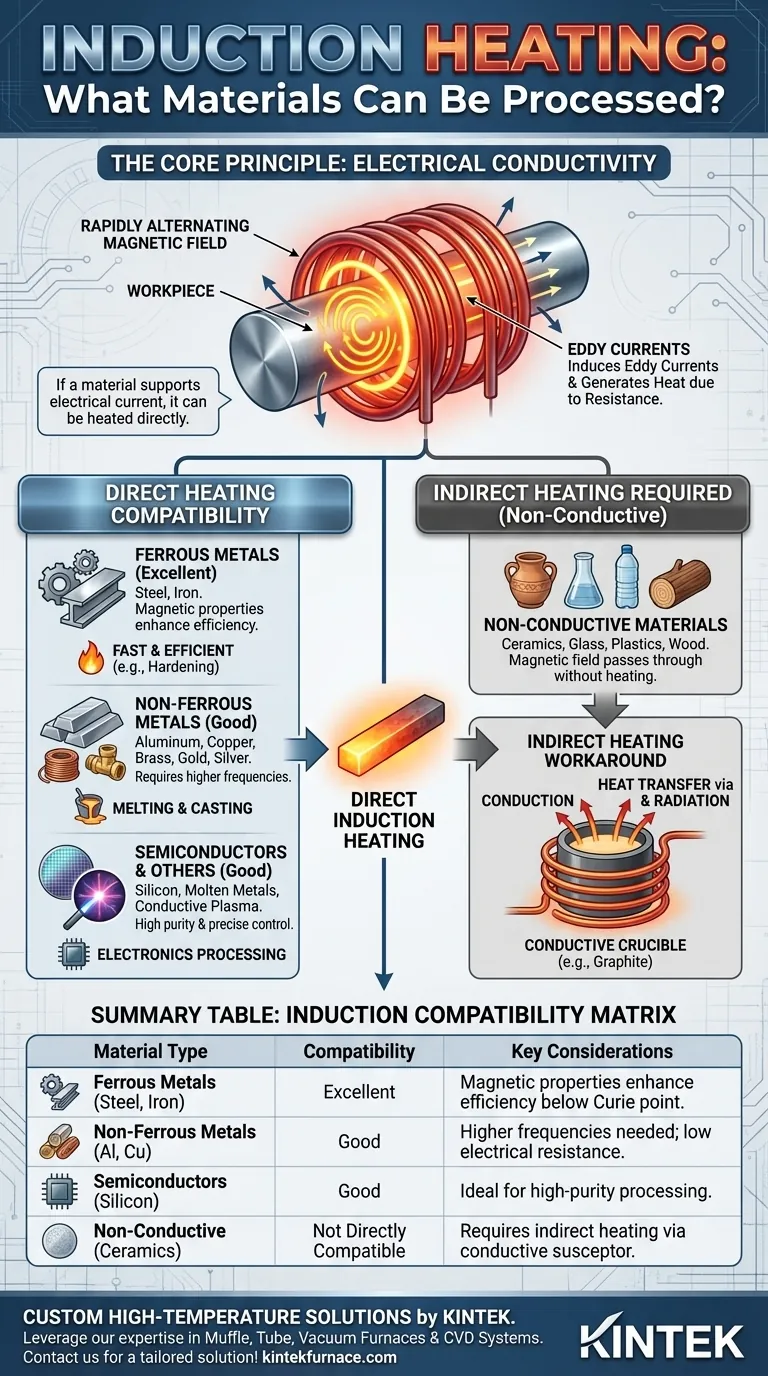
At its core, induction heating is a highly versatile process that works on any material capable of conducting electricity. This includes a vast range of metals like steel, copper, aluminum, and brass, as well as semiconductors such as silicon. The technology is also effective on conductive liquids, like molten metals, and even some gases, like plasma.
The defining factor for induction heating is not the material's type, but its physical property of electrical conductivity. If a material can support an electrical current, it can be heated directly by induction.
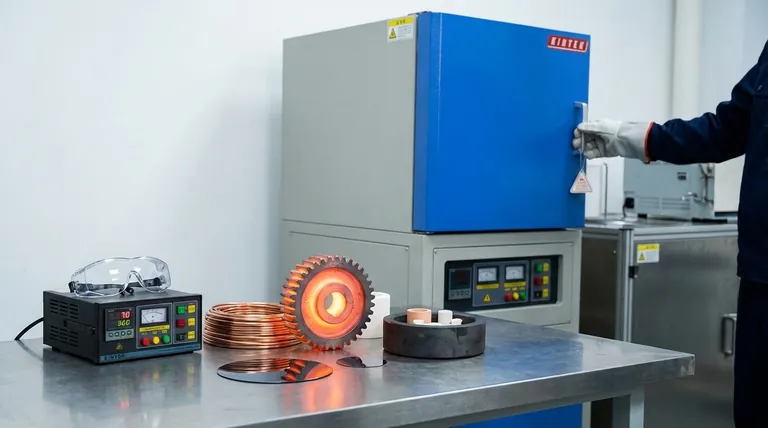

The Fundamental Principle: Electrical Conductivity
To understand which materials are compatible, we must first understand how the process works. The technology is based on two fundamental physics principles: electromagnetic induction and Joule heating.
How Induction Generates Heat
An induction heater uses a coil to generate a powerful, rapidly alternating magnetic field. When an electrically conductive material (the "workpiece") is placed within this field, it induces small, circular electrical currents within the material. These are known as eddy currents.
The material has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance creates friction and generates precise, localized heat within the workpiece itself, without any direct contact or open flame.
Why Conductivity is the Deciding Factor
A material must be conductive to allow eddy currents to form. Without conductivity, the magnetic field passes through the material with no effect, and no heat is generated.
This is why metals are the primary candidates for induction heating. Their free-moving electrons respond readily to the magnetic field, creating the strong eddy currents needed for efficient heating.
A Breakdown of Compatible Materials
While conductivity is the prerequisite, different materials respond differently to induction, requiring adjustments to the system's frequency and power.
Ferrous Metals (Iron, Steel)
Ferrous metals are ideal for induction heating. In addition to their good electrical conductivity, their magnetic properties create an additional heating effect at lower temperatures (below the Curie point), making the process exceptionally fast and efficient. This is why induction is dominant in applications like hardening steel components.
Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Copper, Brass)
Non-ferrous metals are excellent conductors. However, their very low electrical resistance means they can be more challenging to heat efficiently than steel.
Heating these materials effectively often requires higher frequencies to concentrate the eddy currents near the surface. Despite this, induction is widely used for melting and casting aluminum, copper, and precious metals like gold and silver.
Semiconductors and Other Conductors
The versatility of induction extends beyond common metals. It is a critical tool for processing semiconductors like silicon in the electronics industry, where purity and precise control are paramount.
Furthermore, the principle applies to any conductive state of matter, including molten metals in a holding furnace or even specific gases that can be turned into a conductive plasma.
Understanding the Key Limitation
The primary strength of induction heating—its reliance on conductivity—is also its main limitation.
The Challenge with Non-Conductive Materials
Materials that are electrical insulators cannot be heated directly by induction. This includes most ceramics, glass, plastics, wood, and textiles. The magnetic field will pass through them without inducing any heating currents.
Indirect Heating: A Common Workaround
When a non-conductive material must be heated in an induction system, the solution is indirect heating.
This involves placing the non-conductive material inside a conductive vessel, such as a graphite crucible. The induction coil heats the crucible, which then transfers its heat to the material inside through conduction and radiation. This allows you to leverage the speed and control of induction even for non-conductive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material choice dictates your approach to using induction technology.
- If your primary focus is hardening, tempering, or forging metals: Induction offers unparalleled speed and control for directly heating steel, iron, and other alloys.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous or precious metals: Induction is a clean and efficient method, but your system must be properly tuned for the high conductivity of materials like copper, aluminum, or gold.
- If your primary focus is processing non-conductive materials like ceramics or glass: You cannot heat the material directly and must plan for indirect heating using a conductive susceptor or crucible.
Ultimately, mastering induction heating comes down to understanding that conductivity is the key that unlocks this powerful, non-contact technology.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Induction Heating Compatibility | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals (e.g., Steel, Iron) | Excellent | Magnetic properties enhance heating efficiency below the Curie point. |
| Non-Ferrous Metals (e.g., Aluminum, Copper, Brass) | Good | Requires higher frequencies due to low electrical resistance. |
| Semiconductors (e.g., Silicon) | Good | Ideal for high-purity processing in electronics. |
| Non-Conductive Materials (e.g., Ceramics, Glass, Plastics) | Not Directly Compatible | Requires indirect heating via a conductive susceptor (e.g., graphite crucible). |
Need a Custom High-Temperature Solution for Your Materials?
Whether you're hardening steel, melting precious metals, or processing non-conductive materials with indirect heating, KINTEK's advanced furnace systems deliver the precision and reliability you need. Our expertise in high-temperature processing, combined with our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities, ensures you get a solution tailored to your unique requirements.
Our product line includes:
- Muffle Furnaces: Ideal for uniform heating of metals and ceramics.
- Tube Furnaces: Perfect for controlled atmosphere processing of semiconductors.
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces: Essential for oxidation-sensitive materials.
- CVD/PECVD Systems: For advanced thin-film deposition on conductive substrates.
Leverage our deep customization capability to optimize your induction heating or alternative thermal processes. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis



















