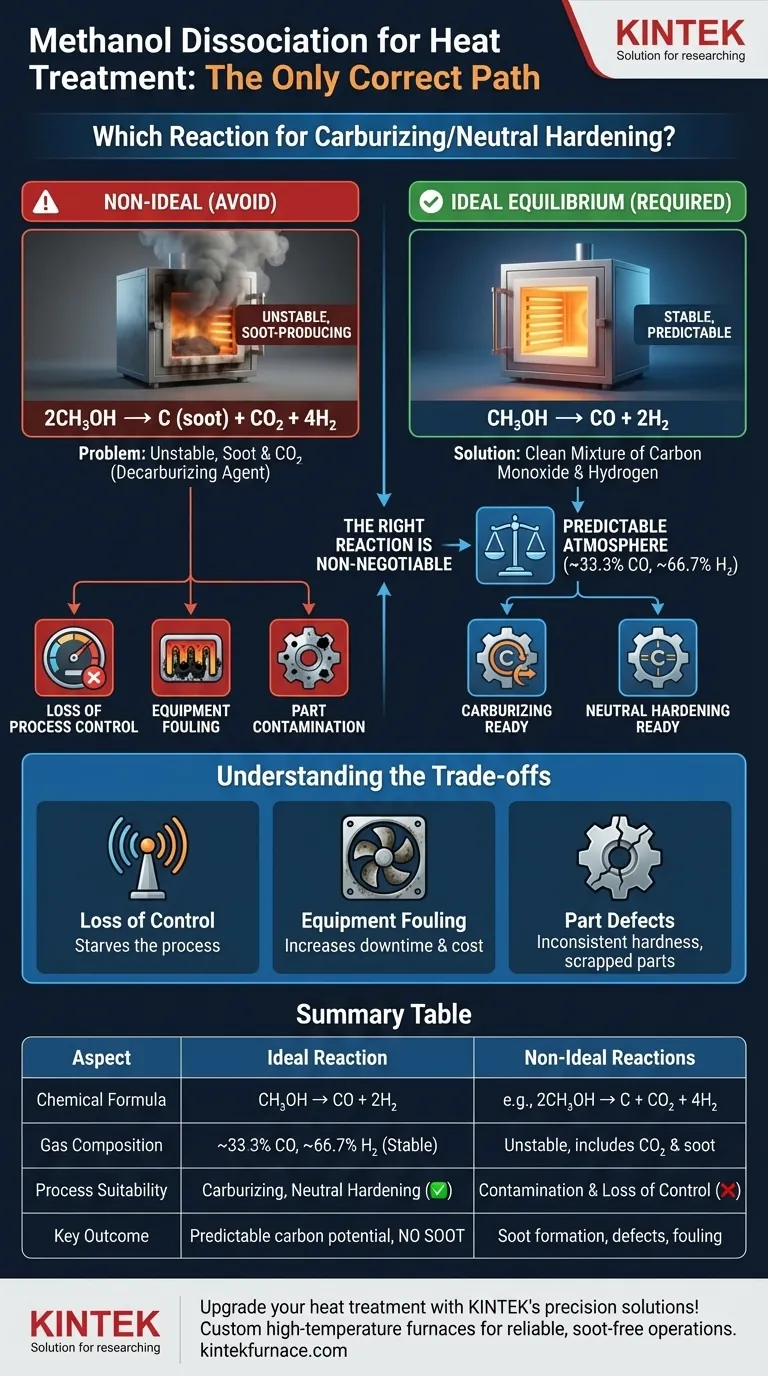
For any controlled heat treatment process, the only appropriate methanol dissociation reaction is the one that produces a clean mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen: CH₃OH -> CO + 2H₂. This is the ideal, high-temperature equilibrium reaction. Any other reaction path indicates an unstable, non-equilibrium process that produces soot, undermining the entire goal of atmospheric control.
The core challenge in using methanol for heat treatment is not just creating a protective atmosphere, but creating one that is stable, predictable, and free of contaminants. The choice of reaction isn't a choice at all—it's a requirement for success. Only the complete dissociation into carbon monoxide and hydrogen provides the control necessary for modern metallurgy.

Why the Right Reaction is Non-Negotiable
Methanol is used as a safe, storable liquid precursor to generate a furnace atmosphere on-demand. It serves as a modern alternative to traditional endothermic gas generators. The goal is to break it down into a precise mixture of gases that can then be used to control the surface carbon of steel parts.
The Goal: A Defined Carburizing Potential
The ability of a furnace atmosphere to add or remove carbon from steel is known as its carburizing potential. This is governed by the specific ratios of active gases, primarily carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), hydrogen (H₂), and water vapor (H₂O).
To control this potential, you must start with a known, clean gas composition. The ideal dissociation of methanol provides exactly that.
The Ideal Equilibrium Reaction: CH₃OH -> CO + 2H₂
This reaction is the foundation of using methanol for heat treatment. At sufficiently high temperatures (typically above 850°C / 1550°F), methanol breaks down cleanly and completely.
This produces a predictable atmosphere consisting of approximately 33.3% carbon monoxide and 66.7% hydrogen. This clean slate is the perfect starting point for either carburizing (by adding a carbon-enriching gas like propane) or neutral hardening.
The Problem with Side Reactions
When the dissociation process is incomplete or occurs at too low a temperature, undesirable side reactions take over. These are the non-equilibrium reactions that must be avoided.
Non-Equilibrium Reactions and Soot
While several side reactions can occur, they are all characterized by the formation of solid carbon, or soot. A common example is:
2CH₃OH -> C (soot) + CO₂ + 4H₂
This reaction is disastrous for two reasons. First, it produces soot, a major contaminant. Second, it creates carbon dioxide (CO₂), which is a decarburizing agent and throws off the balance of the entire atmosphere.
An Unstable, Uncontrollable Process
These side reactions are called "non-equilibrium" because the gas composition is unstable and constantly changing. The atmosphere will attempt to reach equilibrium by having the soot and CO₂ react further, but this process is slow and unpredictable.
Attempting to control a process based on an unstable atmosphere is impossible. Your sensors will give unreliable readings, and the effect on the steel will be inconsistent.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Soot
Choosing conditions that lead to the correct reaction is not a simple preference; it is a critical operational decision. Allowing sooting side reactions has severe consequences.
Loss of Process Control
The carbon that forms soot is carbon that is no longer available in the gas phase (CO) to perform its function. This starves the carburizing process and makes it impossible to maintain a target carbon potential.
Equipment Fouling
Soot is a physical contaminant that builds up on everything inside the furnace: the walls, the heating elements, the circulation fans, and the parts themselves. This buildup reduces efficiency, leads to costly downtime for burnout cycles, and can permanently damage sensitive equipment.
Part Contamination
A layer of soot on the part surface can interfere with the heat treatment process and subsequent operations like quenching. It can lead to inconsistent hardness, soft spots, and cosmetic defects that result in scrapped parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Achieving the correct methanol dissociation is a matter of ensuring the right conditions, primarily temperature. The methanol must be injected into a furnace zone hot enough to favor the complete CH₃OH -> CO + 2H₂ reaction.
- If your primary focus is carburizing: You must achieve the
CH₃OH -> CO + 2H₂reaction to create a predictable base atmosphere with a high concentration of CO, which you will enrich to drive carbon into the steel. - If your primary focus is neutral hardening: You must achieve the
CH₃OH -> CO + 2H₂reaction to create a base atmosphere whose carbon potential can be precisely trimmed to match the steel's, preventing both carbon gain and loss. - If your primary focus is process reliability: Avoiding soot-producing side reactions is paramount to prevent equipment damage, reduce maintenance, and ensure consistent, repeatable results for every batch.
Ultimately, mastering methanol chemistry is about achieving a state of predictable equilibrium, which is the cornerstone of all modern heat treatment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Ideal Reaction | Non-Ideal Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | CH₃OH -> CO + 2H₂ | e.g., 2CH₃OH -> C + CO₂ + 4H₂ |
| Gas Composition | ~33.3% CO, ~66.7% H₂ | Unstable, includes CO₂ and soot |
| Process Suitability | Carburizing, neutral hardening | Leads to contamination and loss of control |
| Key Outcome | Predictable carbon potential, no soot | Soot formation, equipment fouling, part defects |
Upgrade your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's precision solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental needs are met for reliable, soot-free operations. Don't let unstable atmospheres compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your carburizing and neutral hardening efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















