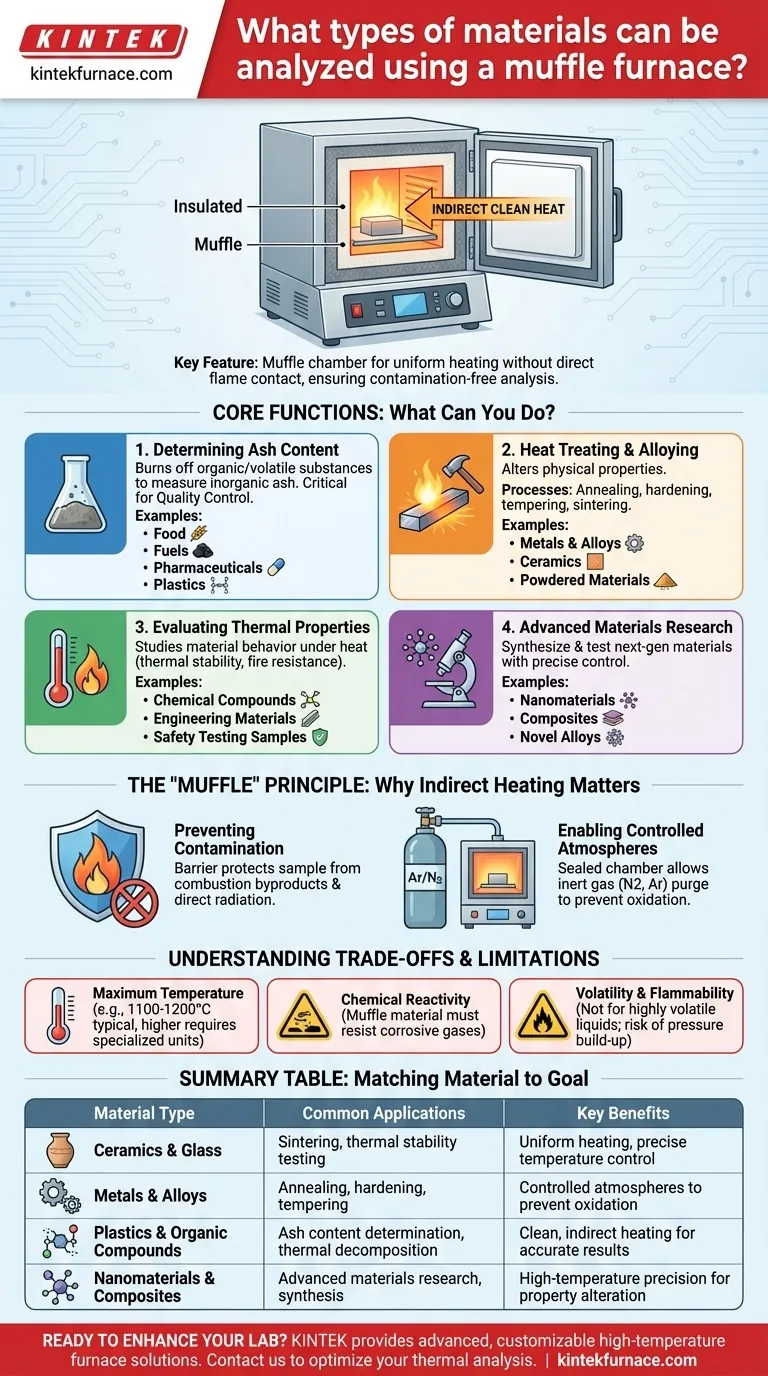
In essence, a muffle furnace is designed to analyze a wide range of materials by subjecting them to precisely controlled high temperatures. Common examples include ceramics, glass, metals, certain plastics, and various organic compounds used in everything from food science to advanced materials research. The furnace's key feature is its "muffle," an insulating chamber that heats the sample without direct contact from flames or electric elements, ensuring a clean and uniform thermal environment.
A muffle furnace's true value lies in its ability to heat materials without direct flame contact. This indirect heating allows for clean, precise thermal analysis—such as determining ash content, heat-treating metals, or testing thermal stability—making it a versatile tool for quality control and materials science.

Core Functions: What Can You Do with a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is an analytical instrument. Its applications are defined by what you need to learn or change about a material using heat.
Determining Ash Content
This is one of the most common applications. By heating a sample to a very high temperature, all organic and volatile substances are burned off.
The remaining non-combustible material is inorganic ash. Weighing this residue is a critical quality control step for materials like food, fuels, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
Heat Treating and Alloying
In metallurgy and materials science, muffle furnaces are used to alter the physical properties of materials.
Processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering metals improve their strength and durability. The furnace is also used for sintering, where powdered materials like ceramics are heated until their particles fuse together.
Evaluating Thermal Properties
Understanding how a material behaves under extreme heat is crucial for engineering and safety.
Muffle furnaces are used for fire resistance testing or to study the thermal stability of chemical compounds. This helps determine the temperature at which a material breaks down, deforms, or loses its structural integrity.
Advanced Materials Research
The precise temperature control of a muffle furnace is indispensable for developing next-generation materials.
Researchers use them to synthesize and test nanomaterials, composites, and novel alloys, where even minor temperature fluctuations can dramatically alter the final material's properties.
The "Muffle" Principle: Why Indirect Heating Matters
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is its method of heating, which separates the sample from the source of heat. This design has two critical advantages.
Preventing Contamination
The muffle chamber acts as a barrier, protecting the sample from any byproducts of combustion or direct radiation from electric heating elements.
This ensures that the analysis, such as measuring ash content, is not skewed by contaminants. The results reflect the properties of the material itself, not a reaction with its heating environment.
Enabling Controlled Atmospheres
Because the chamber is sealed, the internal atmosphere can be modified. Some materials, particularly metals, will oxidize (or rust) rapidly at high temperatures in the presence of oxygen.
Advanced muffle furnaces allow you to purge the chamber and introduce an inert gas, like nitrogen or argon. This creates a low-oxygen environment, making it possible to heat-treat sensitive materials without unwanted chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Its suitability depends on the material, the required temperature, and the furnace's own construction.
Maximum Temperature
A furnace's maximum operating temperature is its primary limitation. While many models reach 1100-1200°C, which is sufficient for ashing and many heat treatments, melting certain metals or processing high-performance ceramics may require specialized high-temperature units.
Chemical Reactivity
Heating certain materials can release aggressive or corrosive gases. The furnace's inner muffle must be able to withstand this chemical attack.
Muffles made from high-purity ceramics or quartz offer excellent resistance and are suitable for a wider range of chemical experiments than basic metal-lined chambers.
Volatility and Flammability
Muffle furnaces are not designed for highly volatile or flammable liquids. Heating these substances can create a dangerous buildup of pressure or an explosive atmosphere inside the chamber. Specialized equipment and ventilation are required for such applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of material you can analyze is directly tied to your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is Quality Control (Ashing): You will primarily analyze organic-based materials like food, coal, plastics, or pharmaceuticals to accurately measure their inorganic content.
- If your primary focus is Metallurgy or Ceramics: You will work with metals, alloys, and powdered compounds to perform heat treatments, sintering, or create new compositions.
- If your primary focus is Research and Development: You will test a broad array of samples, including composites, nanomaterials, and chemicals, often requiring controlled atmospheres to study their fundamental thermal behavior.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace's power comes from using controlled, indirect heat to reveal or transform a material's essential properties.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramics & Glass | Sintering, thermal stability testing | Uniform heating, precise temperature control |
| Metals & Alloys | Annealing, hardening, tempering | Controlled atmospheres to prevent oxidation |
| Plastics & Organic Compounds | Ash content determination, thermal decomposition | Clean, indirect heating for accurate results |
| Nanomaterials & Composites | Advanced materials research, synthesis | High-temperature precision for property alteration |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a tailored muffle furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're in quality control, metallurgy, or advanced materials research. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your thermal analysis processes and drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















