheres are broadly classified into two categories based on their function.
The Protective Shield: Inert Atmospheres
An inert atmosphere is composed of gases that are chemically non-reactive with the material being treated. The most common inert gases used are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar).
The sole purpose of an inert atmosphere is to prevent unwanted reactions. By purging the furnace and replacing all the air, it creates a neutral environment. This ensures the part's surface chemistry remains completely unchanged throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
The Active Agent: Reactive Atmospheres
In contrast, a reactive atmosphere is intentionally designed to cause a specific, desirable chemical reaction on the material's surface. These are not inert; they are active participants.
For example, a reducing atmosphere (often containing Hydrogen, H₂) is used to strip oxygen from existing oxides on a part's surface. Other reactive atmospheres, known as carrier gases, are used to transport elements to the surface, such as in carburizing, where carbon is added to harden steel.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere requires balancing process goals with practical constraints. Simply flooding a furnace with an inert gas is not always the best or most efficient solution.
Purity vs. Cost
High-purity Argon provides the best possible inert protection but is significantly more expensive than Nitrogen. Nitrogen is often sufficient, but it can react with certain metals (like titanium) at very high temperatures, forming nitrides.
Incomplete Purging Risks
The effectiveness of an inert atmosphere depends entirely on the successful removal of air. If the furnace is not properly purged, the residual oxygen will still cause oxidation, defeating the purpose of the process and wasting expensive gas.
Choosing the Wrong Type of Atmosphere
Using a reactive atmosphere when an inert one is needed is a critical error. For instance, using a hydrogen-rich atmosphere on certain high-carbon steels can unintentionally cause decarburization (the removal of carbon), softening the surface when the goal was simply to anneal it without oxidation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace atmosphere is directly tied to the desired outcome for your material. Your choice should be deliberate and based on the specific surface properties you need to achieve or preserve.
- If your primary focus is preserving the exact surface finish and chemistry: Use a true inert atmosphere like Argon or high-purity Nitrogen to create a protective shield.
- If your primary focus is cleaning a surface by removing existing oxides: Use a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen to chemically strip oxygen from the part.
- If your primary focus is hardening the surface of a steel component: Use a carburizing atmosphere to actively diffuse carbon into the material.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective general protection from gross oxidation: Use commercial-grade Nitrogen, ensuring the furnace is properly purged of air.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is how you gain precise control over the final properties and quality of your heat-treated component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects materials from oxidation and other surface reactions during high-temperature heat treatment. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) |
| Benefits | Prevents scaling, maintains dimensional accuracy, improves fatigue strength, and avoids costly secondary processes. |
| Key Considerations | Balance purity vs. cost (e.g., Argon vs. Nitrogen), ensure proper purging to remove air, and select the right atmosphere type for specific goals. |
Upgrade your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise control over inert atmospheres to prevent oxidation and enhance material quality. Don't let surface defects compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your laboratory efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















