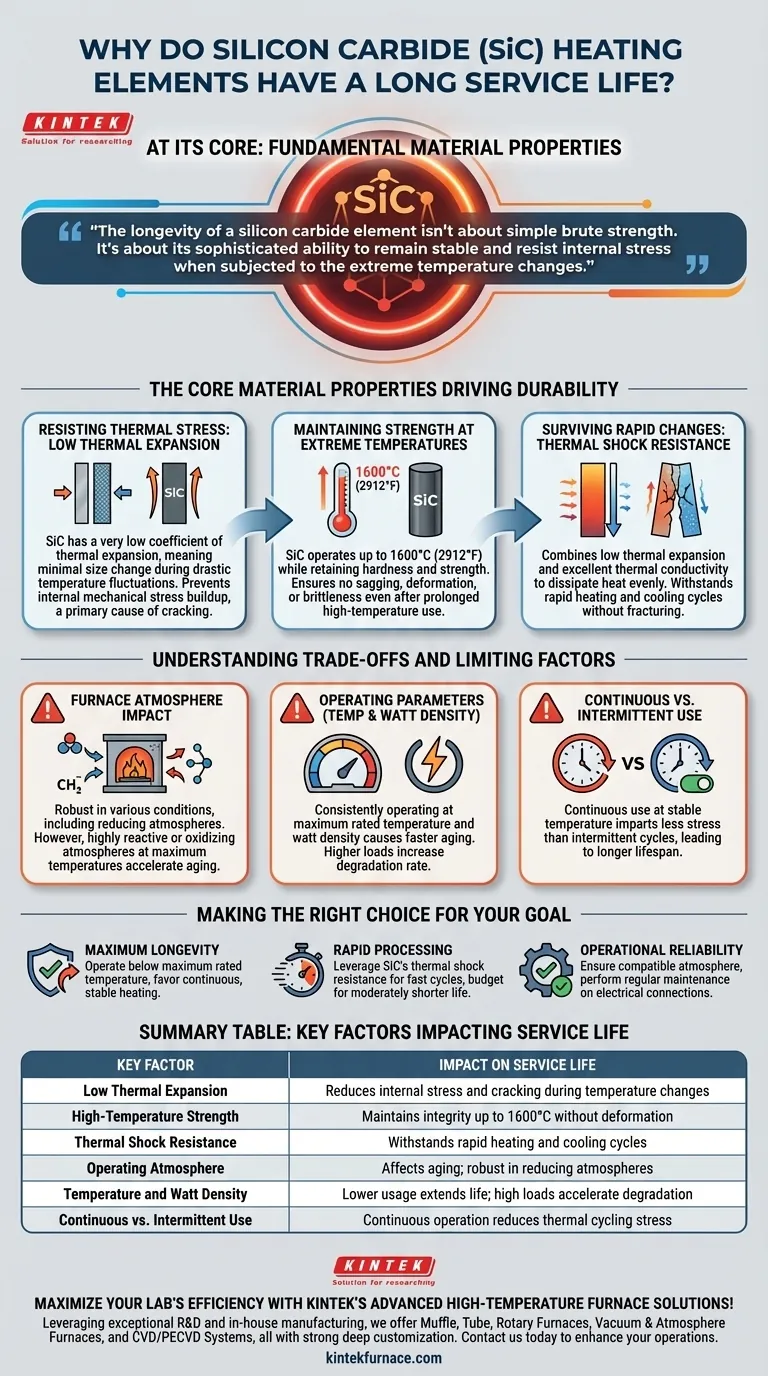
At its core, the long service life of a silicon carbide (SiC) heating element stems from its fundamental material properties. Unlike traditional metallic elements, SiC is an advanced ceramic that possesses exceptional hardness, high-temperature strength, and a critically low coefficient of thermal expansion. This unique combination makes it inherently resistant to the primary causes of failure in high-temperature environments: mechanical stress from heat cycling and material degradation.
The longevity of a silicon carbide element isn't about simple brute strength. It's about its sophisticated ability to remain stable and resist internal stress when subjected to the extreme temperature changes that would cause lesser materials to fatigue and crack.
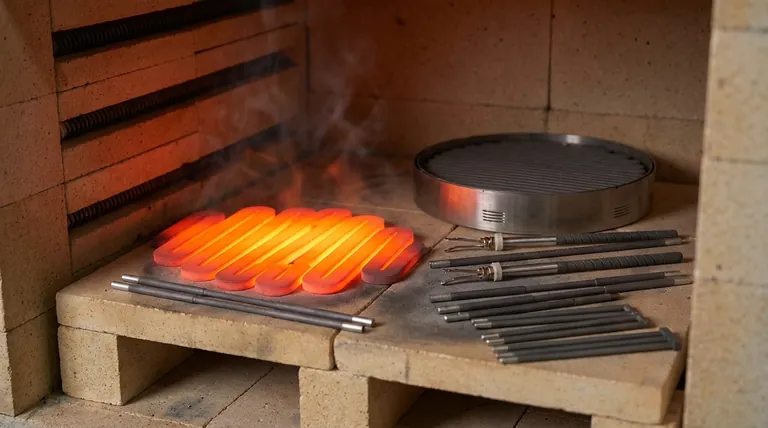

The Core Material Properties Driving Durability
To understand why SiC elements are so durable, we must look at the specific physical characteristics that protect them from wear.
Resisting Thermal Stress: The Role of Low Thermal Expansion
A material's coefficient of thermal expansion dictates how much it expands when heated and contracts when cooled.
Silicon carbide has a very low thermal expansion coefficient. This means it changes size only minimally during drastic temperature fluctuations. This stability prevents the buildup of internal mechanical stress, which is a primary cause of cracking and failure in other materials over repeated heating cycles.
Maintaining Strength at Extreme Temperatures
Many materials lose their structural integrity as they get hotter. SiC is an exception.
SiC elements can operate at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F) while retaining their hardness and strength. This high thermal stability ensures the element does not sag, deform, or become brittle even after prolonged use at the upper end of its operational range.
Surviving Rapid Temperature Changes: Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock occurs when a material cracks due to rapid temperature change. SiC's properties give it a high resistance to this phenomenon.
The combination of low thermal expansion and excellent thermal conductivity means the element experiences less internal stress and dissipates heat evenly. This allows it to withstand the rapid heating and cooling common in laboratory and industrial processes without fracturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limiting Factors
While exceptionally durable, the lifespan of an SiC element is not infinite. Its longevity is influenced by its operating environment and usage patterns.
The Impact of Furnace Atmosphere
The chemical environment inside a furnace can affect the element. SiC elements are notably robust and perform well in various conditions, including reducing atmospheres where other types (like MoSi2) may be weaker.
However, certain highly reactive or oxidizing atmospheres, especially when combined with maximum temperatures, can accelerate aging and shorten the element's effective life.
Operating Parameters: Temperature and Watt Density
Every element has a maximum rated temperature and watt density (a measure of power output per surface area).
Consistently operating an element at its absolute limit will cause it to age faster than operating at a more moderate 80-90% of its capacity. Higher temperatures and power loads increase the rate of material degradation.
Continuous vs. Intermittent Use
Thermal cycling is the process of heating up and cooling down. While SiC is highly resistant to thermal shock, every cycle still imparts a small amount of stress on the material.
Therefore, an element used continuously at a stable temperature will generally last longer than one used intermittently, as it undergoes far fewer stressful thermal cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles allows you to actively manage the lifespan of your heating elements based on your specific application needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity: Operate the elements below their maximum rated temperature and favor continuous, stable heating over frequent on-off cycles.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing: Leverage SiC's excellent thermal shock resistance for fast cycles, but budget for a moderately shorter service life compared to continuous use.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Ensure your furnace atmosphere is compatible and perform regular maintenance to confirm secure electrical connections, which prevents localized hot spots and premature failure.
By understanding the fundamental properties of silicon carbide, you can move from simply using a component to strategically managing a critical asset for your operations.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Service Life |
|---|---|
| Low Thermal Expansion | Reduces internal stress and cracking during temperature changes |
| High-Temperature Strength | Maintains integrity up to 1600°C without deformation |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles |
| Operating Atmosphere | Affects aging; robust in reducing atmospheres |
| Temperature and Watt Density | Lower usage extends life; high loads accelerate degradation |
| Continuous vs. Intermittent Use | Continuous operation reduces thermal cycling stress |
Maximize your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our silicon carbide heating elements can enhance your operations and ensure long-lasting performance tailored to your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















