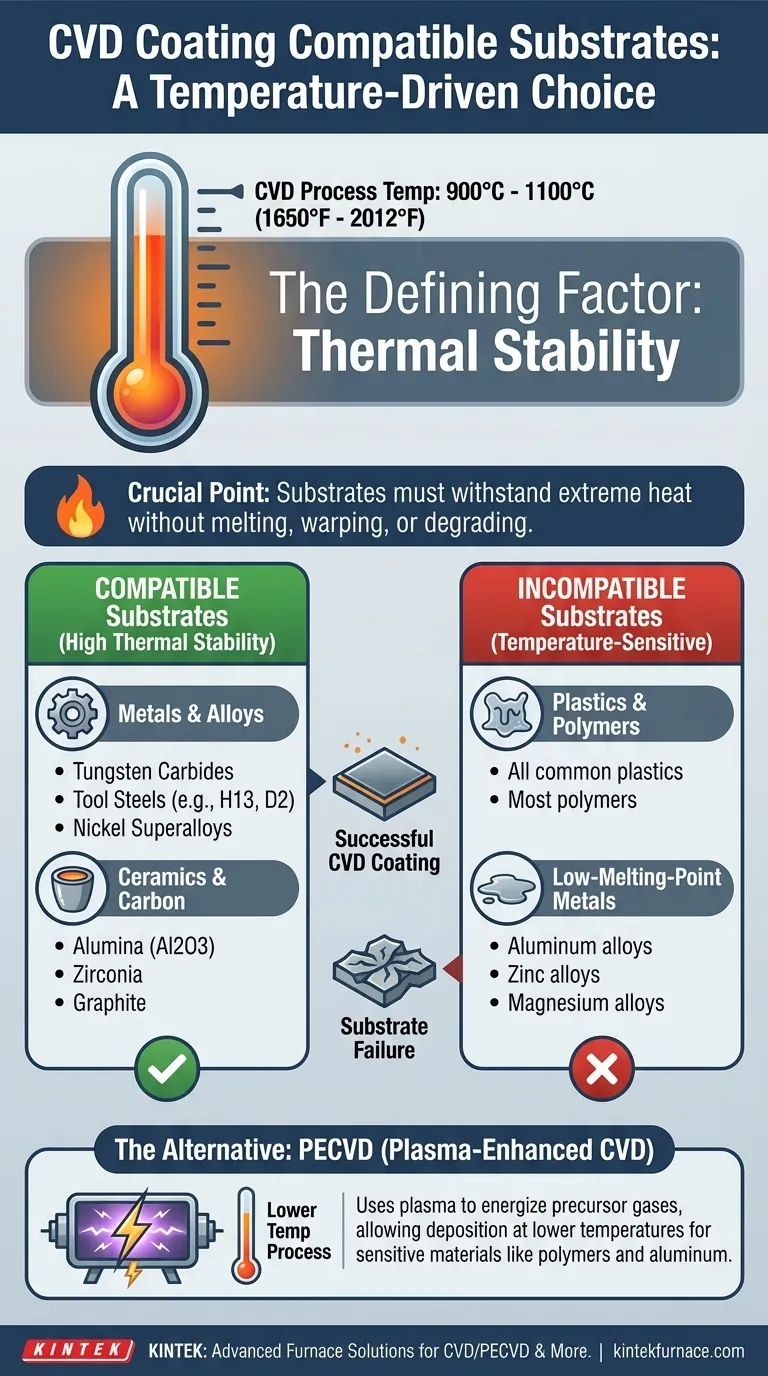
Choosing the right substrate for a CVD coating is a decision dictated almost entirely by temperature. Substrate materials that are compatible with standard Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are those that can withstand very high heat without deforming or degrading. This includes materials like tungsten carbides, various tool steels, high-temperature nickel alloys, ceramics, and graphite.
The core principle of CVD compatibility is not about chemical reactivity between the coating and the substrate, but whether the substrate can survive the extreme temperatures required for the deposition process to occur. If the substrate material is stable at high heat, it is likely a candidate for CVD.

The Defining Factor: Thermal Stability
The entire CVD process is built around heat. Understanding this makes substrate selection a straightforward engineering decision rather than a complex chemical puzzle.
Why High Temperature is Inherent to CVD
Chemical Vapor Deposition works by introducing volatile precursor gases into a chamber containing the substrate. These gases are heated to a point where they react or decompose, causing the desired material to deposit as a thin solid film onto the substrate's surface.
Without sufficient heat, these chemical reactions will not happen. This makes high temperature a non-negotiable requirement of the process.
The Critical Temperature Threshold
Typical CVD processes operate at very high temperatures, often in the range of 900°C to 1100°C (1650°F to 2012°F).
Any material that melts, warps, anneals, or otherwise loses its critical structural properties below this temperature range is fundamentally incompatible with standard CVD.
A Breakdown of Compatible Substrate Families
The list of compatible materials shares one key trait: an exceptionally high melting point and excellent structural integrity at elevated temperatures.
Metals and Metal Alloys
This group includes materials designed for hardness and high-performance applications.
Common examples are tungsten carbides, tool steels (like H13 or D2), and high-temperature nickel superalloys. These materials are chosen specifically because they maintain their strength and shape well within the CVD temperature window.
Ceramics and Carbon
Materials like alumina (Al2O3), zirconia, and other technical ceramics are excellent substrates. They are inherently stable at extreme temperatures because they are often created in similar high-heat environments.
Graphite is also a common substrate due to its extremely high temperature tolerance, making it ideal for specialized applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, CVD is not a universal solution. Its primary limitation is the very temperature that makes it work.
The Primary Constraint: Thermal Sensitivity
Any material that cannot withstand the process heat is automatically disqualified. This rules out a vast number of common engineering materials.
Plastics, polymers, and most low-melting-point metals (like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium alloys) are not suitable substrates for conventional, high-temperature CVD. Applying this process would destroy them.
The Challenge of Complex Geometries
Even with a compatible material, achieving a perfectly uniform coating on substrates with very complex shapes, deep holes, or high aspect ratios can be difficult. The flow of precursor gases may not reach all surfaces equally, leading to variations in coating thickness.
When Standard CVD Isn't the Answer: PECVD
For temperature-sensitive substrates, alternative methods exist. Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is a key example.
PECVD uses plasma to energize the precursor gases, allowing the deposition reaction to occur at much lower temperatures. This opens the door to coating materials like polymers, silicones, and a wider variety of metals that would be damaged by standard CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends on matching the material's properties to the process requirements and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance on cutting tools: Use tungsten carbide or tool steel substrates, as they provide a robust foundation for hard coatings like TiN, TiC, or Al2O3.
- If your primary focus is performance in corrosive or high-heat environments: Use nickel superalloys, ceramics, or graphite, which maintain their integrity under the extreme conditions where these coatings excel.
- If your substrate is temperature-sensitive (like a polymer or aluminum part): Standard CVD is unsuitable; you must investigate lower-temperature alternatives like PECVD.
Ultimately, a successful outcome depends on matching your substrate's thermal properties to the fundamental demands of the deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Substrate Material Type | Examples | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Metals and Alloys | Tungsten carbides, Tool steels (e.g., H13, D2), High-temperature nickel superalloys | High melting point, excellent structural integrity at high temperatures |
| Ceramics and Carbon | Alumina (Al2O3), Zirconia, Graphite | Inherent thermal stability, ideal for extreme heat environments |
| Incompatible Materials | Plastics, polymers, low-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, zinc alloys) | Cannot withstand CVD temperatures, prone to deformation or degradation |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your CVD coating needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab



















