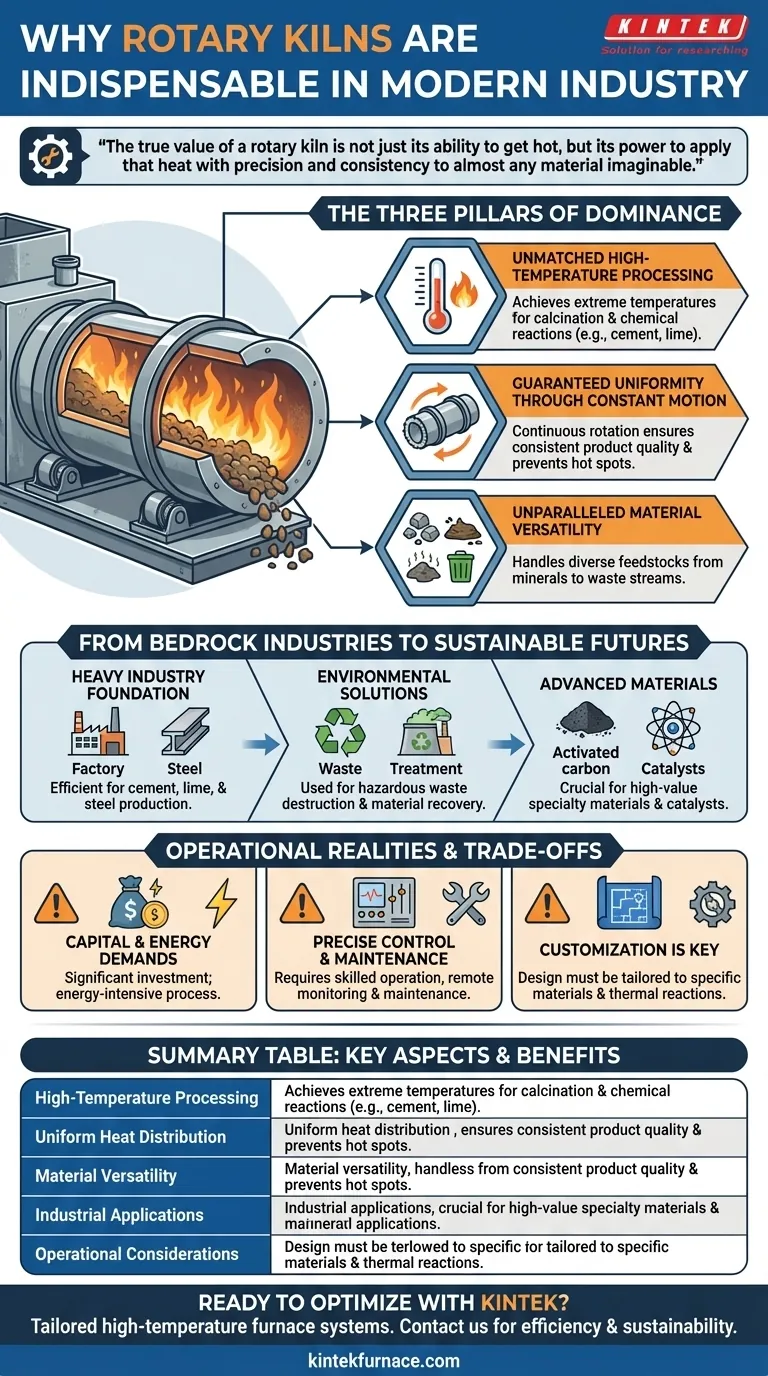
In the landscape of industrial processing, the rotary kiln remains indispensable due to a unique synthesis of three core capabilities: the ability to achieve extremely high temperatures, ensure uniform heat distribution through continuous motion, and process an unparalleled variety of materials. This combination allows it to serve as the backbone for foundational sectors like cement and steel while simultaneously evolving to meet the demands of modern environmental and recycling applications.
The true value of a rotary kiln is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to apply that heat with precision and consistency to almost any material imaginable. This adaptability is what bridges its century-old legacy with its critical role in the future of sustainable industry.

The Three Pillars of a Rotary Kiln's Dominance
The enduring relevance of the rotary kiln isn't accidental; it is engineered from three fundamental principles that work in concert. Understanding these pillars reveals why this technology has not been superseded.
Unmatched High-Temperature Processing
A rotary kiln is essentially a contained, high-temperature environment. It is designed to reach and sustain temperatures required for demanding thermal processes like calcination, where materials are chemically altered by heat.
This capability is non-negotiable for producing fundamental commodities like cement and lime, where specific chemical reactions can only be triggered at extreme temperatures.
Guaranteed Uniformity Through Constant Motion
The kiln’s slow, constant rotation is its defining feature. As material tumbles through the cylindrical chamber, every particle is continuously exposed to the heat source.
This movement prevents hot spots and ensures that the entire batch is processed evenly. The result is a highly consistent and predictable final product, a critical requirement for quality control in any industrial setting.
Unparalleled Material Versatility
Perhaps its greatest strength is its ability to handle an enormous range of feedstocks. It can process free-flowing granular solids, small waste stones, minerals, ores, chemical sludges, and various waste streams.
This "material-agnostic" nature makes the rotary kiln a versatile problem-solver, adaptable to different industries and evolving needs without requiring a fundamental change in its core design.
From Bedrock Industries to Sustainable Futures
The rotary kiln's versatility is best demonstrated by its application across a wide spectrum of industries, from the traditional to the cutting-edge. It is a technology that has successfully pivoted to solve new challenges.
The Foundation of Heavy Industry
For decades, rotary kilns have been the workhorse for producing cement, lime, and steel. Their ability to run continuously and process massive volumes of raw ore and minerals makes them the most efficient and reliable choice for these high-output sectors.
A Critical Tool for Environmental Solutions
The same principles that make a kiln effective for mineral processing are now being applied to waste management and environmental remediation.
By heating hazardous waste to extreme temperatures, kilns can safely destroy harmful organic compounds, reduce waste volume, and even recover valuable materials for recycling. This positions the kiln as a key technology in the circular economy.
Enabling Specialized and Advanced Materials
Beyond bulk commodities, rotary kilns are crucial for producing high-value specialty materials. They are used to create and reactivate activated carbon for air and water purification, prepare catalysts for chemical manufacturing, and process advanced plastics and ceramics.
Understanding the Operational Realities
While indispensable, operating a rotary kiln involves managing specific trade-offs. Acknowledging these realities is key to leveraging the technology effectively.
Significant Capital and Energy Demands
Rotary kilns are massive pieces of industrial equipment that represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, achieving and maintaining high temperatures is an energy-intensive process, making energy efficiency a primary focus of modern kiln design and operation.
The Need for Precise Control and Maintenance
The kiln’s versatility depends on precise operational control. Factors like rotation speed, temperature profile, and material feed rate must be carefully managed to achieve the desired outcome.
Modern systems incorporate remote monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize performance and prevent costly downtime, highlighting the need for skilled operation.
Customization Is Key
A "one-size-fits-all" approach does not work. The kiln's design, from its length and diameter to its refractory lining, must be customized to the specific material being processed and the desired thermal reaction. This modularity ensures optimal efficiency but requires expert configuration.
Aligning Kiln Technology with Your Strategic Goals
Choosing to invest in or optimize a rotary kiln depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume commodity production: The rotary kiln's unmatched reliability and capacity for continuous, uniform processing make it the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is waste management or recycling: The kiln's material versatility and ability to safely transform diverse and hazardous feedstocks into inert or valuable products is its key advantage.
- If your primary focus is specialty material manufacturing: The kiln's precise control over temperature and its uniform heating action are essential for guaranteeing the quality and performance of high-value products.
The rotary kiln endures because it is a fundamentally adaptable tool, continuously proving its value by solving both the oldest and the newest challenges in industrial processing.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Processing | Achieves extreme temperatures for calcination and chemical reactions in cement, lime, and steel production. |
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Ensures consistent product quality through continuous rotation, preventing hot spots. |
| Material Versatility | Handles diverse materials, from minerals to waste streams, supporting various industries. |
| Industrial Applications | Used in heavy industry, environmental solutions, and advanced materials manufacturing. |
| Operational Considerations | Involves energy demands, precise control, and customization for optimal performance. |
Ready to optimize your industrial processes with advanced rotary kiln solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique requirements, whether for high-volume production, waste management, or specialty materials. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















