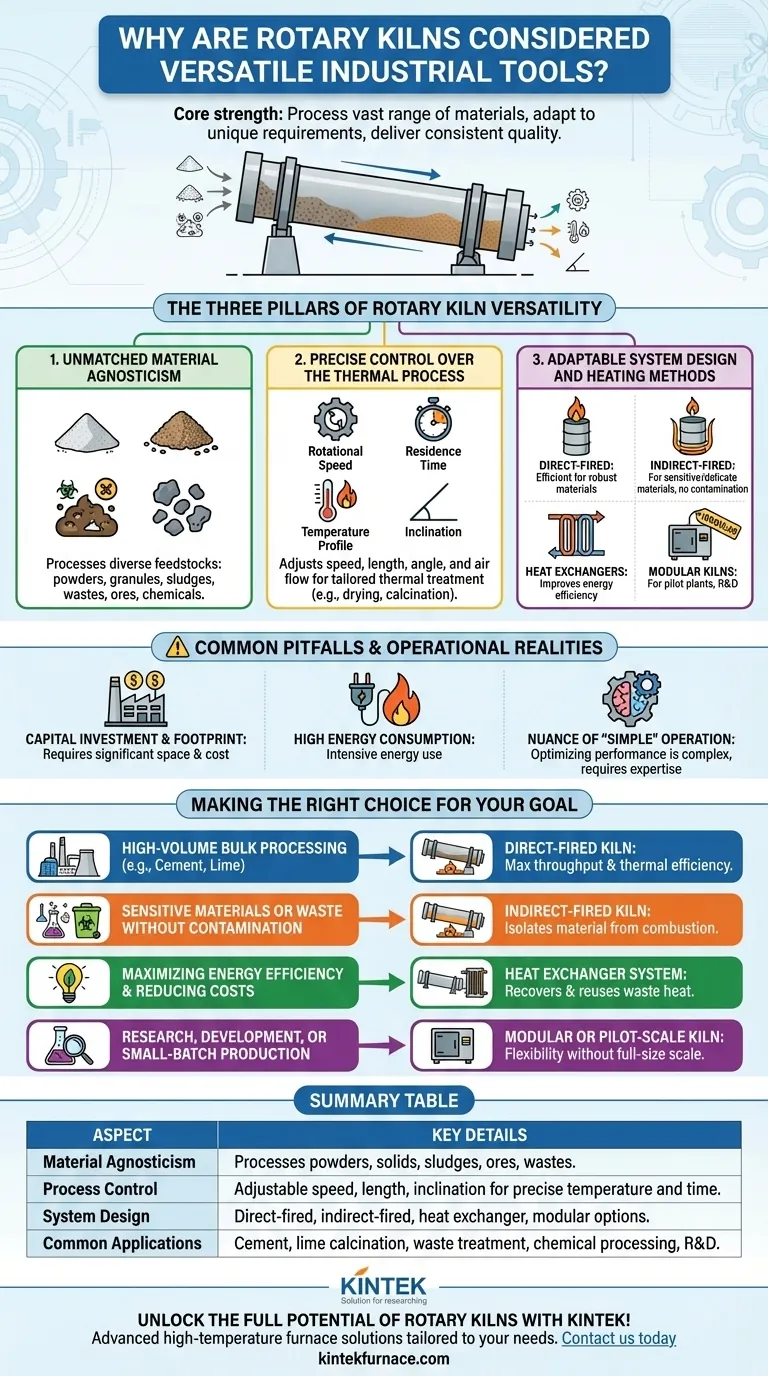
At its core, a rotary kiln is considered an exceptionally versatile industrial tool because of its unique ability to process a vast range of materials, adapt to different process requirements through extensive customization, and deliver consistent, high-quality results. This versatility stems from its fundamental design—a rotating, inclined cylinder that can be precisely configured to control temperature, residence time, and the processing atmosphere for nearly any granular solid, sludge, or waste stream.
The true value of a rotary kiln is not just that it can handle many materials, but that it can be engineered into a specific thermal solution. Its versatility comes from its capacity for customization, allowing it to be tailored to the unique physical and chemical requirements of both the feedstock and the desired end product.
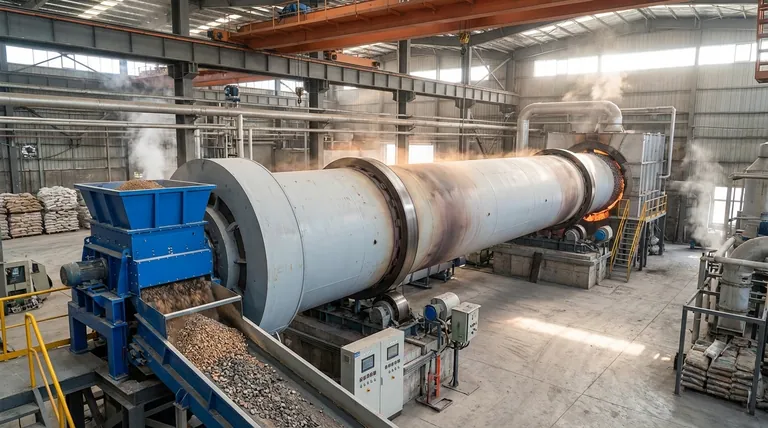

The Three Pillars of Rotary Kiln Versatility
The adaptability of a rotary kiln is not accidental; it is the result of three core engineering principles working in concert. Understanding these pillars reveals why this technology remains a cornerstone of heavy industry.
1. Unmatched Material Agnosticism
A rotary kiln’s primary strength is its ability to process an incredible diversity of feedstocks. The slow, tumbling action inside the rotating drum ensures that materials are mixed thoroughly and exposed evenly to heat.
This makes it suitable for everything from fine powders and granular solids to sludgy wastes and small, irregular objects. It can handle ores, minerals, chemical compounds, hazardous waste, sewage sludge, and materials for recycling with equal effectiveness.
2. Precise Control Over the Thermal Process
Versatility requires control. The design of a rotary kiln provides several levers to precisely manage the thermal treatment of the material.
By adjusting the rotational speed, length, and angle of inclination (typically 2-3 degrees), operators can dictate the exact residence time—how long the material spends inside the kiln. This, combined with the ability to achieve extremely high and uniform temperatures, allows for a wide range of thermal processes, from simple drying to complex chemical reactions like calcination.
3. Adaptable System Design and Heating Methods
Rotary kilns are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they are highly configurable systems. This customization is key to their application across different industries.
Different models optimize the process for specific needs:
- Direct-Fired Kilns: The flame and combustion gases directly contact the material. This is highly efficient and ideal for robust materials like cement and lime.
- Indirect-Fired Kilns: The rotating cylinder is heated from the outside. This prevents any contact between the material and combustion gases, making it perfect for processing delicate materials, chemicals, or waste streams where contamination is a concern.
- Kilns with Heat Exchangers: These designs capture and reuse waste heat from the process, significantly improving energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- Modular Kilns: Compact, pre-engineered systems are available for smaller-scale applications, such as pilot plants or research and development labs.
Common Pitfalls and Operational Realities
While incredibly versatile, rotary kilns are not without their operational trade-offs. Acknowledging these realities is critical for any project evaluation.
Capital Investment and Footprint
Rotary kilns are heavy-duty industrial machines, often constructed from massive steel tubes lined with refractory brick. Industrial-scale units can be hundreds of feet long, requiring significant capital investment and a large physical footprint.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures required for many processes is energy-intensive. While designs with heat exchangers can mitigate this, energy remains a primary operational cost that must be carefully managed.
The Nuance of "Simple" Operation
The basic principle of a rotary kiln is simple, but optimizing its performance for a specific material and desired outcome is a complex task. It requires deep expertise to balance feed rate, temperature profiles, rotation speed, and air flow to ensure consistent product quality and efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of rotary kilns means the "best" configuration depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk material processing (like cement or lime): A large, direct-fired kiln offers the highest throughput and thermal efficiency for these robust materials.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials or waste without contamination: An indirect-fired kiln is the correct choice to ensure the material is isolated from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and reducing operating costs: Prioritize a design that incorporates a robust heat exchanger system to recover and reuse waste heat.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-batch production: A modular or pilot-scale kiln provides operational flexibility without the cost and scale of a full-size industrial unit.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln's enduring power lies in its ability to be engineered from a simple concept into a precise thermal solution for nearly any material processing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Material Agnosticism | Processes powders, solids, sludges, and wastes like ores and hazardous materials |
| Process Control | Adjustable speed, length, and inclination for precise temperature and residence time |
| System Design | Options include direct-fired, indirect-fired, heat exchanger, and modular kilns |
| Common Applications | Cement production, lime calcination, waste treatment, chemical processing, and R&D |
Unlock the full potential of rotary kilns for your operations with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in heavy industry, research, or waste management, we can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your material processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















