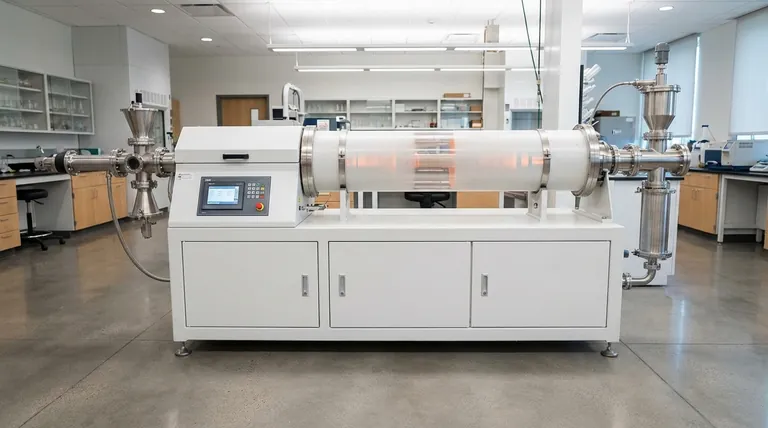
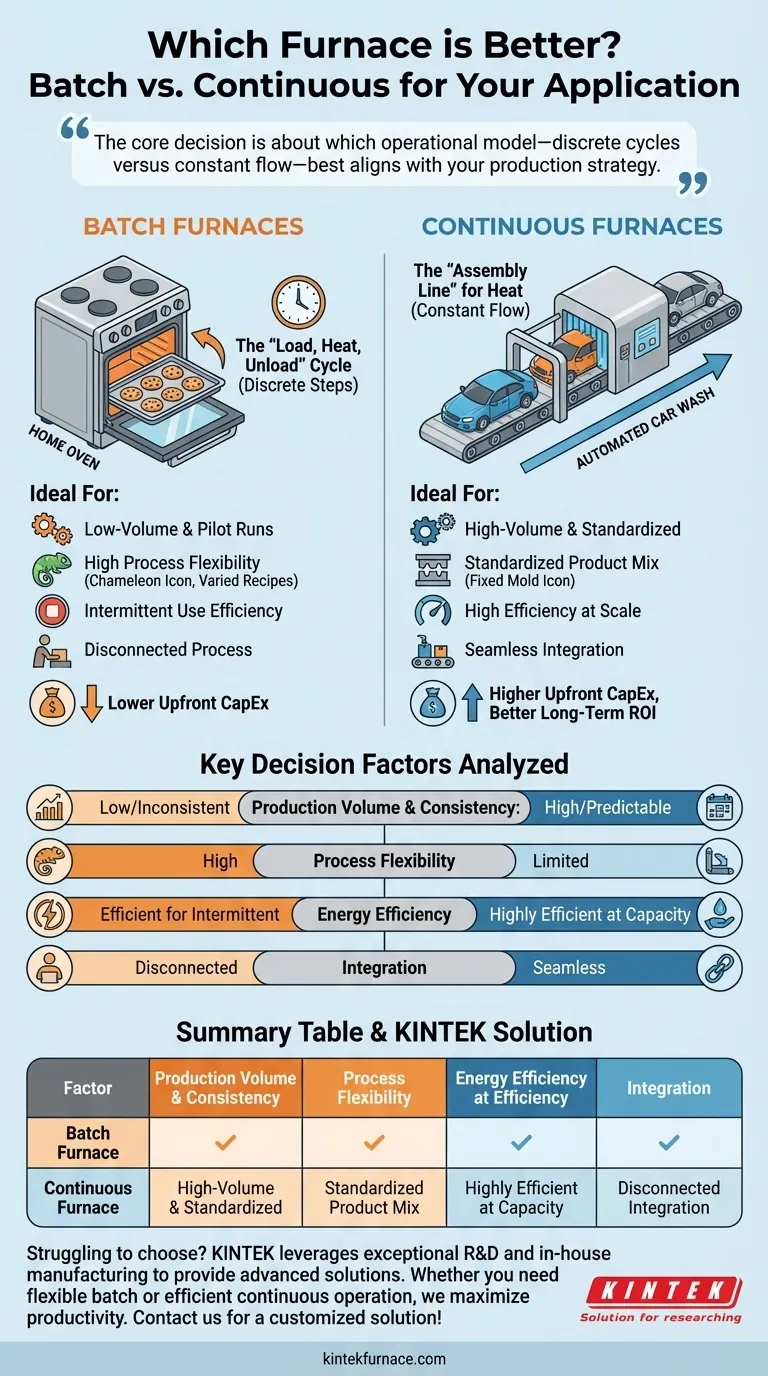
To determine which furnace is "better," you must first define your operational goals, as the ideal choice depends entirely on production volume, process consistency, and integration needs. Batch furnaces excel in flexible, low-volume, or specialized applications, while continuous furnaces are engineered for high-volume, standardized production where efficiency at scale is paramount.
The core decision is not about which furnace technology is superior, but which operational model—discrete cycles versus constant flow—best aligns with your production strategy and economic drivers.

The Fundamental Difference: Process Flow
The primary distinction between these two furnace types is not just their construction, but the philosophy of how material moves through the heating process. Understanding this is the first step to making an informed choice.
Batch Furnaces: The "Load, Heat, Unload" Cycle
A batch furnace operates in discrete, sequential steps. A single load (or "batch") of product is placed inside, the door is closed, the furnace heats up to the target temperature for a set time, and then the entire batch is removed.
This is analogous to a conventional home oven. You load a tray of cookies, bake them, and then take the entire tray out before starting the next one. This stop-and-go process defines its applications.
Continuous Furnaces: The "Assembly Line" for Heat
A continuous furnace, often called a tunnel or conveyor furnace, operates as an integrated part of a production line. Product is constantly fed into one end, moves through various heating and cooling zones on a conveyor, and exits the other end ready for the next manufacturing step.
Think of this like an automated car wash. Cars enter one after another, move steadily through different stations, and emerge clean on the other side without the system ever stopping.
Key Decision Factors Analyzed
Your choice will be dictated by a few critical operational and financial variables. An honest assessment of these factors will make the correct path clear.
Production Volume and Consistency
This is the single most important factor. A continuous furnace is designed for high-volume, predictable production runs of the same or similar products. Its efficiency is realized when it runs for long periods without interruption.
A batch furnace is far more economical for low-volume production, pilot runs, or operations with inconsistent demand. Running a large continuous furnace for a small amount of product is extremely inefficient.
Process Flexibility and Product Mix
If your operation requires frequent changes in temperature, heating duration, or atmospheric conditions for different products, a batch furnace offers superior flexibility. Each cycle can be programmed for a specific recipe.
Continuous furnaces are optimized for a specific thermal profile. While some have multiple zones, they are not designed for rapid or drastic changes and are best suited for a highly standardized product mix.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Cost
For high-throughput applications, a continuous furnace is significantly more energy-efficient. By maintaining a constant operating temperature, it avoids the massive energy loss that occurs when a batch furnace must be cooled, unloaded, reloaded, and reheated.
The per-unit energy cost in a continuous system is lower, but only when running at or near its designed capacity. For intermittent use, a batch furnace's ability to be shut down between cycles is more cost-effective.
Integration with Production Lines
Continuous furnaces are purpose-built for seamless integration into automated manufacturing lines. Their constant input and output flow eliminates bottlenecks and reduces material handling labor.
Batch furnaces inherently create a disconnected process. They require manual or robotic loading and unloading, which can act as a buffer or a bottleneck in an otherwise automated production flow.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither option is a perfect solution. Recognizing the inherent compromises of each is crucial for realistic planning and budgeting.
The Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term ROI
Batch furnaces almost always have a lower initial capital expenditure (CapEx). They are simpler in design and require less complex installation.
Continuous furnaces represent a much larger upfront investment due to their size, conveyors, and sophisticated control systems. However, for high-volume producers, the lower per-unit operational cost delivers a superior return on investment (ROI) over time.
The Hidden Costs of Misapplication
Using a batch furnace for a high-volume process that should be continuous leads to high labor costs, significant wasted energy from repeated heat-up/cool-down cycles, and production bottlenecks.
Conversely, using a continuous furnace for low-volume or highly varied work results in massive energy waste from idling at temperature and a poor return on the initial high investment. The furnace is constantly "on" but underutilized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your furnace based on a clear-eyed assessment of your primary operational priority.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for a diverse product mix: A batch furnace provides the agility to change thermal profiles from one load to the next.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace is the only choice for achieving efficiency and low per-unit cost at scale.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment: A batch furnace offers the lowest barrier to entry for thermal processing capabilities.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest energy cost per unit: A continuous furnace, when operated at its designed capacity, is unmatched in efficiency.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's inherent operational model with your production reality is the key to a successful investment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Best for low-volume, inconsistent runs | Ideal for high-volume, standardized production |
| Process Flexibility | High flexibility for varied product mixes | Limited flexibility, optimized for specific profiles |
| Energy Efficiency | Efficient for intermittent use; high energy loss in cycles | Highly efficient at full capacity; constant operation |
| Integration | Disconnected process; manual or robotic handling | Seamless integration into automated production lines |
| Cost | Lower initial CapEx; higher per-unit cost for high volume | Higher initial CapEx; lower per-unit cost at scale |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you need flexible batch processing or efficient continuous operation, we can help you achieve precise thermal control and maximize productivity. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation



















