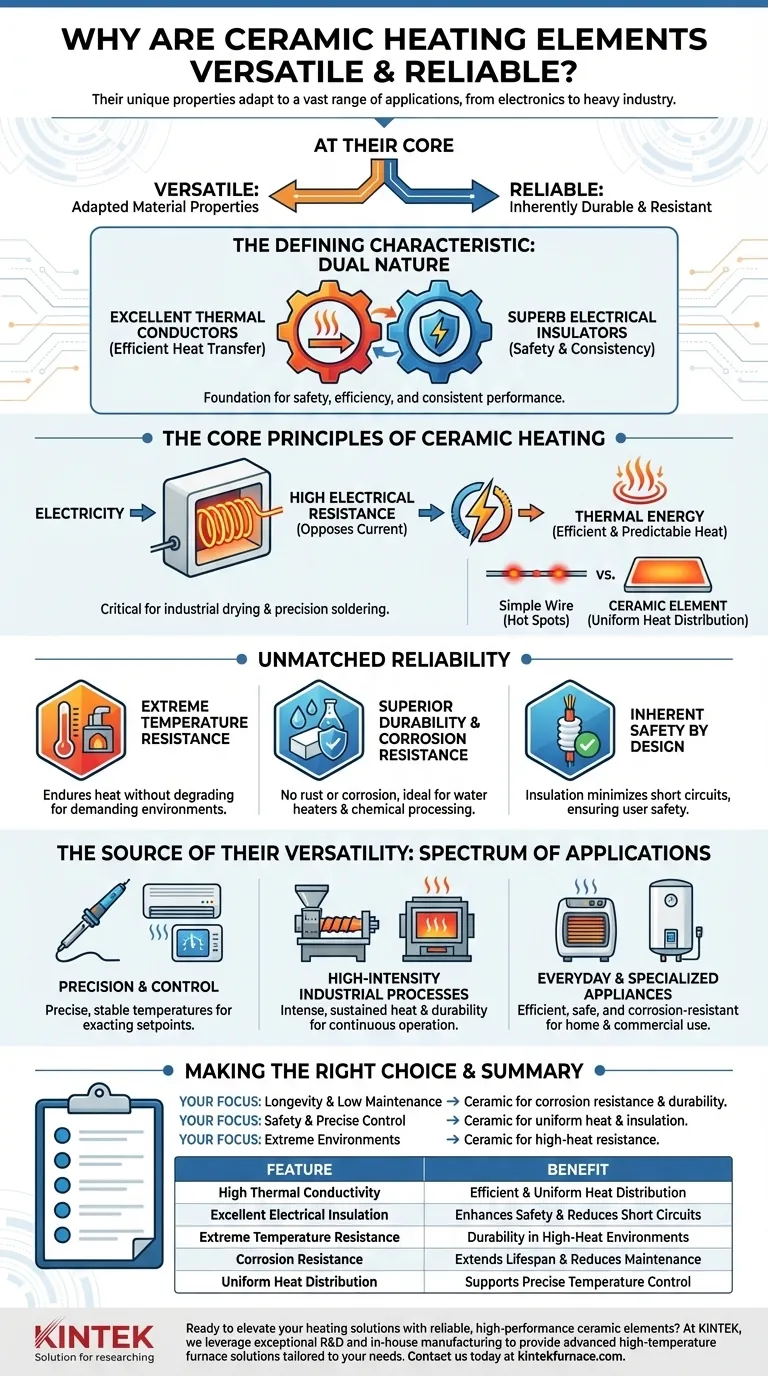
At their core, ceramic heating elements are versatile because their material properties can be adapted for a vast range of applications, from precision electronics to heavy industry. They are reliable because the ceramic material itself is inherently durable, an excellent electrical insulator, and exceptionally resistant to both high temperatures and chemical corrosion.
The defining characteristic of ceramic heaters is a rare combination: they are excellent thermal conductors while also being superb electrical insulators. This dual nature is the foundation for their safety, efficiency, and consistent performance across a wide spectrum of uses.

The Core Principles of Ceramic Heating
To understand their reliability, we must first look at how they function. The fundamental principles are straightforward but lead to significant advantages over other heating technologies.
How They Convert Electricity to Heat
A ceramic heating element works by passing an electric current through a specially formulated ceramic material. This material, often a composite, has a high electrical resistance that opposes the flow of electricity.
This opposition, or resistance, forces the electrical energy to convert directly into thermal energy, generating heat efficiently and predictably.
The Dual Advantage: Conductor and Insulator
Most materials that conduct heat well, like metals, also conduct electricity well. This creates design challenges and potential safety risks like short circuits.
Ceramics break this rule. They allow heat to pass through them effectively (high thermal conductivity) but block the flow of electricity (high electrical insulation). This allows the heating element to operate safely at high temperatures without complex, failure-prone insulation layers.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Unlike a simple wire that can create hot spots, ceramic elements are often engineered as plates or blocks. This larger surface area allows them to heat up evenly across their entire body.
This uniform heat distribution ensures consistent and reliable performance, which is critical for applications like industrial drying or precision soldering where even temperature is paramount.
Why This Translates to Unmatched Reliability
The physical properties of the ceramic material directly contribute to a long and predictable service life, making them a trusted choice for critical applications.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Metals can soften, warp, or melt at very high temperatures, leading to premature failure. Advanced ceramics, however, are designed to endure extreme heat without degrading.
This allows them to operate consistently in demanding environments like industrial furnaces and kilns, where they maintain their structural integrity and performance over countless cycles.
Superior Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metal heating elements, ceramics do not rust or corrode when exposed to moisture or chemicals. This makes them exceptionally reliable for applications like water heaters or equipment used in chemical processing.
This inherent resistance to degradation eliminates a common failure point and drastically reduces maintenance requirements over the heater's lifespan.
Inherent Safety by Design
Because the ceramic material itself is an electrical insulator, the risk of a short circuit is significantly minimized. The live electrical components are safely encased within the non-conductive ceramic body.
This built-in safety feature adds a powerful layer of reliability, especially in consumer appliances and systems where user safety is a primary concern.
The Source of Their Versatility: A Spectrum of Applications
The combination of reliability, precision, and safety allows ceramic heating elements to be deployed across a uniquely broad range of fields.
Precision and Control
Applications like soldering irons and HVAC systems demand precise, stable temperatures. The uniform heating and efficient thermal transfer of ceramic elements make them ideal for maintaining exact temperature setpoints.
High-Intensity Industrial Processes
In plastic extrusion, packaging machinery, and high-temperature furnaces, ceramic heaters provide the intense, sustained heat required. Their durability ensures they can withstand the rigors of continuous industrial operation.
Everyday and Specialized Appliances
From consumer space heaters to specialized water heaters, the safety and corrosion resistance of ceramic elements make them a popular choice. Their ability to deliver consistent heat efficiently is valued in both home and commercial settings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right heating technology depends entirely on your primary goal. The unique properties of ceramic heaters make them the superior choice for specific needs.
- If your primary focus is longevity and low maintenance: The exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature durability of ceramic heaters make them the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is safety and precise control: The combination of uniform heating and inherent electrical insulation provides unmatched performance and peace of mind.
- If your primary focus is operation in extreme environments: The ability of ceramic materials to withstand intense heat without degrading ensures reliability where metal elements would fail.
By understanding these core material advantages, you can confidently determine when a ceramic heating element is the optimal solution for your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Conductivity | Ensures efficient and uniform heat distribution |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Enhances safety and reduces risk of short circuits |
| Extreme Temperature Resistance | Provides durability in high-heat environments |
| Corrosion Resistance | Extends lifespan and reduces maintenance needs |
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Supports precise temperature control for critical applications |
Ready to elevate your heating solutions with reliable, high-performance ceramic elements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications
- What ceramic materials are commonly used for heating elements? Discover the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure



















