At their core, rotary kilns process an exceptionally broad range of materials, from raw minerals and ores to highly engineered chemicals and industrial waste. They are used for materials that require a specific thermal transformation, such as calcination, sintering, or chemical reaction, which is achieved by tumbling the material through a heated, rotating cylinder. This versatility makes them a cornerstone of industries like cement manufacturing, metallurgy, and chemical production.
The key to understanding rotary kilns is to shift focus from what materials they process to why they process them. The suitability of a material is determined not by its chemical name, but by its physical form and the specific thermal process it must undergo.

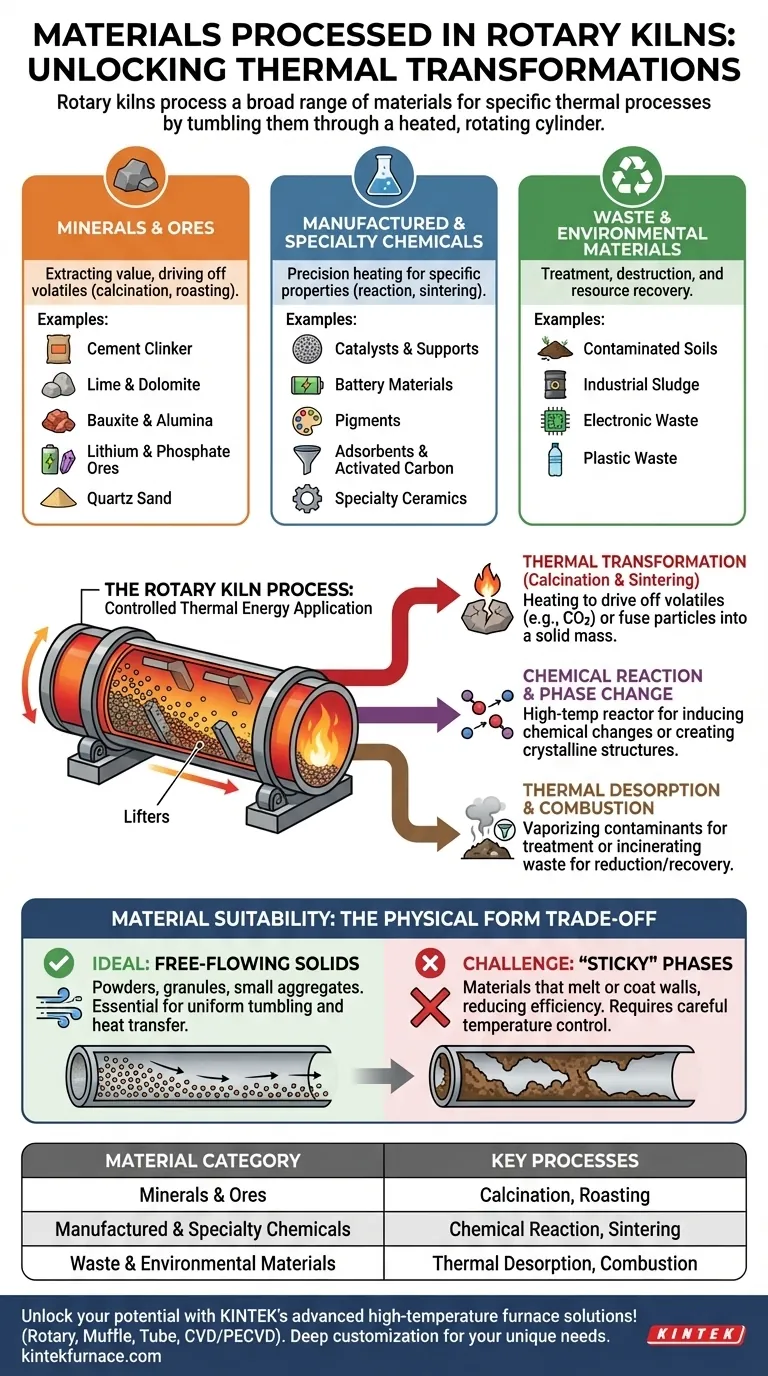
A Framework for Kiln Materials
While the full list is extensive, the materials processed in rotary kilns can be grouped into several major categories. This reflects the kiln's role in both foundational industries and advanced manufacturing.
Minerals and Ores
This is the most traditional application, focused on extracting value from raw geological materials. The goal is often to drive off water, carbonates (calcination), or sulfur (roasting) to prepare the material for further processing.
Common examples include:
- Cement Clinker
- Lime and Dolomite
- Bauxite and Alumina
- Kaolin and other Clays
- Lithium, Chrome, and Phosphate Ores
- Quartz Sand
Manufactured & Specialty Chemicals
In this high-value category, precision is paramount. Rotary kilns provide the controlled temperature and residence time needed to create materials with specific chemical properties and particle structures.
These include:
- Catalysts and Catalyst Supports
- Battery Materials (e.g., lithium iron phosphate cathodes)
- Pigments (e.g., titanium dioxide)
- Adsorbents and Activated Carbon
- Specialty Ceramics and Proppants
Waste & Environmental Materials
A growing application for rotary kilns is in waste treatment and resource recovery. Their high processing temperatures are ideal for destroying hazardous compounds or recovering valuable components from waste streams.
Materials in this category are:
- Contaminated Soils (for thermal desorption of pollutants)
- Industrial Sludge (e.g., waste lime sludge, bauxite residue)
- Electronic Waste (for precious metal recovery)
- Plastic Waste (for thermal decomposition or energy recovery)
Why a Rotary Kiln? It's About the Process
The common thread linking these diverse materials is their need for a specific, controlled thermal process. The kiln's primary function is to apply heat to a moving bed of material to achieve a desired transformation.
Thermal Transformation (Calcination & Sintering)
Calcination is a process of heating a solid to high temperatures to drive off a volatile component, such as water or carbon dioxide. The creation of lime from limestone is a classic example.
Sintering involves heating a material to just below its melting point, causing particles to fuse together into a solid, stronger mass. This is fundamental to making cement clinker and ceramic roofing granules.
Chemical Reaction & Phase Change
Many processes use the kiln as a high-temperature reactor. This can involve reacting the material with gases in the kiln atmosphere (e.g., reduction of iron ore) or simply using heat to induce a chemical change within the material itself.
Activating catalysts and creating specific crystalline structures in battery materials are prime examples of these controlled reactions.
Thermal Desorption & Combustion
For waste materials, the goal is often removal or destruction. Thermal desorption uses heat to vaporize contaminants from solids like soil, allowing the vapors to be collected and treated separately.
Combustion uses the kiln as an incinerator, completely destroying organic waste and reducing its volume while allowing for potential energy recovery.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Suitability
A rotary kiln is not a universal solution. A material's suitability depends heavily on its physical behavior at processing temperatures.
The Importance of Physical Form
The ideal material for a rotary kiln is a free-flowing solid. The tumbling action created by the kiln's rotation is essential for ensuring uniform heat transfer throughout the material bed.
This is why kilns are excellent for processing powders, granules, small aggregates, and slurries that dry into a solid form.
The Challenge of "Sticky" Phases
A significant limitation is any material that becomes overly sticky or melts into a thick liquid at processing temperatures. This can cause the material to coat the inside of the kiln wall, reducing heat transfer and potentially forcing a shutdown for cleaning. Careful temperature control is required to avoid this "sticky phase."
Process Control Requirements
The material must be able to achieve its desired transformation within the kiln's operational limits. This involves matching the material's needs to the kiln's achievable temperature profile, residence time, and internal atmosphere (e.g., oxidizing or reducing).
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal dictates which aspect of the rotary kiln is most important.
- If your primary focus is bulk mineral processing (e.g., cement, lime): Your concern is high throughput and thermal efficiency for well-understood calcination or sintering reactions.
- If your primary focus is high-value specialty materials (e.g., catalysts, batteries): Your concern is precise control over temperature profile, residence time, and kiln atmosphere to ensure consistent product quality and performance.
- If your primary focus is waste treatment or remediation: Your concern is achieving the target destruction or removal efficiency while safely managing emissions and off-gases.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a uniquely versatile tool defined by its ability to apply controlled thermal energy to a vast array of tumbling materials.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Minerals and Ores | Cement Clinker, Lime, Bauxite | Calcination, Roasting |
| Manufactured & Specialty Chemicals | Catalysts, Battery Materials, Pigments | Chemical Reaction, Sintering |
| Waste & Environmental Materials | Contaminated Soils, Industrial Sludge, E-Waste | Thermal Desorption, Combustion |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with rotary furnaces and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, whether you're processing minerals, chemicals, or waste. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















