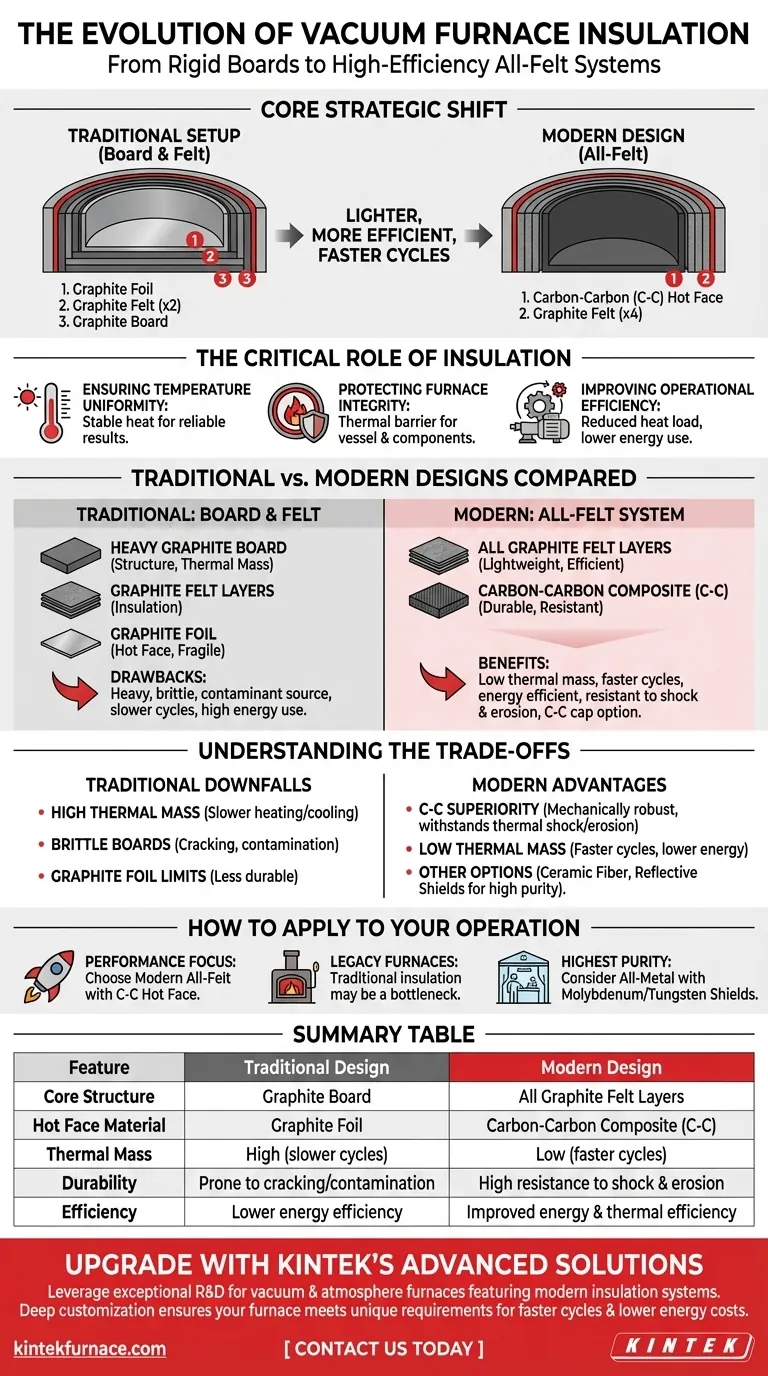
At its core, the evolution of vacuum furnace insulation reflects a strategic shift from a rigid, multi-material approach to a lighter, more efficient, all-felt system. The traditional setup combined a one-inch graphite board with two half-inch layers of graphite felt, shielded by graphite foil. Modern designs have replaced this with four half-inch graphite felt layers behind a durable, thin carbon-carbon composite hot face.
The fundamental change in vacuum furnace insulation is a move away from heavy, brittle graphite boards toward lighter, more thermally efficient all-felt packages. This modern approach, protected by a durable carbon-carbon hot face, improves performance, reduces cycle times, and enhances longevity.

The Critical Role of Furnace Insulation
Before dissecting the design changes, it's essential to understand why insulation is so foundational to vacuum furnace operation. It is not merely about containing heat.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
Proper insulation is the primary mechanism for maintaining a stable and uniform temperature within the hot zone. This consistency is non-negotiable for achieving reliable and repeatable metallurgical results.
Protecting Furnace Integrity
The extreme temperatures inside the hot zone can damage the furnace's outer vessel and critical components. The insulation package acts as a vital thermal barrier, protecting the system's structural integrity.
Improving Operational Efficiency
An effective insulation package directly impacts efficiency. It minimizes the heat load on the vacuum pumping system, which can reduce pump-down times and lower overall energy consumption during a cycle.
Traditional vs. Modern Insulation Designs
The change in insulation strategy was driven by the pursuit of better thermal performance, durability, and operational efficiency.
The Traditional "Board and Felt" Approach
The classic design was a layered system. A graphite board provided structural rigidity, while layers of graphite felt served as the primary insulation. This entire package was typically protected from the hot zone environment by a graphite foil layer.
This combination was functional but had inherent drawbacks. The board was heavy, brittle, and could absorb contaminants over time.
The Modern "All-Felt" System
Today's standard replaces the board entirely. It uses multiple layers of graphite felt (often four half-inch layers) to create a lighter and more thermally efficient insulation package.
The key innovation is the hot face. Instead of fragile foil, modern furnaces use a thin sheet of carbon-carbon composite (C-C). This material is exceptionally strong, lightweight, and highly resistant to thermal shock and gas erosion.
For high-velocity gas quench systems, a C-C cap shield may also be added to protect the top and bottom of the insulation from intense "wind" erosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The move to an all-felt and C-C design was a direct response to the limitations of the traditional approach.
The Downside of Graphite Boards
Graphite boards, while providing structure, also add significant thermal mass. This means they absorb and retain more heat, leading to longer heating and cooling cycles and higher energy use. They are also prone to cracking and creating dust, which can contaminate the furnace.
The Superiority of Carbon-Carbon Composites
C-C composites offer the ideal combination of properties for a hot face. They are mechanically robust, can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, and are far more resistant to erosion from process gases than simple graphite foil.
Other Material Considerations
While carbon-based insulation is common, it is not the only option. For certain applications, other materials are used.
Ceramic fiber panels offer good insulation but can have limitations at very high temperatures or in certain atmospheres. Reflective shields, typically made of molybdenum or tungsten, are used in ultra-high vacuum or high-purity applications where carbon outgassing is a concern.
How to Apply This to Your Operation
Understanding this evolution helps you make informed decisions about furnace maintenance, upgrades, and selection.
- If your primary focus is performance and efficiency: The modern all-felt system with a carbon-carbon hot face is the definitive choice for faster cycles, lower energy costs, and longer service life.
- If you are operating a legacy furnace: Be aware that the traditional board-and-felt insulation may be a bottleneck for cycle time and a potential source of particulate contamination.
- If your process demands the highest purity: You may need to look beyond carbon and consider a furnace with an all-metal hot zone using reflective shields made of molybdenum or tungsten.
By choosing the insulation package that aligns with your specific process goals, you directly control the efficiency, reliability, and quality of your thermal processing operations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Design | Modern Design |
|---|---|---|
| Core Structure | Graphite Board | All Graphite Felt Layers |
| Hot Face Material | Graphite Foil | Carbon-Carbon Composite (C-C) |
| Thermal Mass | High (slower cycles) | Low (faster cycles) |
| Durability | Prone to cracking/contamination | High resistance to shock & erosion |
| Efficiency | Lower energy efficiency | Improved energy & thermal efficiency |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with vacuum & atmosphere furnaces featuring modern, high-performance insulation systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your furnace precisely meets unique experimental requirements for faster cycles, lower energy costs, and superior results. Contact us today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating



















