Virtually any industry requiring precise, durable, and clean heat can benefit from ceramic heating elements. This includes sectors from high-tech manufacturing like semiconductors, aerospace, and medical devices, to heavy industries such as metallurgy and glass production, and even consumer applications in food processing and HVAC systems. Their adoption is driven by a unique set of properties that outperform traditional metal elements in specific, demanding environments.
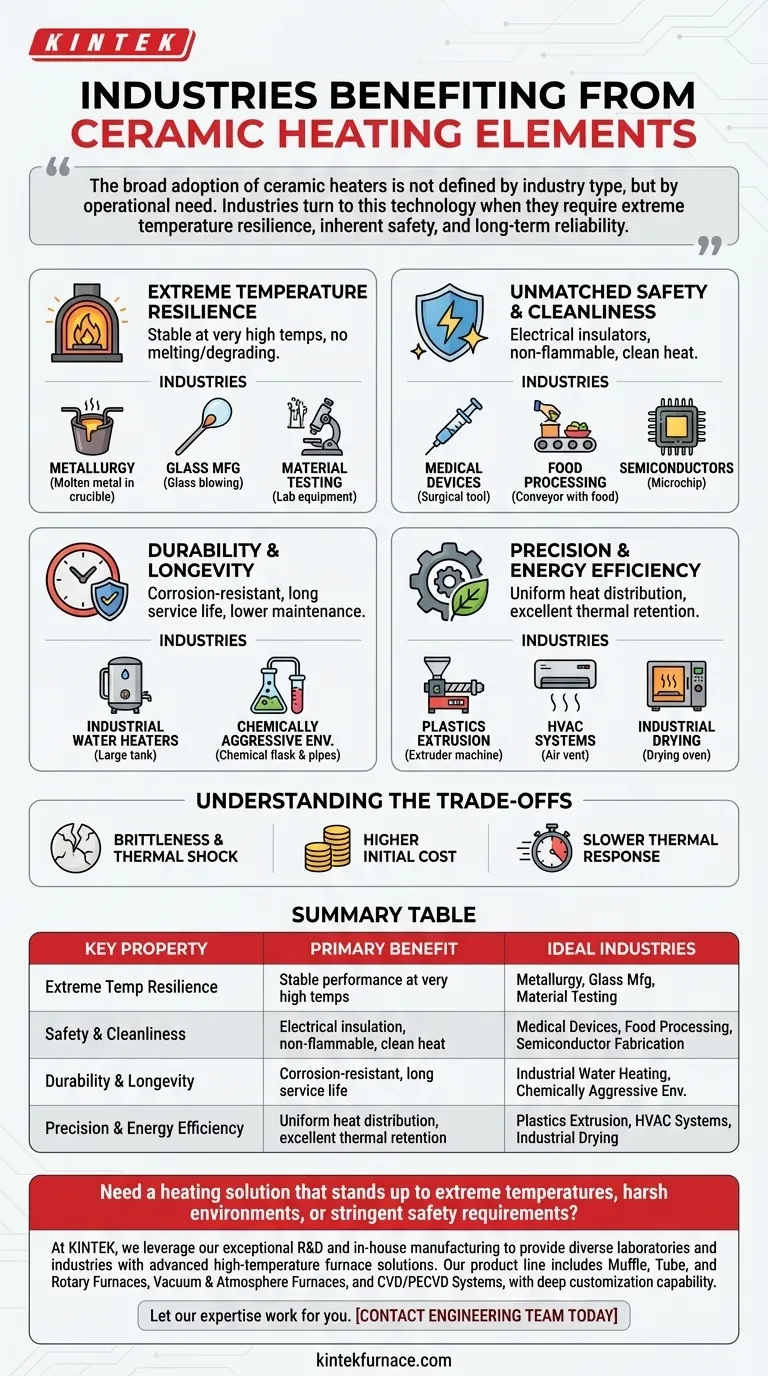
The broad adoption of ceramic heaters is not defined by industry type, but by operational need. Industries turn to this technology when they require a combination of extreme temperature resilience, inherent safety, and long-term reliability where conventional heating solutions would fail.

Why Industries Choose Ceramic: The Core Properties
The decision to use a ceramic heating element is an engineering choice rooted in solving specific challenges. The benefits stem directly from the material's fundamental characteristics.
Extreme Temperature Resilience
Ceramic materials are exceptionally stable and can endure very high temperatures without melting, warping, or degrading. This makes them essential for processes that operate far beyond the limits of most metals.
This property is critical in metallurgy for high-temperature furnaces, glass manufacturing, and material testing applications where consistent, extreme heat is foundational to the process.
Unmatched Safety and Cleanliness
Ceramics are excellent electrical insulators. This inherent property dramatically reduces the risk of short circuits and electrical hazards, enhancing operational safety in any setting.
Furthermore, they are non-flammable and deliver exceptionally clean heat, free from the oxidation or contamination that can occur with metal elements. This is non-negotiable in sensitive industries like medical device manufacturing, food processing, and semiconductor fabrication.
Durability and Longevity
Unlike metals, ceramics do not rust or corrode when exposed to moisture or many chemical agents. This resistance leads to a significantly longer service life and lower maintenance costs over time.
This makes them ideal for applications like industrial water heaters, packaging machinery, and equipment used in chemically aggressive environments where metal elements would require frequent replacement.
Precision and Energy Efficiency
Ceramic heaters provide highly uniform heat distribution, which is critical for processes requiring precise temperature control, such as plastics extrusion and soldering equipment.
They also possess excellent thermal retention, meaning they hold heat effectively once at temperature. This translates directly to higher energy efficiency, as the heater requires less power to maintain its set point, benefiting applications from HVAC systems to industrial dryers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, ceramic heaters are not a universal solution. Acknowledging their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Brittleness and Thermal Shock
Ceramics are harder but more brittle than metals. They can be susceptible to cracking from physical impact or from extremely rapid temperature changes (thermal shock). Designs must account for proper mounting and controlled heating/cooling cycles.
Higher Initial Cost
The manufacturing process for high-quality ceramic components is typically more complex and expensive than for standard metal-sheathed elements. This can result in a higher upfront investment, though it is often offset by a lower total cost of ownership due to longevity and efficiency.
Slower Thermal Response
While their ability to hold heat is an efficiency advantage, it can also mean they heat up and cool down more slowly than some thin-profile metal elements. For applications requiring very rapid temperature cycling, this response time must be evaluated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing or harsh chemical environments: The material stability of ceramic heaters makes them the superior, and often only, viable option.
- If your primary focus is safety and contamination control: The electrical insulation and clean heat from ceramics are critical for medical, food, and electronics manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability with minimal maintenance: The corrosion resistance and durability of ceramics provide a lower total cost of ownership in applications like water heating or industrial drying.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling and the lowest possible initial cost: A traditional metal element might be a better fit, but you must carefully weigh the trade-offs in lifespan and long-term safety.
Ultimately, selecting a ceramic heater is a strategic decision to prioritize long-term performance, safety, and durability in demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Benefit | Ideal Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Resilience | Stable performance at very high temperatures | Metallurgy, Glass Manufacturing, Material Testing |
| Safety & Cleanliness | Electrical insulation, non-flammable, clean heat | Medical Devices, Food Processing, Semiconductor Fabrication |
| Durability & Longevity | Corrosion-resistant, long service life | Industrial Water Heating, Chemically Aggressive Environments |
| Precision & Energy Efficiency | Uniform heat distribution, excellent thermal retention | Plastics Extrusion, HVAC Systems, Industrial Drying |
Need a heating solution that stands up to extreme temperatures, harsh environments, or stringent safety requirements?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories and industries with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs.
Let our expertise in high-temperature ceramics work for you. Contact our engineering team today to discuss how we can deliver a reliable, high-performance heating solution tailored to your specific challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















